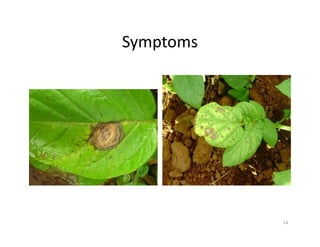
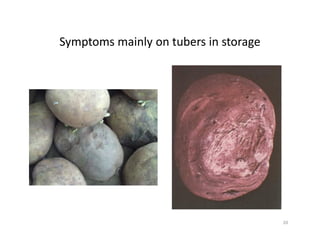
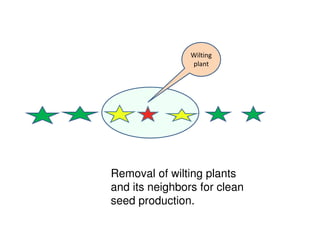
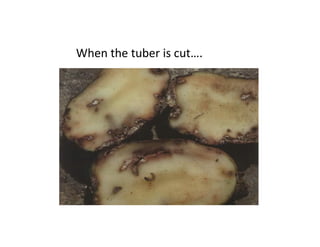
The document discusses integrated potato crop management in Kadahenda, Rwanda, focusing on pest and disease management strategies for potato farmers. It details major potato diseases such as late blight and bacterial wilt, along with their symptoms and recommended control practices, including the use of resistant varieties and crop rotation. Additionally, it highlights significant potato pests and the appropriate insecticides for their management, acknowledging support from research organizations for smallholder farmers.