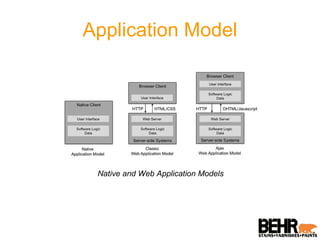
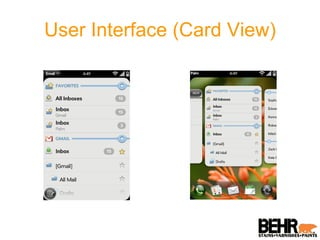
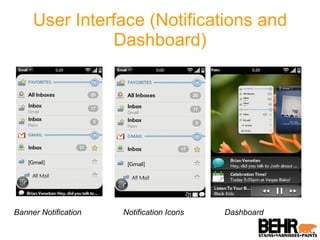
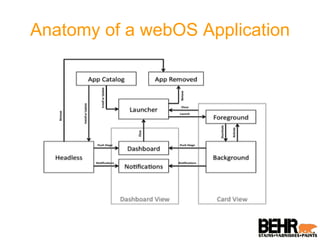
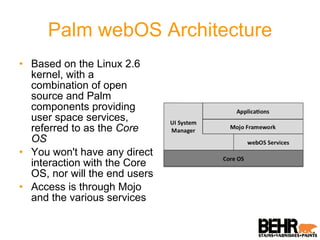
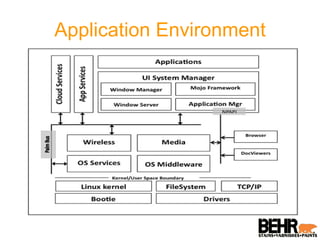
Palm webOS is an advanced operating system designed for a seamless multitasking user experience, integrating a window-based environment with web-browser simplicity. It utilizes standard web technologies for application development, allowing seamless background operation and effective user interactions through a touch-driven interface. The architecture is based on the Linux kernel and incorporates a rich set of UI features and services, all accessible via a JavaScript framework called Mojo.