- The document discusses transactions in BEA WebLogic Server 6.0, including how transactions provide data consistency and monitoring/management capabilities. It outlines benefits such as timeouts, monitoring by transaction name, and overload protection.
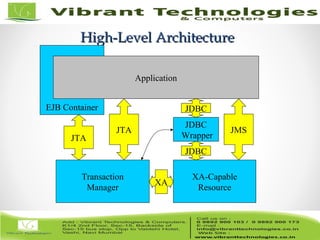
- It describes how multiple servers and resources can participate in distributed transactions using XA. Programming interfaces for transactions are discussed as well as BEA WebLogic extensions.
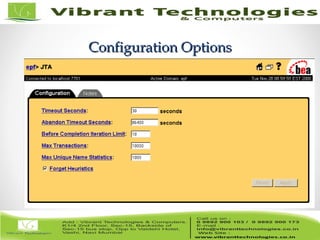
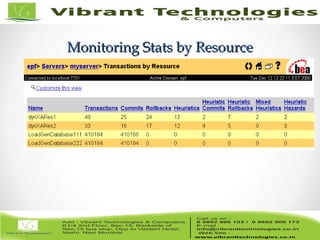
- Configuration parameters for transactions are outlined pertaining to timeouts, transaction logs, and more. Monitoring capabilities like counters and viewing individual transactions are also summarized.