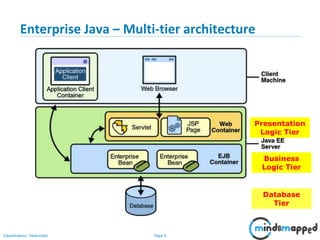
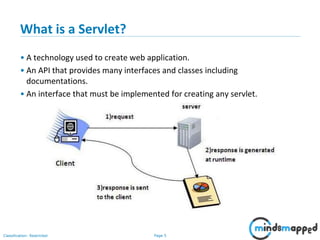
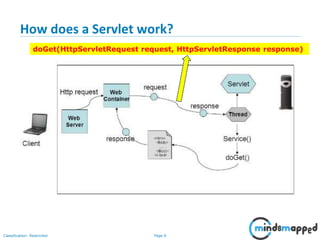
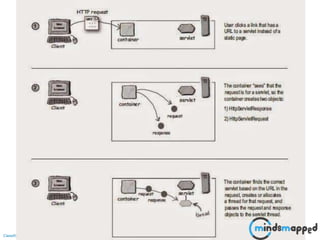
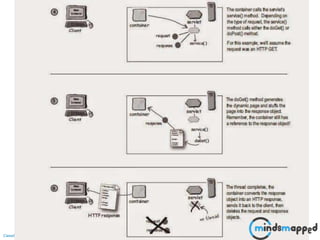
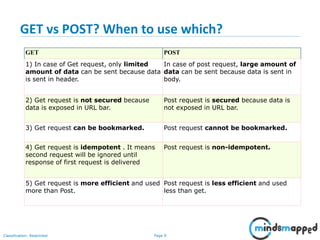
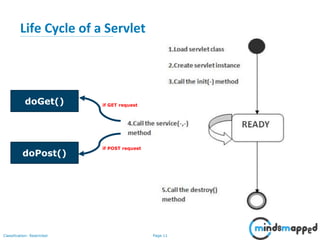
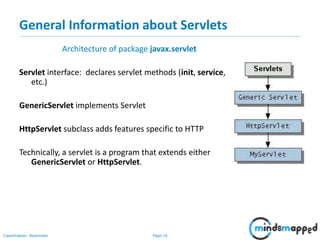
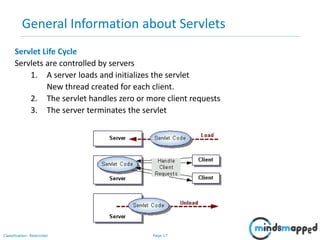
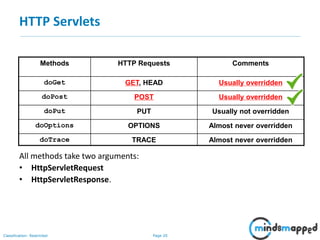
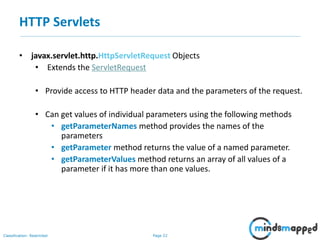
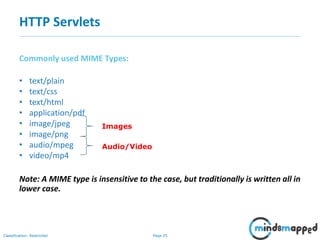
This document provides an overview of servlets and Java EE. It discusses what servlets are, how they work, their lifecycle, and how to handle GET and POST requests. Servlets are Java programs that extend HttpServlet to create dynamic web applications. They receive and respond to requests via doGet() and doPost() methods. The document also covers servlet API, environments for developing servlets, MIME types, and handling GET/POST requests by overriding doGet() and doPost(). The next session will demonstrate a complete web application flow with servlet coding.