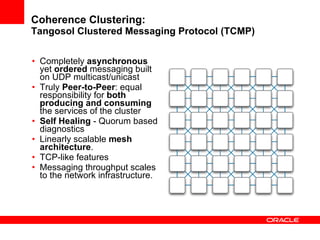
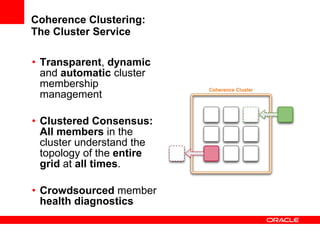
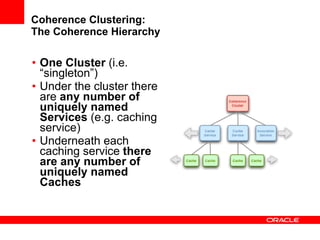
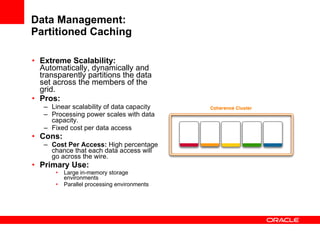
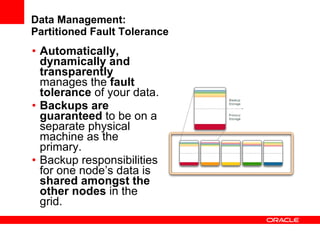
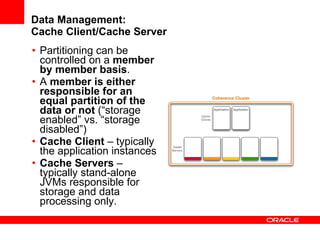
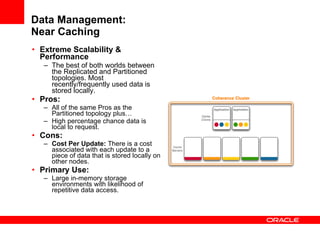
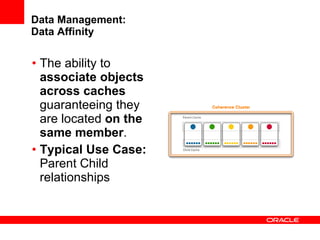
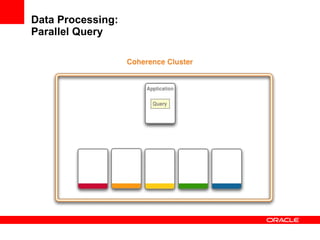
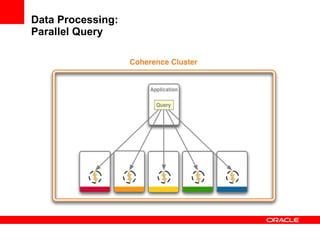
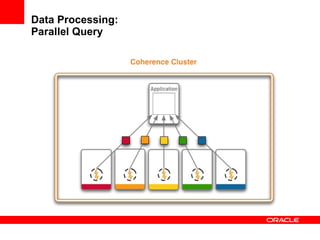
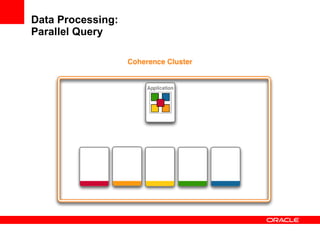
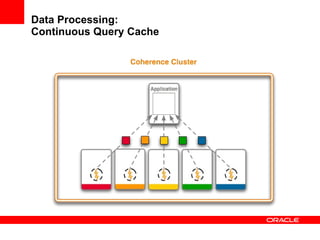
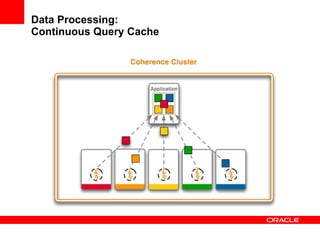
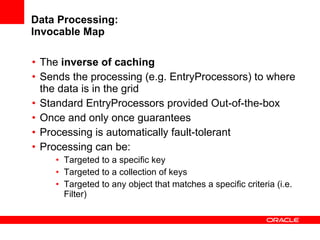
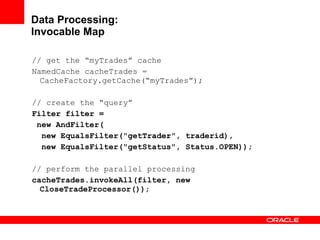
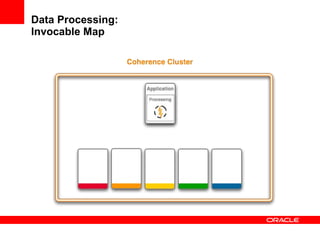
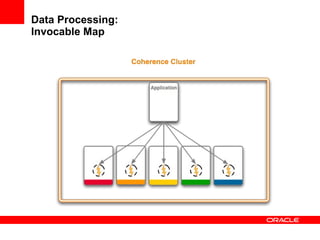
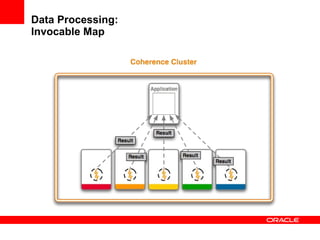
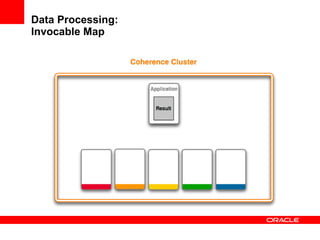
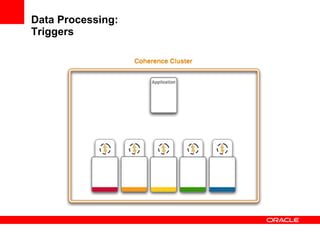
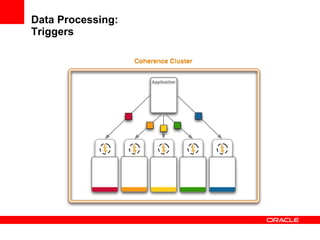
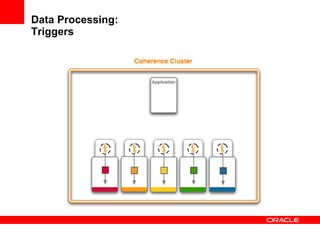
This document provides an overview of Oracle Coherence, an in-memory distributed computing platform. It defines a data grid, describes Coherence clustering and data management options like partitioned caching. It also covers data processing options in Coherence like events, parallel queries, continuous query caches, and invocable maps. The document concludes with an overview of the Coherence Incubator project.