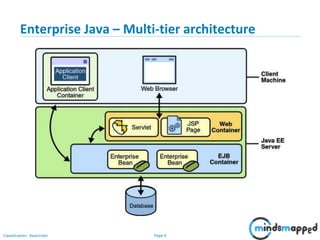
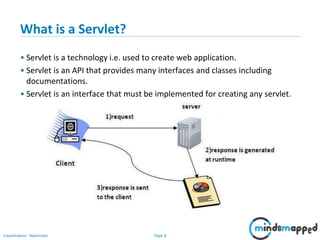
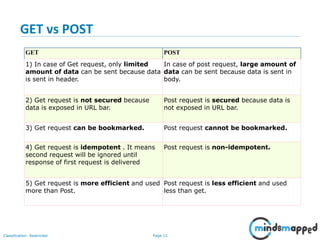
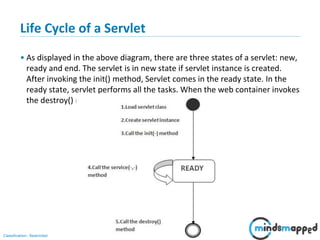
This document provides an introduction to servlets and Java EE. It discusses that servlets are used to create dynamic web content by processing HTTP requests in a non-blocking way using Java code. Servlets provide APIs for session management. The document outlines the servlet lifecycle and how servlets work by having the web container create threads to handle multiple requests. It compares GET and POST requests and discusses the servlet API and basic Tomcat setup. The next session will provide a deeper look at HTTP servlets and Java EE.