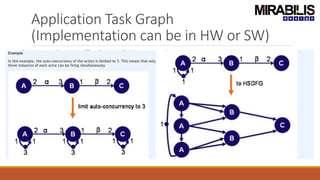
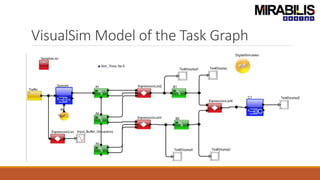
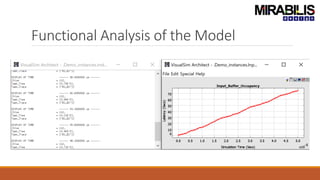
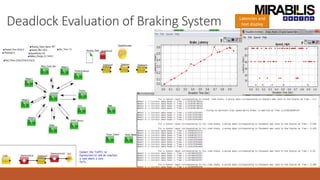
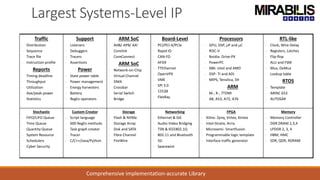
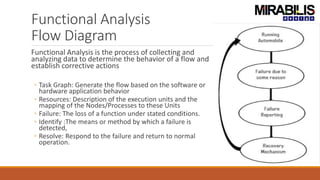
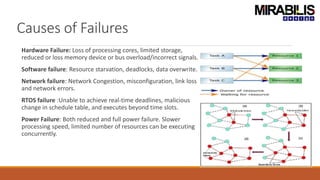
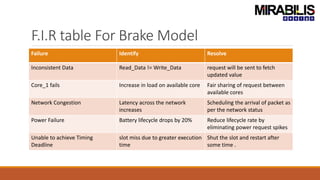
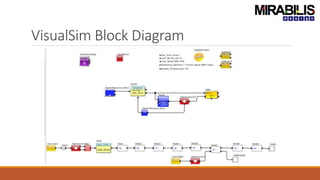
The webinar focuses on detecting deadlocks in electronic systems through time-based simulation and task graph analysis. It covers topics including static vs. dynamic deadlock analysis, system specifications, functional safety, and the capabilities of Mirabilis Design's VisualSim technology. Attendees will learn about architecture exploration, performance analysis, and error resolution in complex systems involving software and hardware components.