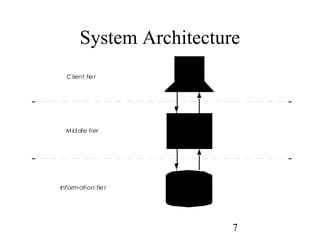
Web servers handle client requests for resources on the internet by providing web pages, documents, and other files. They use the client/server model and communicate with clients using HTTP. A 3-tier architecture divides functionality into separate client, application, and database tiers. Popular web servers include Apache, Tomcat, IIS, and PWS.