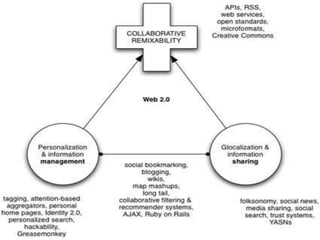
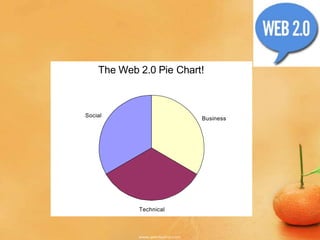
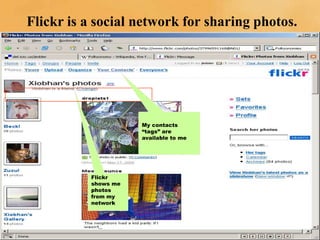
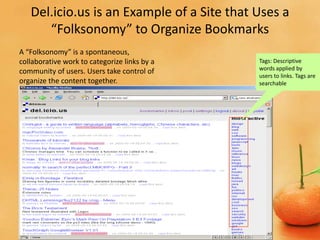
The document discusses the evolution from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0, describing key differences. Web 1.0 was mostly static HTML pages viewed through browsers, while Web 2.0 is more dynamic, featuring user-generated content and applications. Characteristics of Web 2.0 include the web being a platform, read/write functionality, user-generated data stored outside direct control, and often using AJAX. Social trends driving Web 2.0 include broadband adoption, sharing content online, and mass participation. Business models exploit niche communities and web services. Technology advances like XML and browser capabilities enable new types of applications.