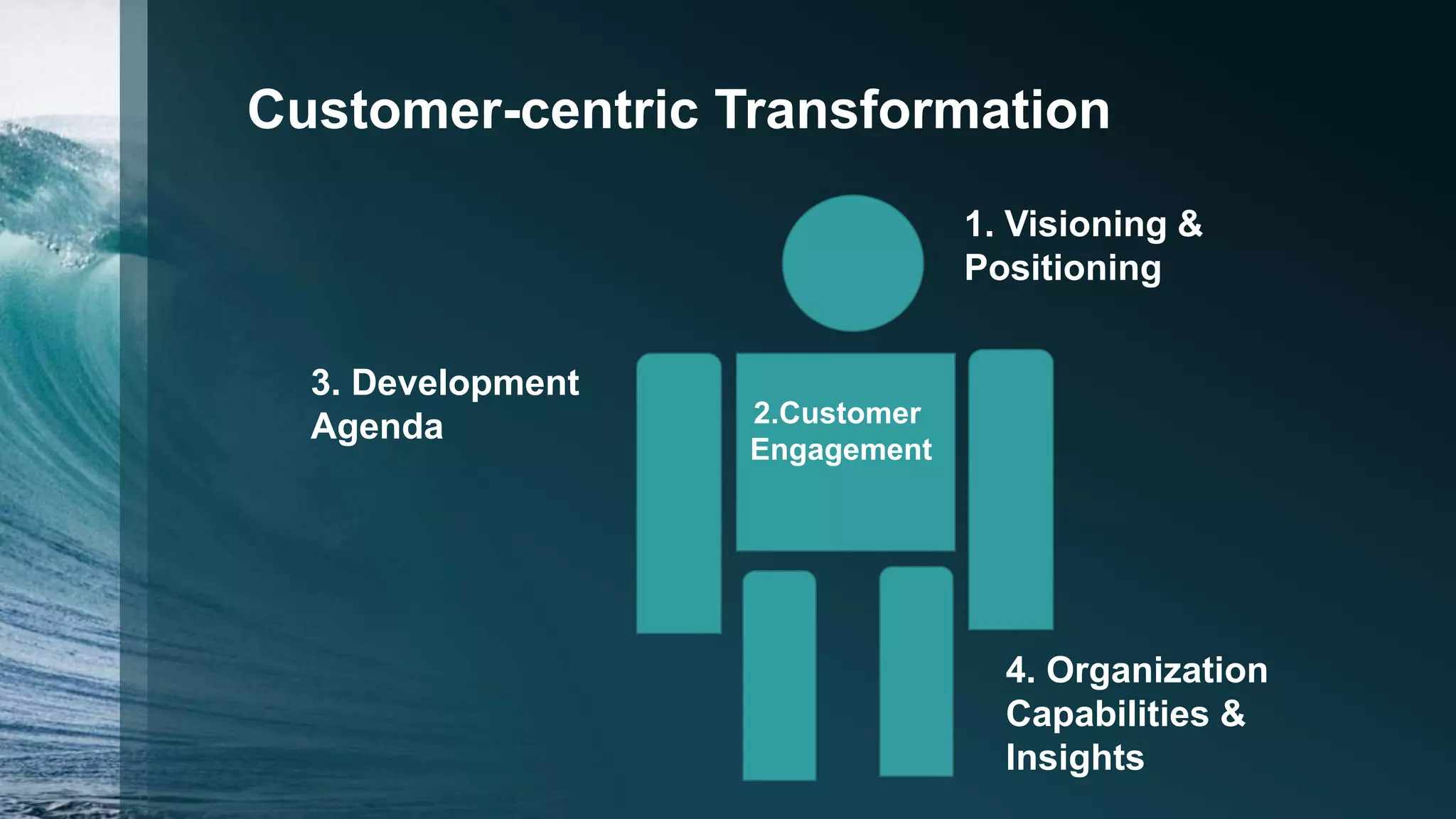
The document emphasizes the necessity for businesses to adopt customer-centric strategies to succeed in a changing world, advocating for a shift from a commodity focus to prioritizing customer needs. It outlines four key areas for customer-centric transformation: vision and positioning, customer engagement, development agenda, and organizational capabilities, with emphasis on deep customer insights and tailored services. Additionally, it suggests that a successful customer-centric culture includes clear articulation of philosophy, continual reinforcement of values, and alignment of employee incentives with customer satisfaction goals.