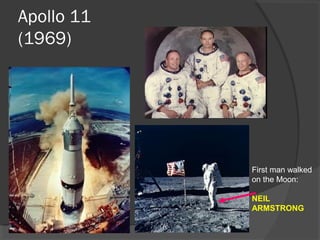
This document provides an overview of space exploration and astronomy. It introduces key topics like what space is, who astronomers are and their contributions, a brief history of space exploration highlighting early missions and achievements, current major space agencies, and visions for future exploration. The conclusion reiterates that continued exploration will use the moon as a stepping stone for missions to Mars and other planets.