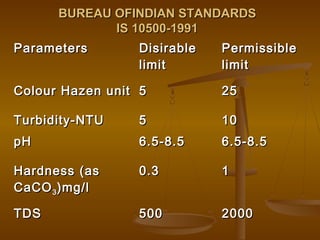
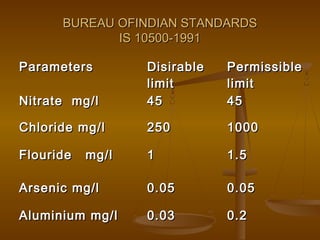
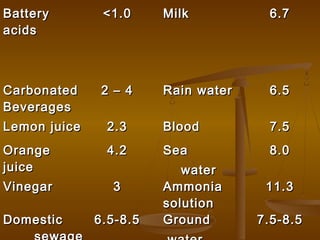
This document discusses water quality standards and parameters for drinking water. It outlines the physical, chemical, and bacteriological contamination sources that can affect water. The key water quality parameters discussed include turbidity, pH, hardness, alkalinity, iron, chloride, nitrate, fluoride, arsenic, and heavy metals. BIS drinking water standards for various parameters are provided. The importance of residual chlorine is also mentioned. Overall, the document provides an overview of water quality issues and the standards used to define safe drinking water.