Embed presentation
Downloaded 25 times


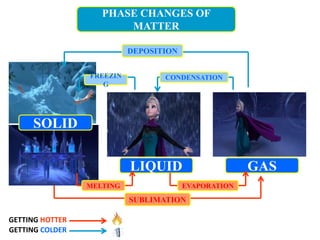
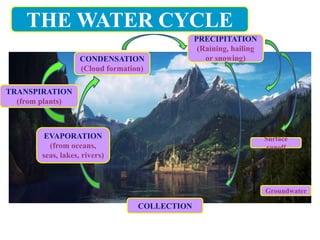
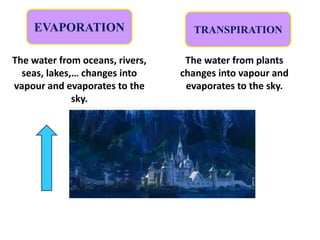



The document describes the water cycle through the following processes: 1) Evaporation occurs when water from bodies of water and transpiration from plants turns into vapor and enters the sky. 2) Condensation happens when the water vapor in the air cools and turns back into liquid water droplets, forming clouds. 3) Precipitation occurs when the water falls back to earth as rain, hail or snow.







