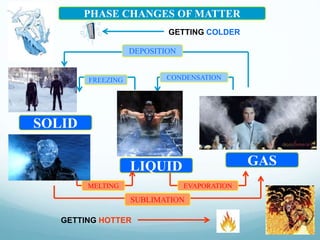
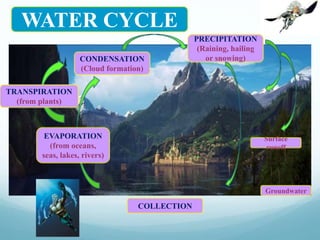
The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. Water can exist in three states: solid (ice/snow), liquid (water/rain), and gas (water vapor). The sun provides energy that evaporates water from oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, and plants, which rises into the air as water vapor. Water vapor condenses to form clouds and precipitates as rain, snow, or hail back to the ground, where it collects in bodies of water or on land as groundwater, sustaining life and continuing the cycle.