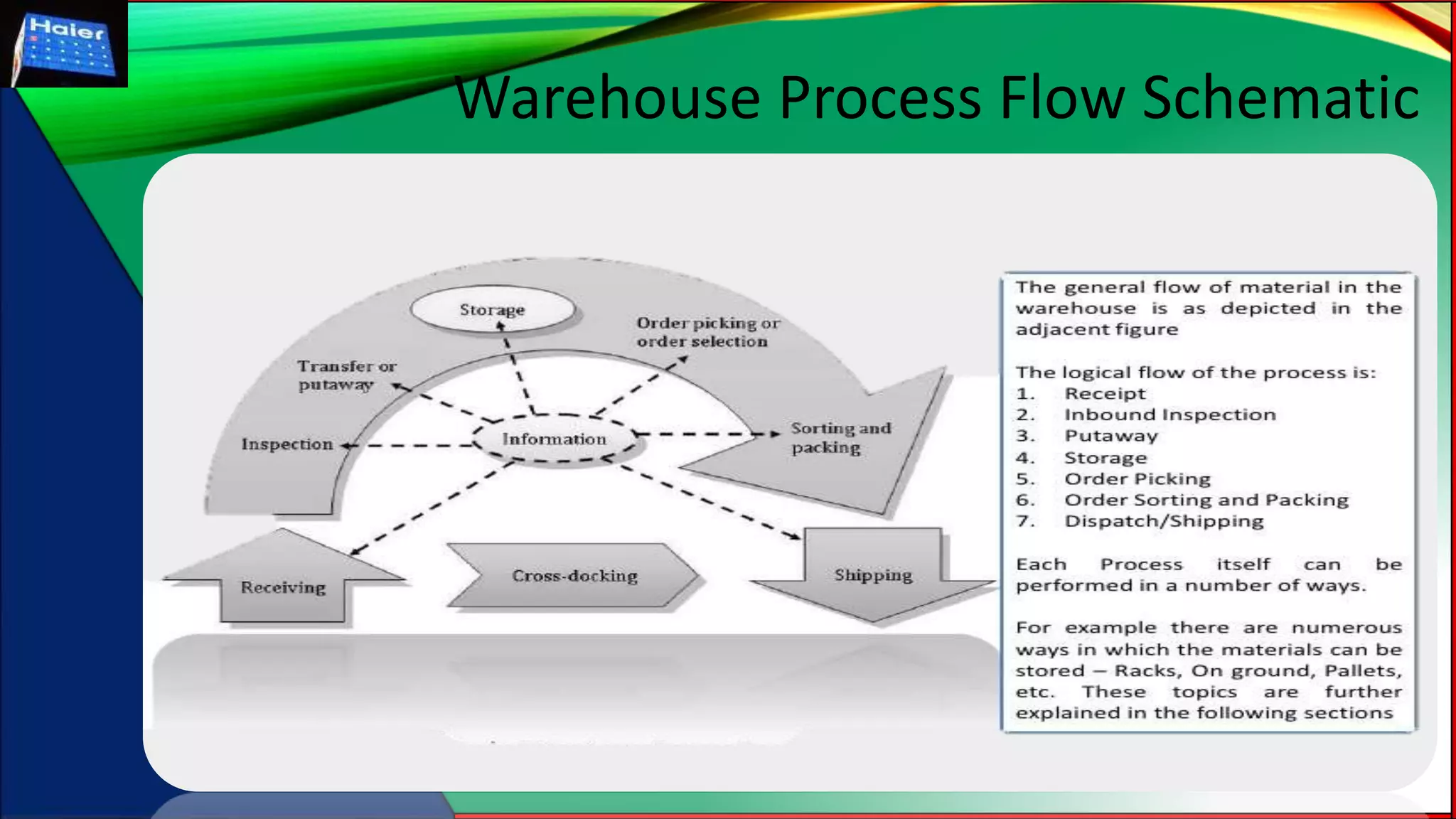
The document outlines a comprehensive warehousing project plan, detailing types of warehouses, site selection criteria, management processes, and layout design. It emphasizes the importance of balancing service costs with operational efficiency while addressing challenges in establishing effective inventory policies. The analysis includes material flow types and storage systems, all aimed at optimizing warehouse functionality and meeting customer demands.