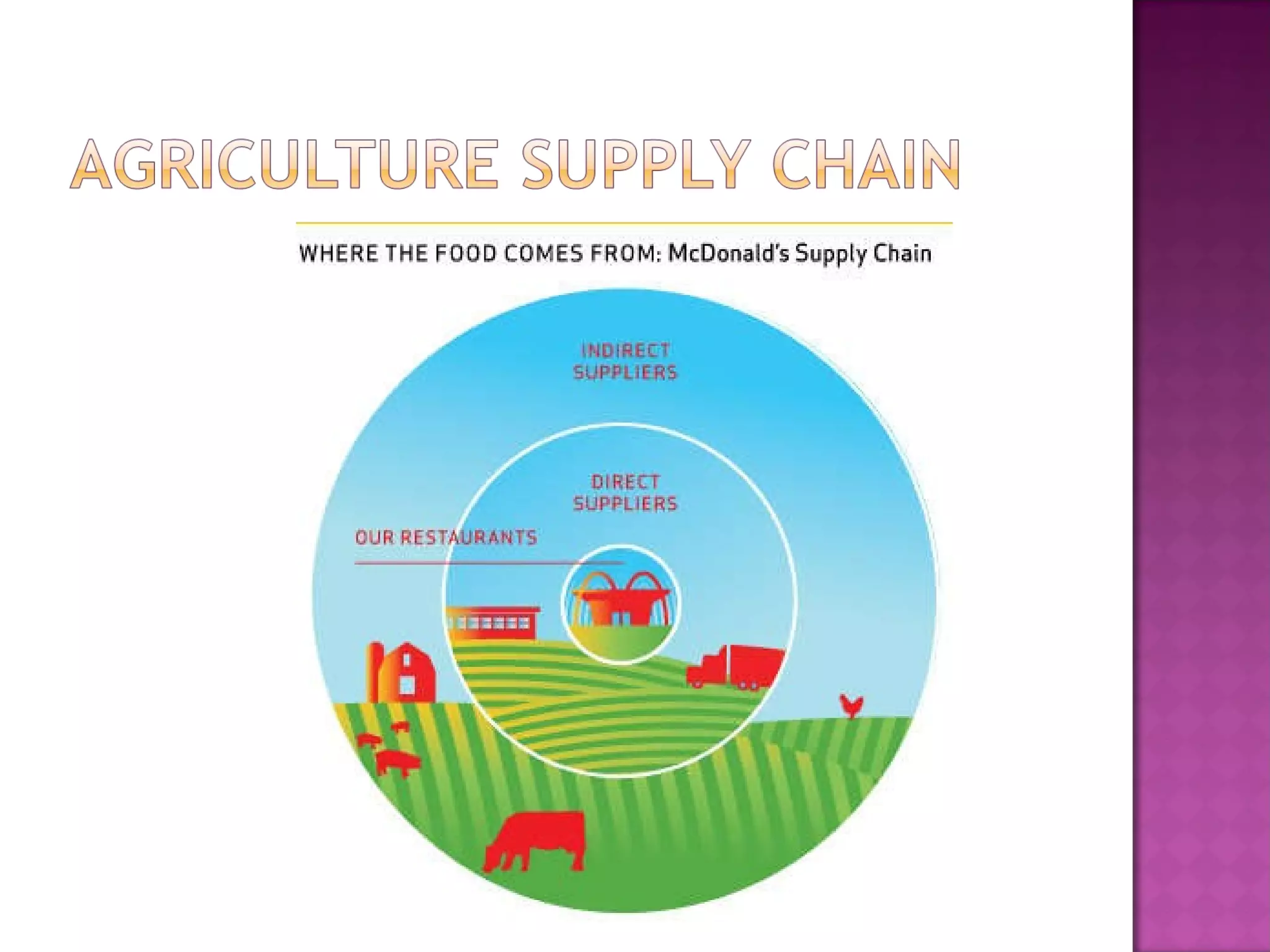
The document discusses logistics and supply chain management. It notes that logistics has evolved into a major business area and can help reduce product costs, making goods more competitive. An effective supply chain management approach coordinates activities from vendor to customer. The document also highlights some of the logistics challenges for developing countries, such as higher transportation costs. It assesses countries' logistics performance using several indicators related to international shipping efficiency and infrastructure. Overall, the document emphasizes the important role of logistics in enabling global business operations and fueling profitability across supply chains.