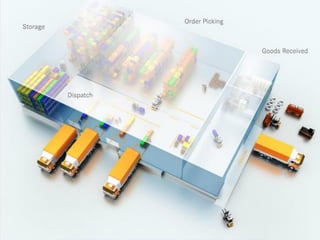
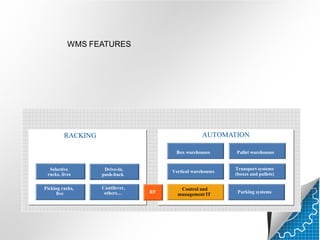
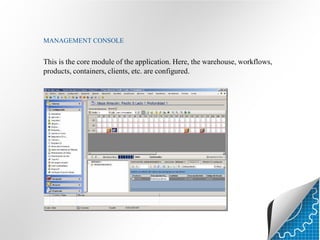
A warehouse management system (WMS) is an IT and management system that helps optimize warehouse operations from goods receipt to shipment. It provides real-time tracking of inventory and activities. A WMS manages tasks like receiving, storage, order preparation and dispatch. It uses hardware like handheld scanners and printers to guide workers through processes. Key features include automation, racking systems, transport systems and control software. Implementing a WMS can increase efficiency, control, visibility and productivity in warehouse operations.