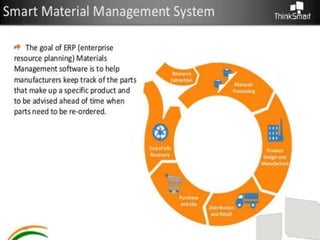
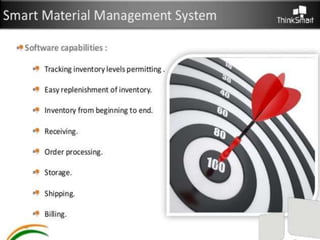
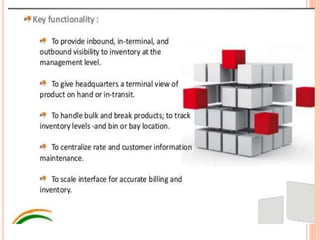
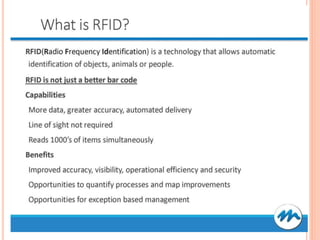
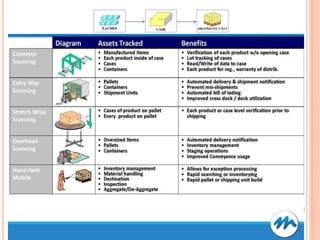
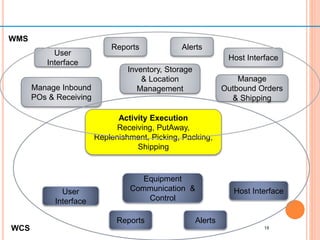
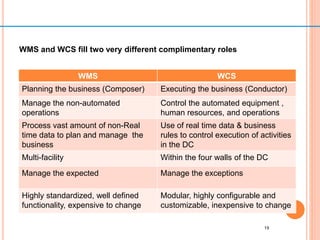
The document discusses different ways to implement smart material management including using IT, RFID warehouse management, automated purchasing, and comparing WCS and WMS systems. It provides details on using IT to generate various reports for materials management, describes the purchase requisition process, challenges of manual processes, and benefits of automating with BPM software. It also outlines the roles of WMS for planning business needs across facilities versus WCS for real-time control of automated equipment and operations within a single facility.