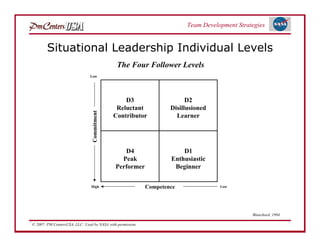
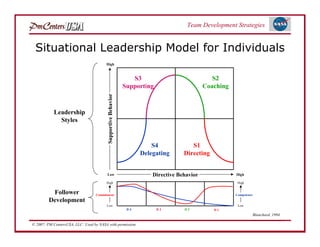
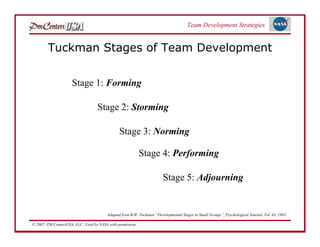
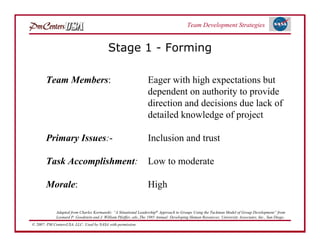
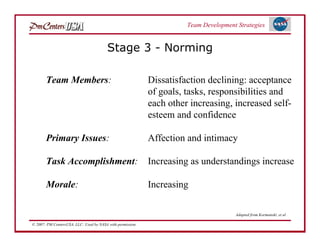
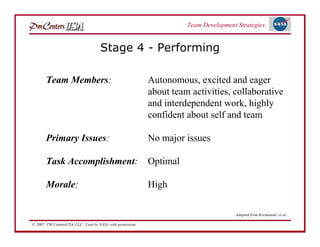
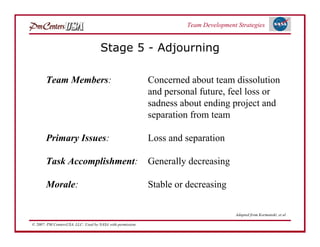
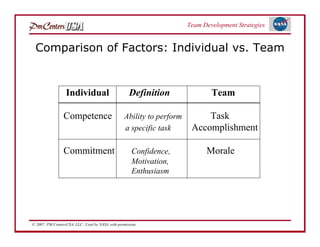
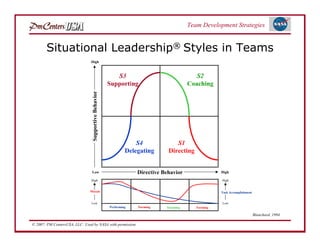
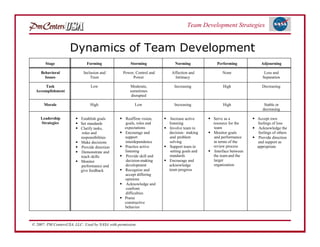
The document discusses strategies for developing project teams. It describes situational leadership theory and how the leadership style should adapt based on the team's stage of development. The five stages in Tuckman's model of team development are outlined as well as the typical behaviors, task focus, and morale at each stage. Leaders are advised to assess what stage their team is at and tailor their approach according to situational leadership, focusing on the needs of the team to guide them through the different stages to high performance.