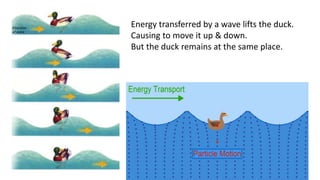
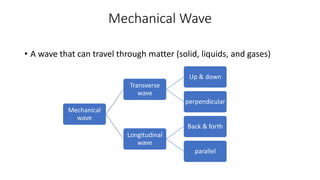
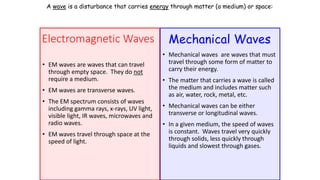
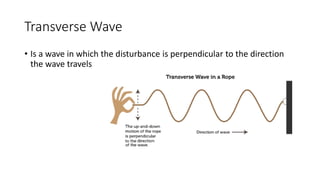
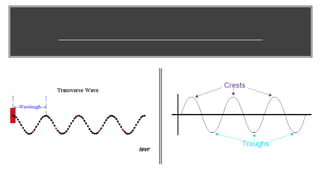
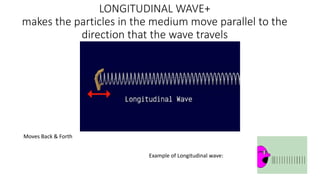
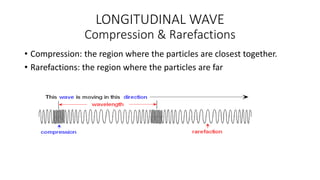
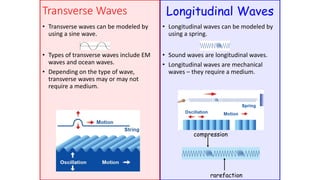
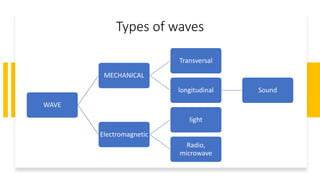
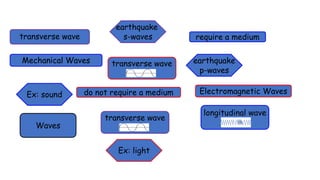
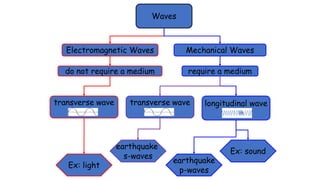
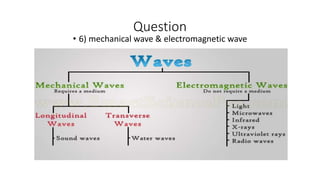
A wave is a disturbance that transfers energy through a medium or space. There are two main types of waves: mechanical waves, which require a medium such as air, water or solid material to travel; and electromagnetic waves, which can travel through empty space. Mechanical waves can be transverse, with the disturbance moving perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer, or longitudinal, with the disturbance moving parallel. Examples of transverse mechanical waves include water waves and seismic S-waves, while longitudinal mechanical waves include sound waves and seismic P-waves. Electromagnetic waves include visible light, radio waves, microwaves and more.