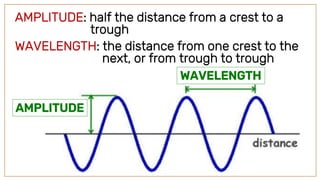
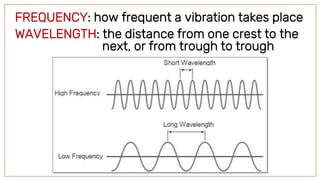
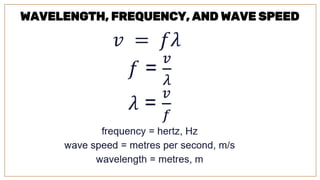
Waves are disturbances that transfer energy from one place to another without transferring matter. There are two main types of waves: mechanical waves, which need a medium to travel and can be transverse or longitudinal; and electromagnetic waves, which can travel through a vacuum. Key parts of a wave include the crest, trough, amplitude, and wavelength. The wavelength is the distance between crests or troughs, while the amplitude is half the distance between crest and trough. Frequency refers to how often a vibration occurs.