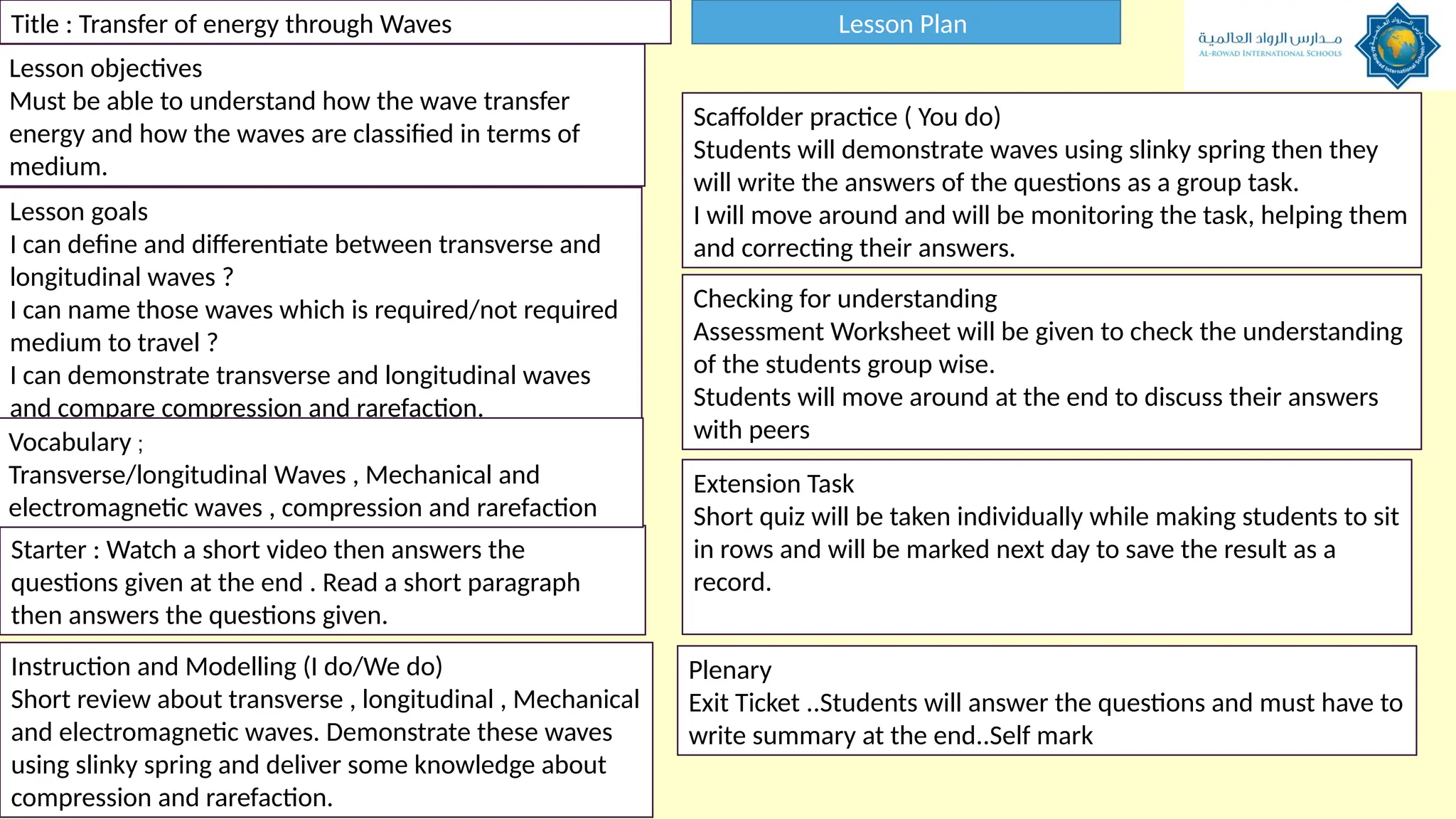
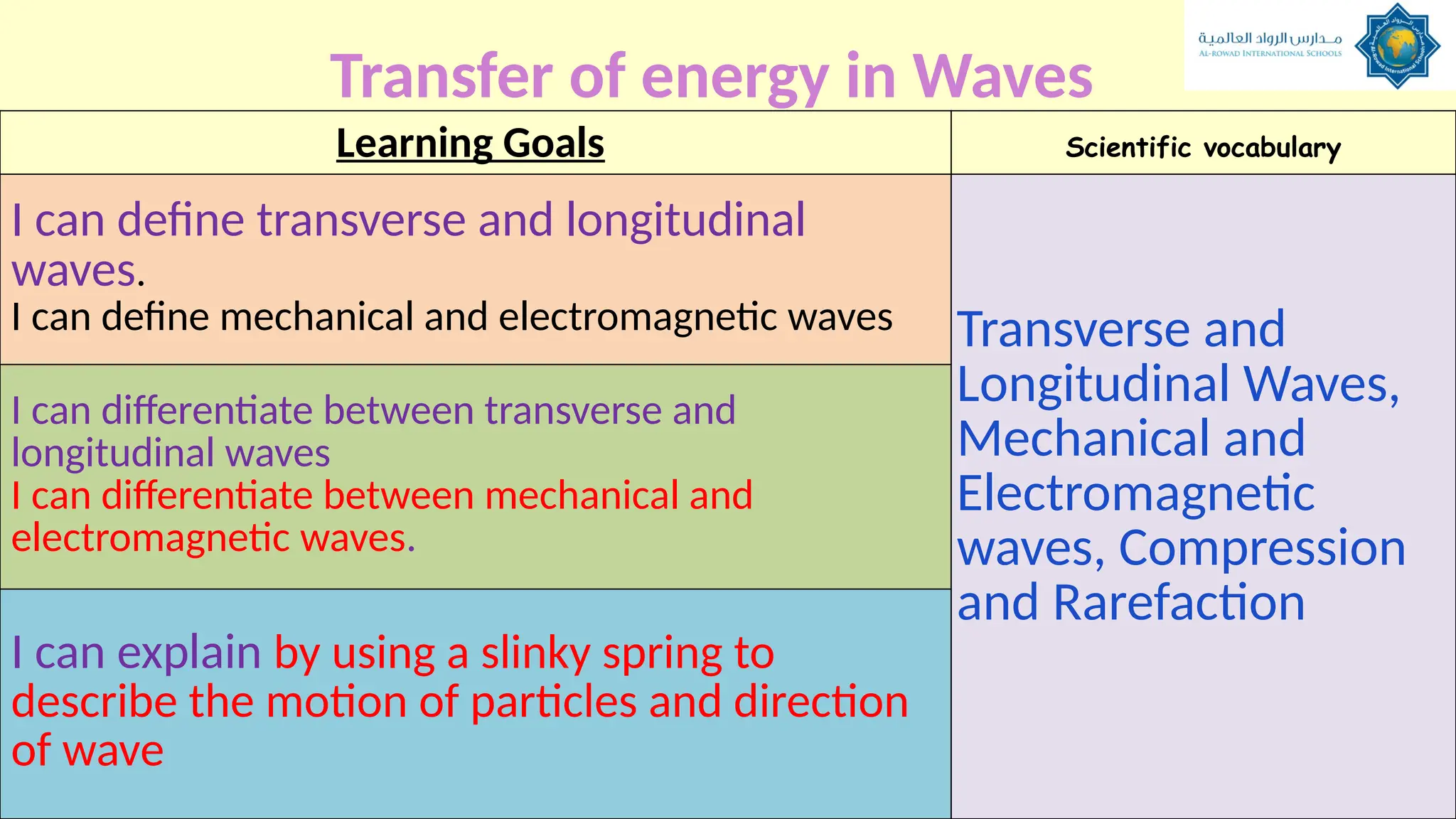
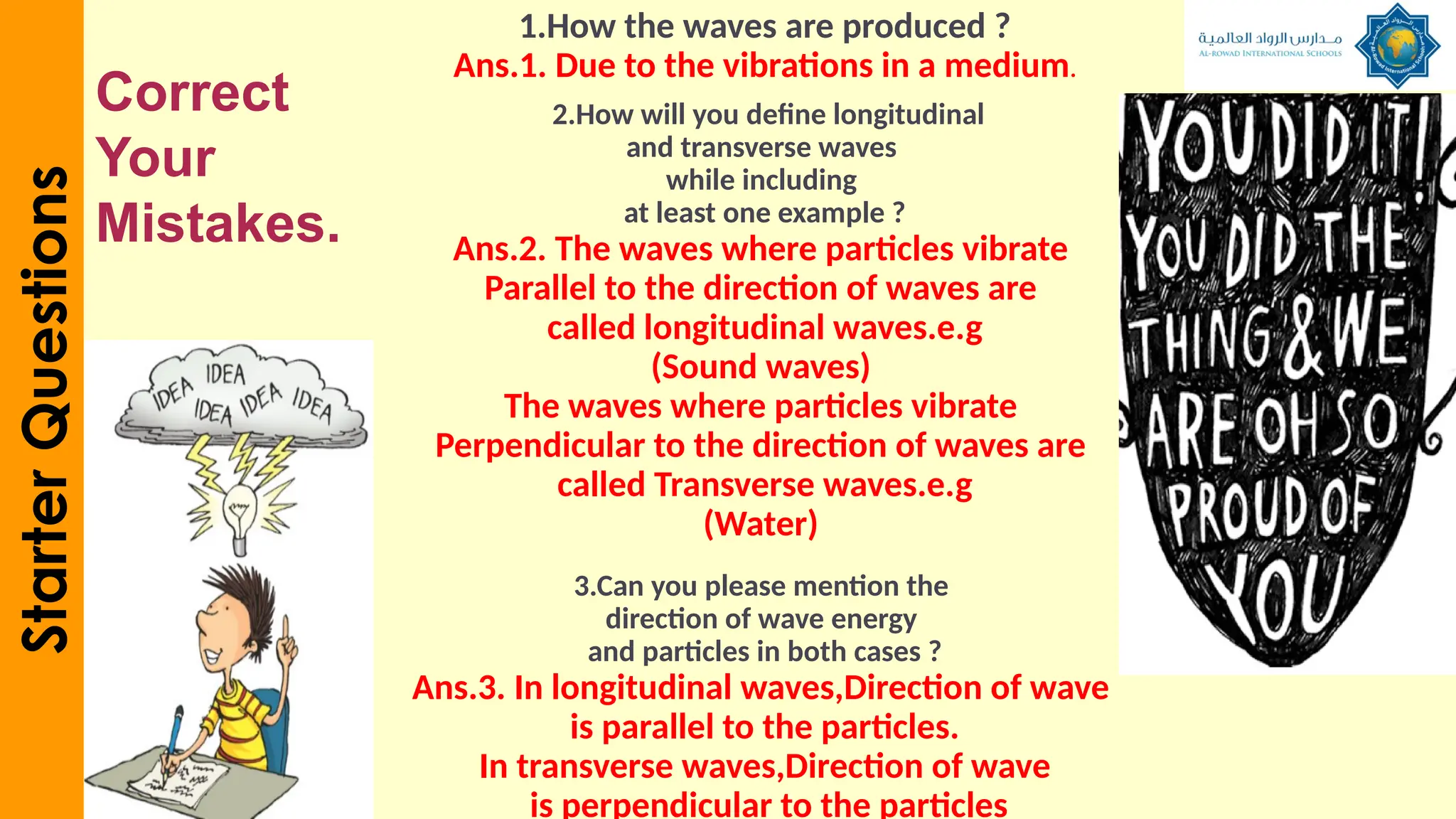
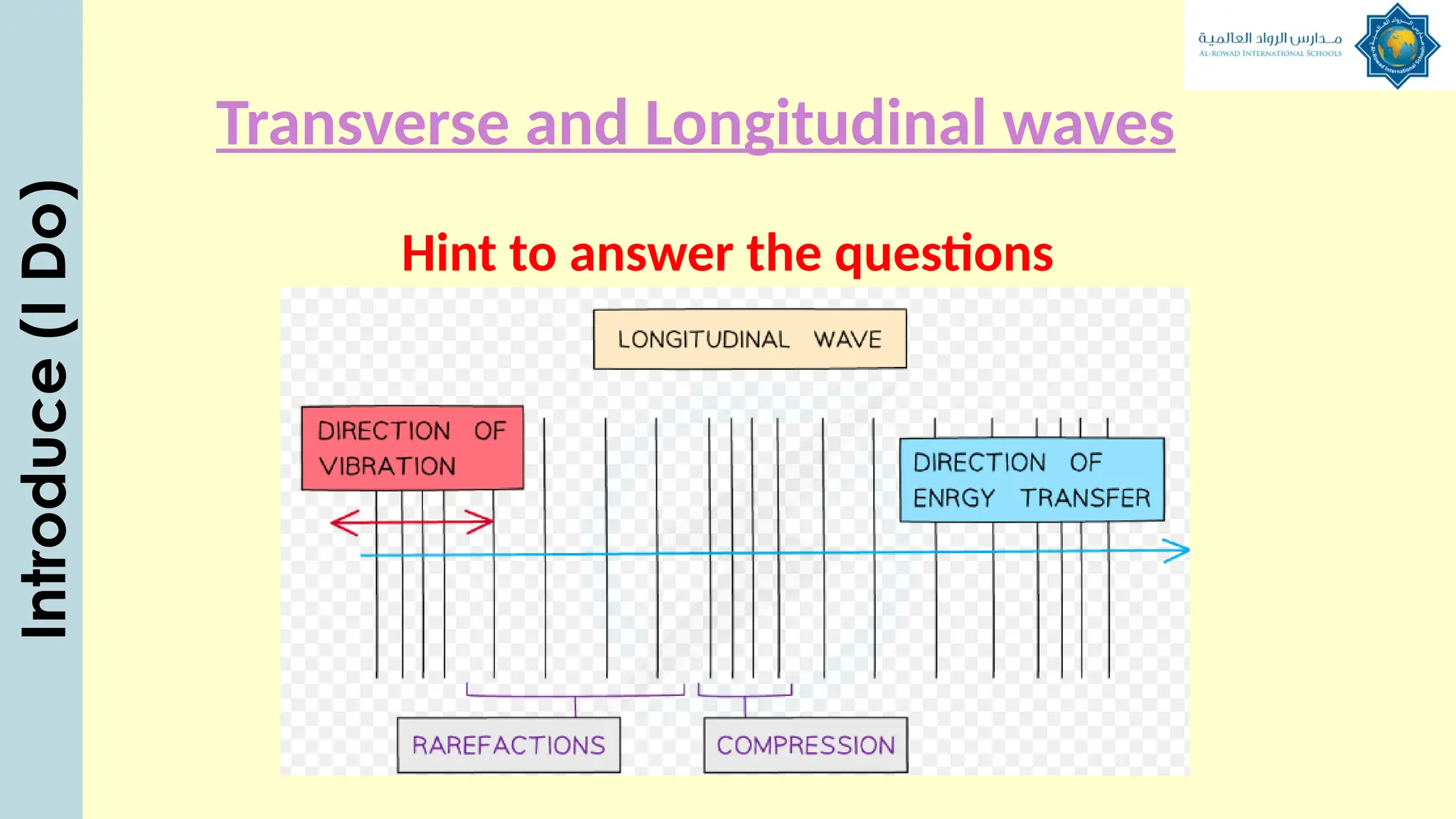
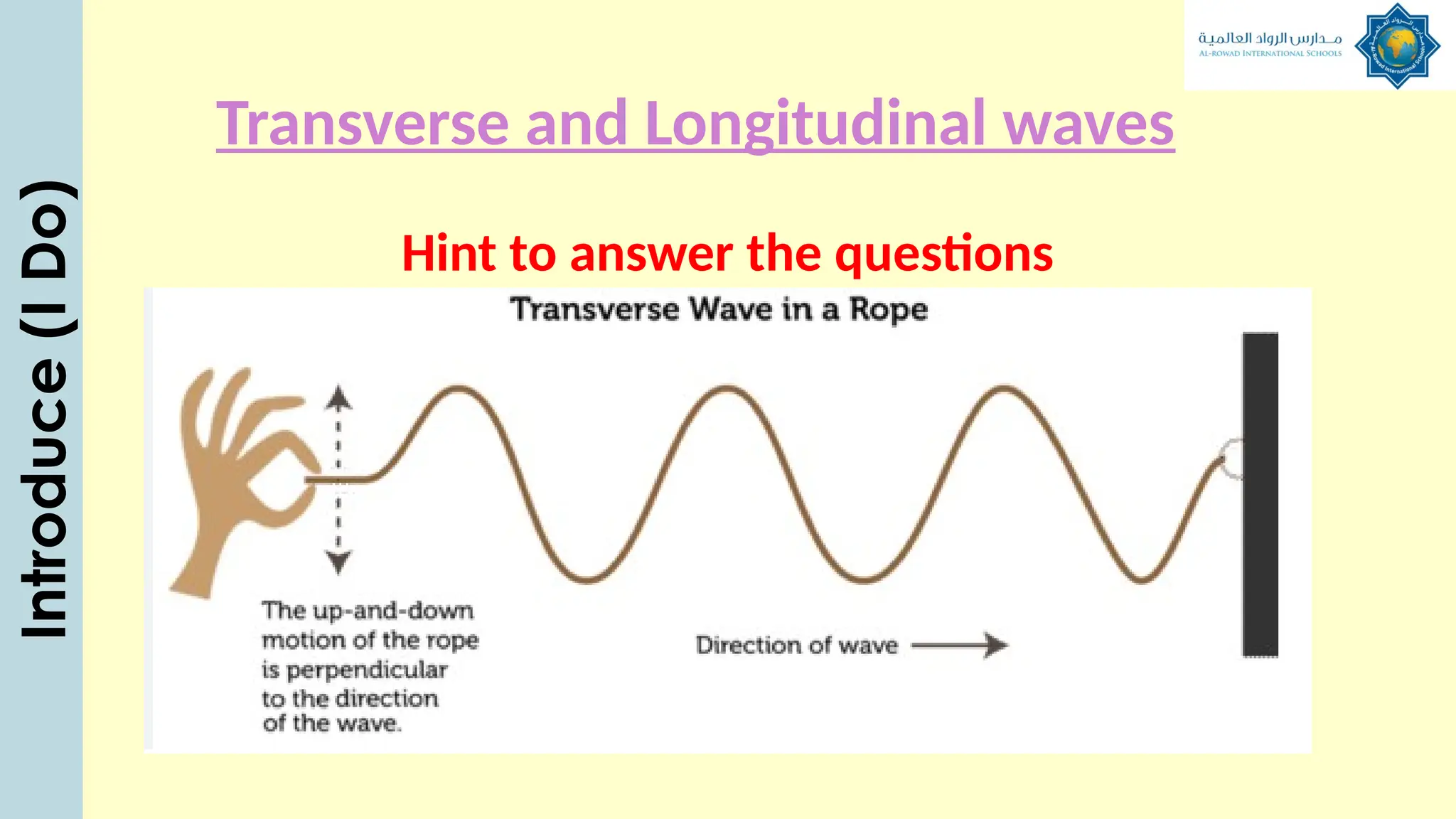
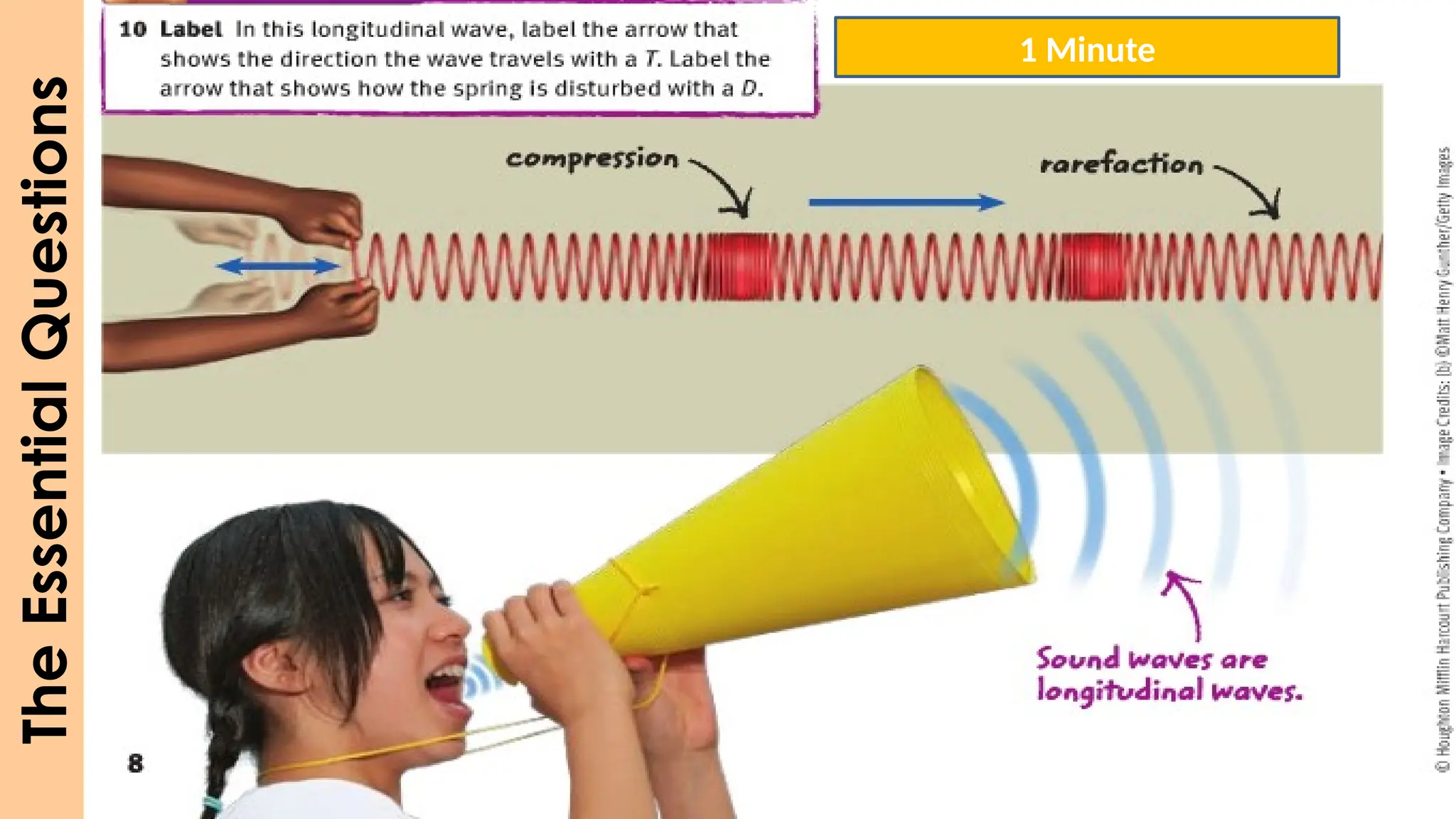
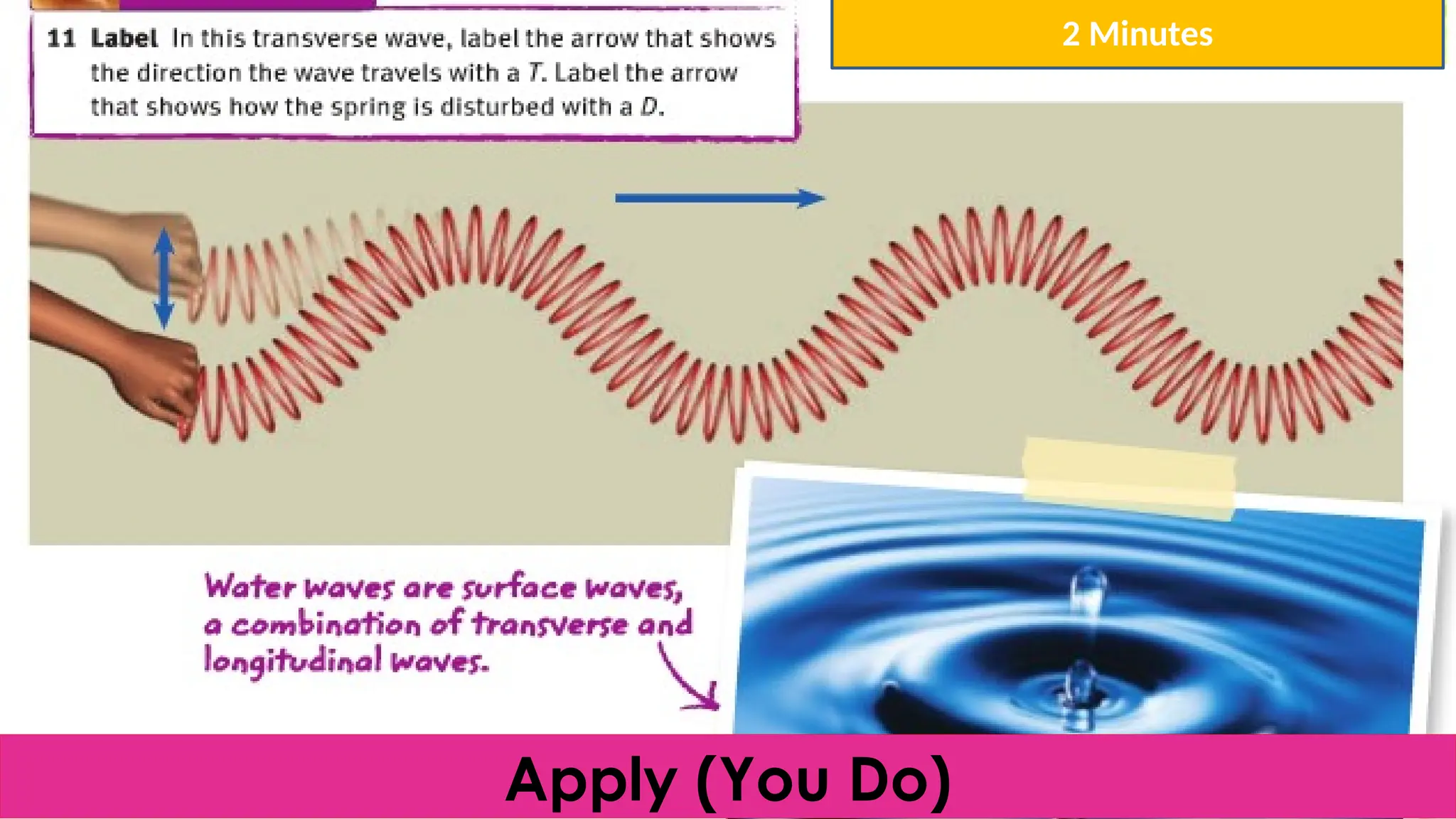
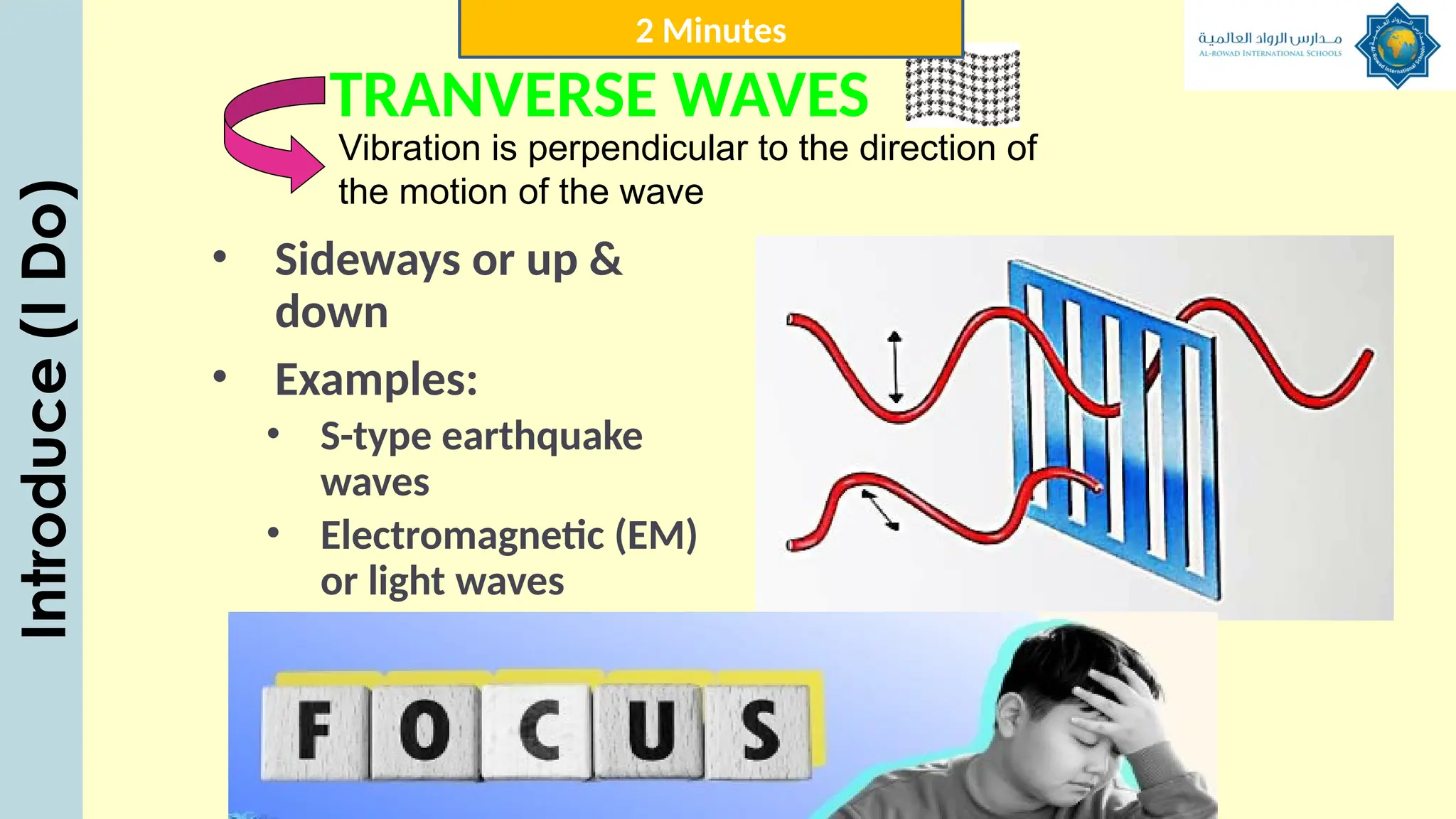
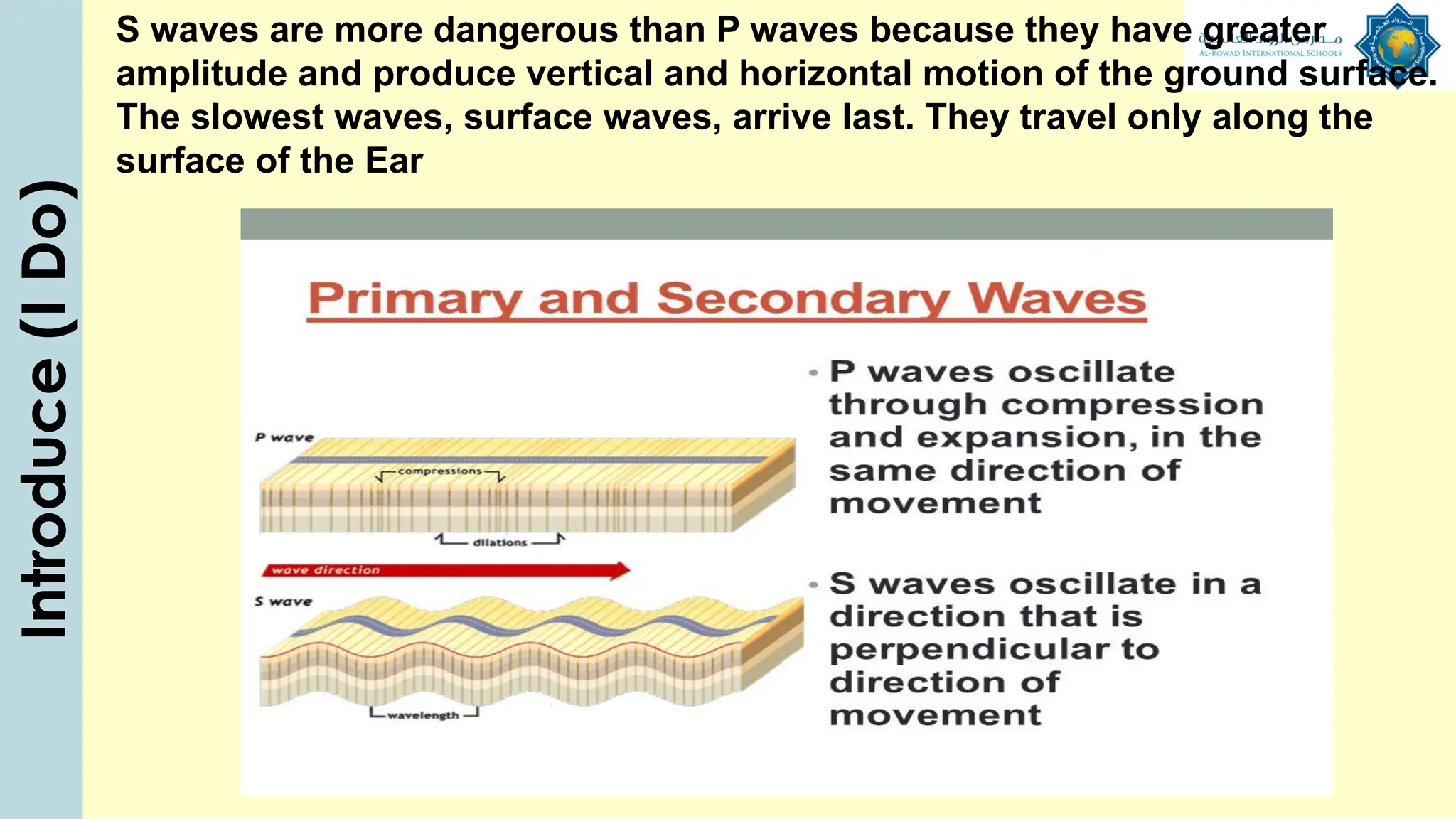
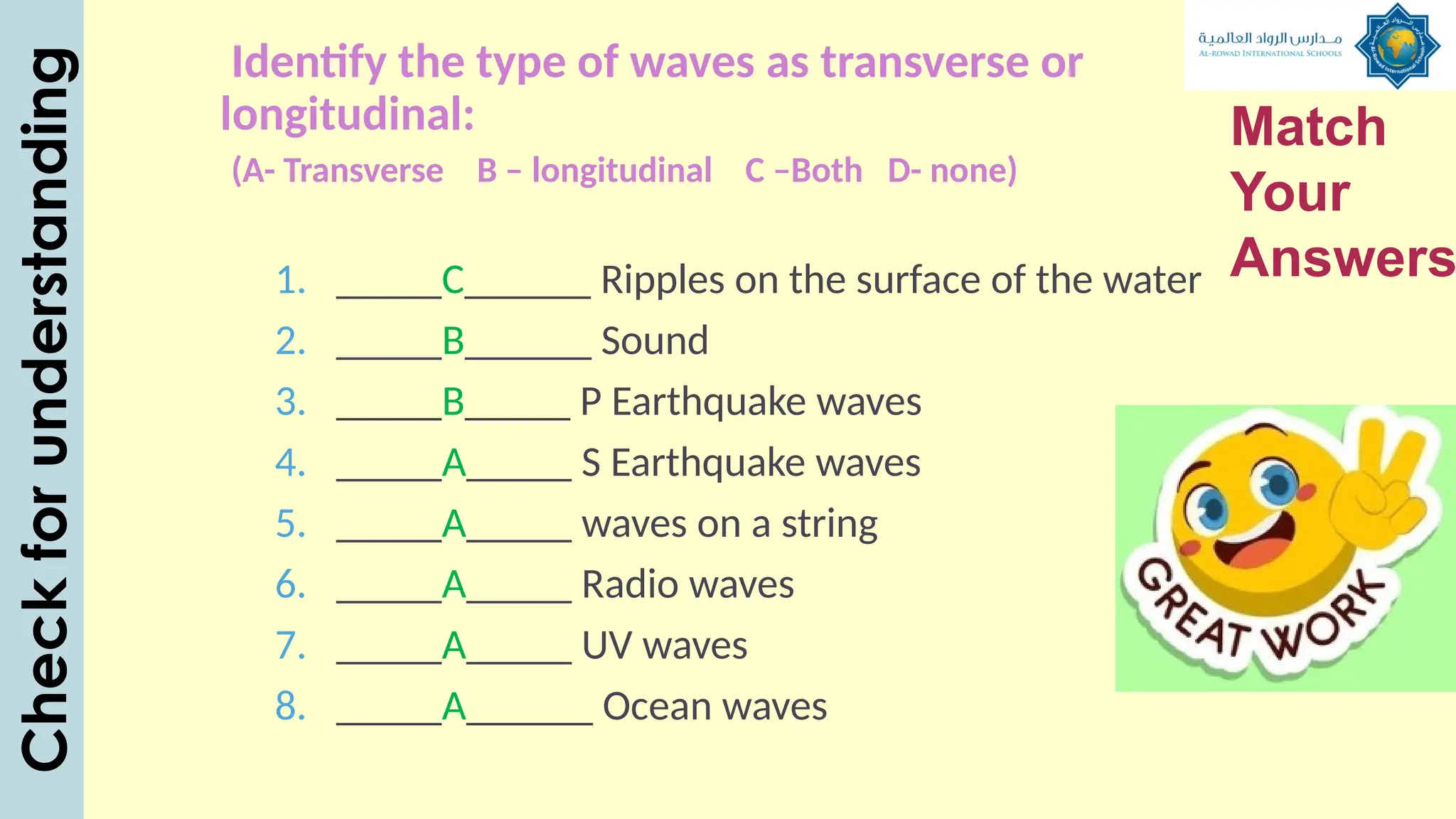
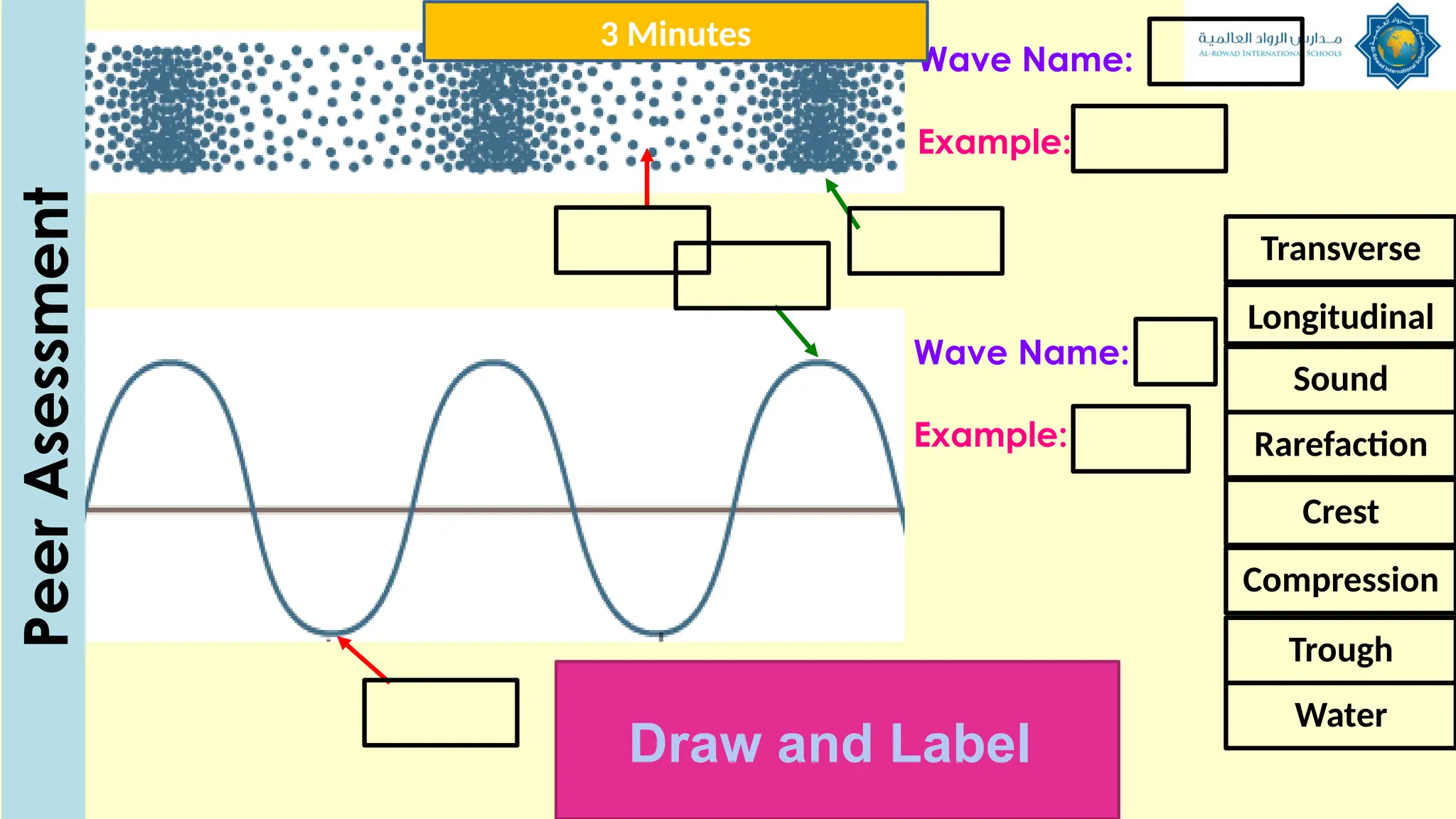
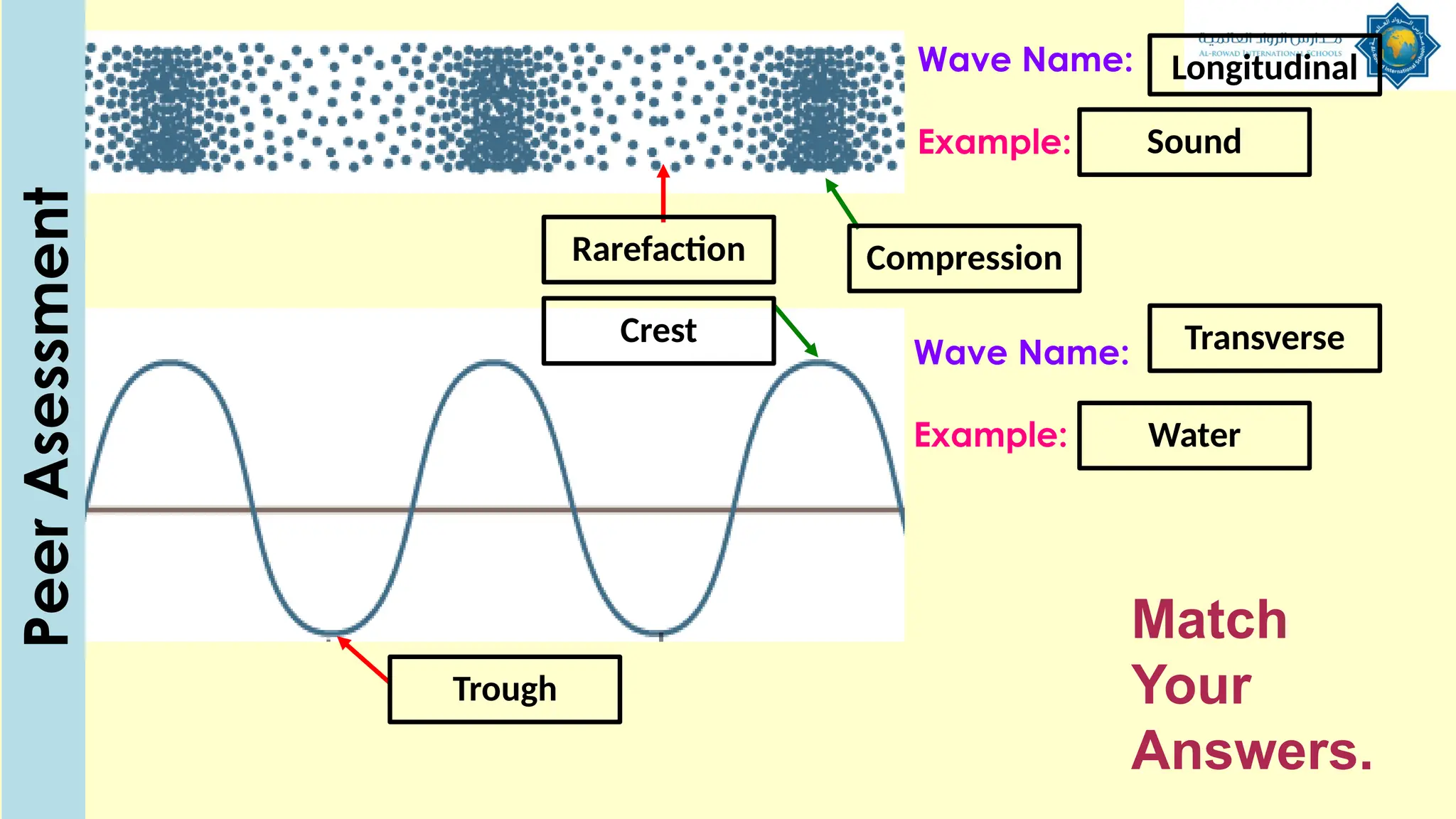
The document outlines a lesson plan focused on understanding the transfer of energy through waves, specifically transverse and longitudinal waves. It includes objectives for students to identify and differentiate these waves, conduct experiments, and engage in discussions about mechanical and electromagnetic waves. Various activities, such as video analysis, group tasks, and assessments, are incorporated to ensure comprehension and retention of concepts related to wave behavior and characteristics.