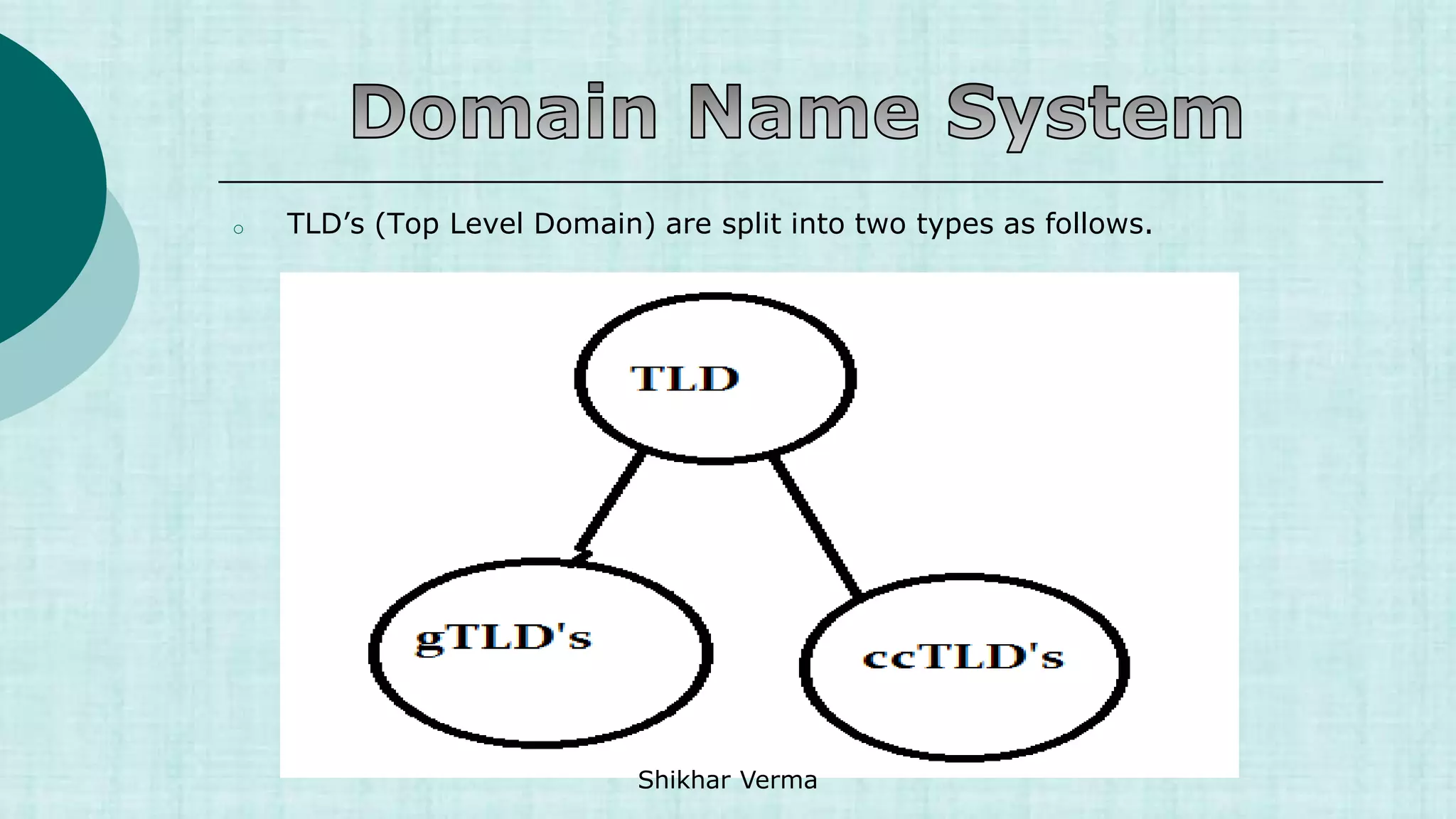
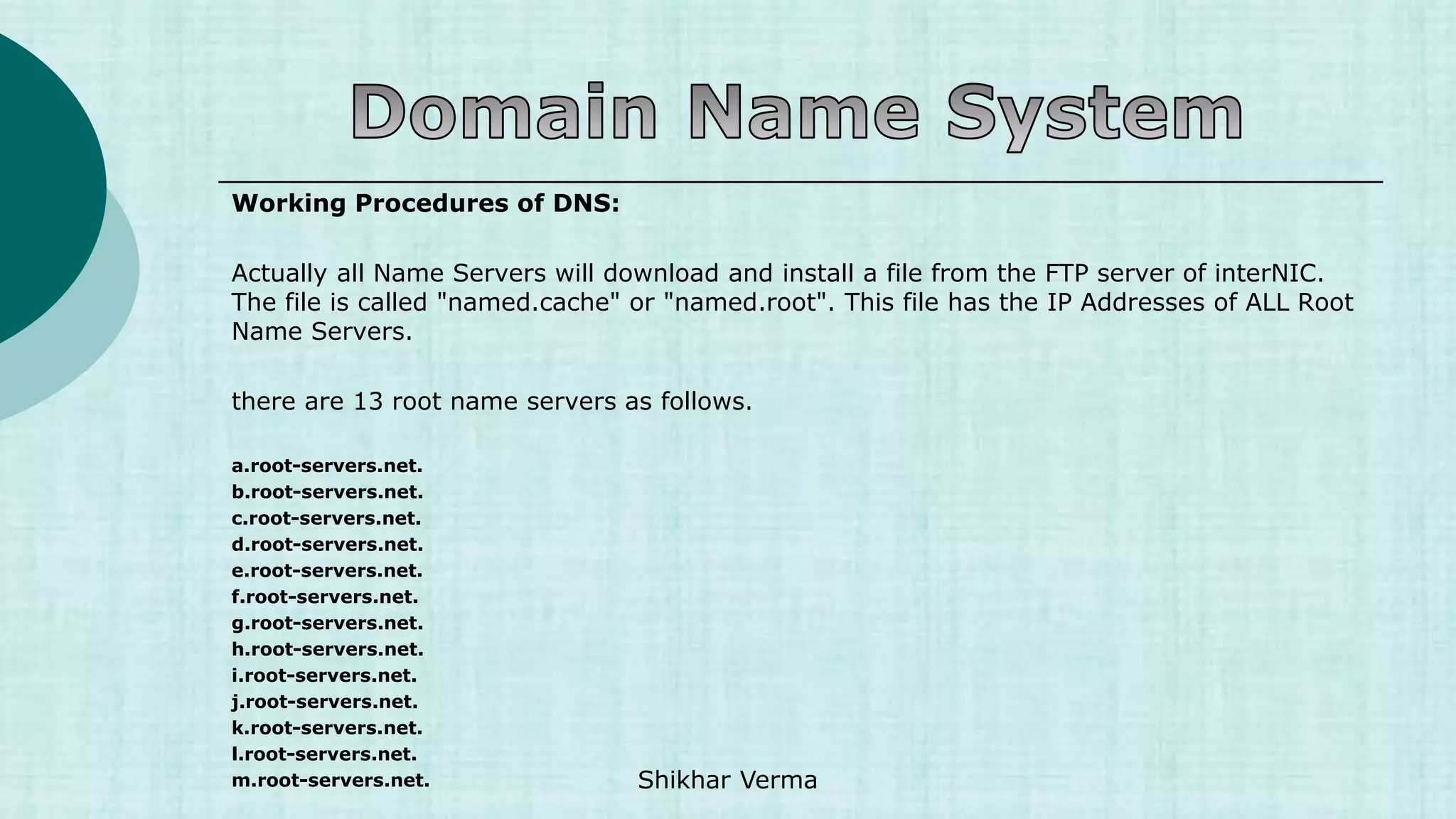
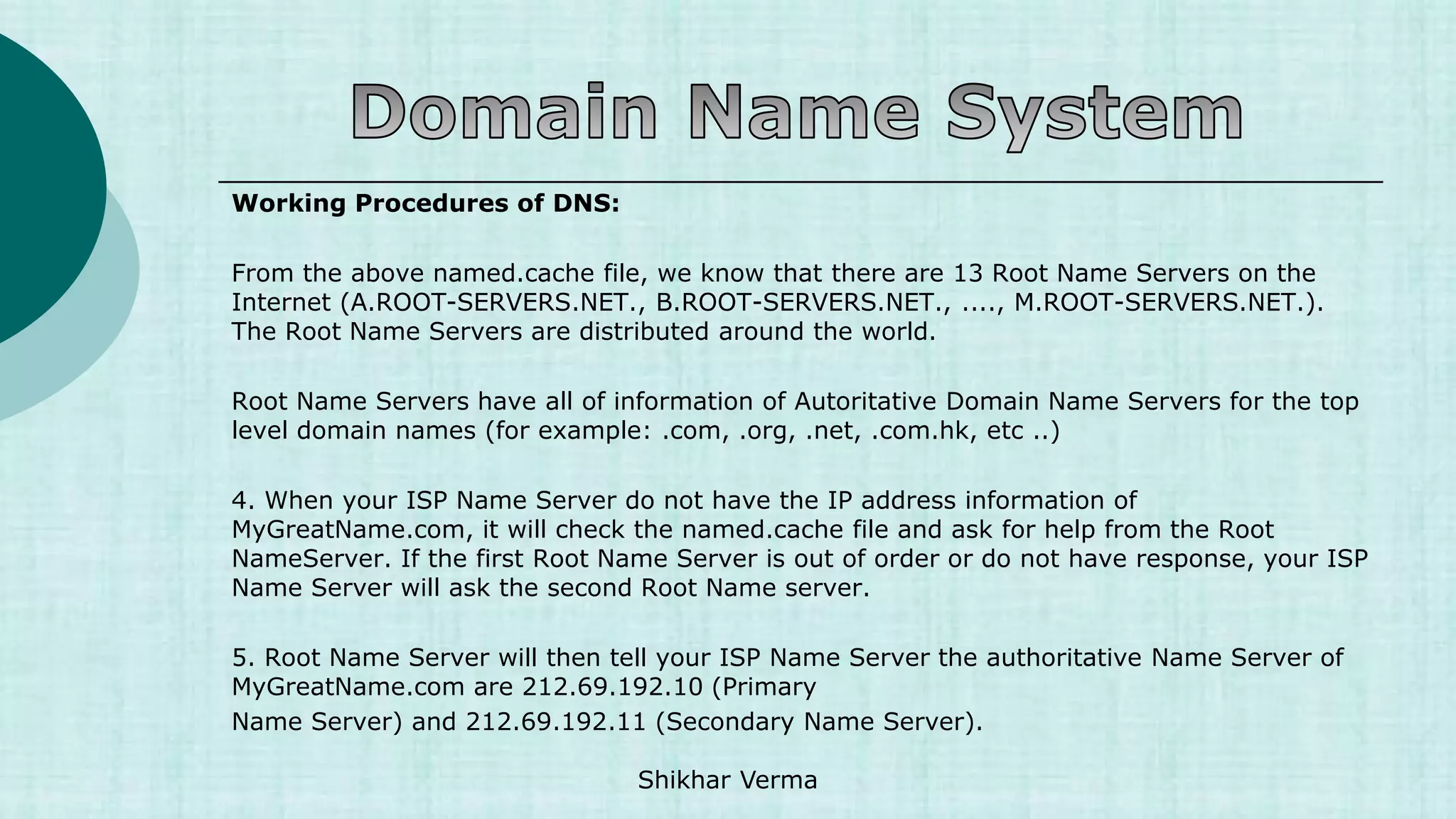
The DNS is an internet service that converts domain names to IP addresses and vice versa. It was implemented to deal with the task of translating domain names to IP addresses for any computer on the internet. When a user enters a domain name, a recursive query is made to root name servers, TLD name servers, and authoritative name servers to ultimately return the IP address associated with that domain name. DNS uses a distributed database across servers with different roles like master, slave, caching, and forwarding servers.





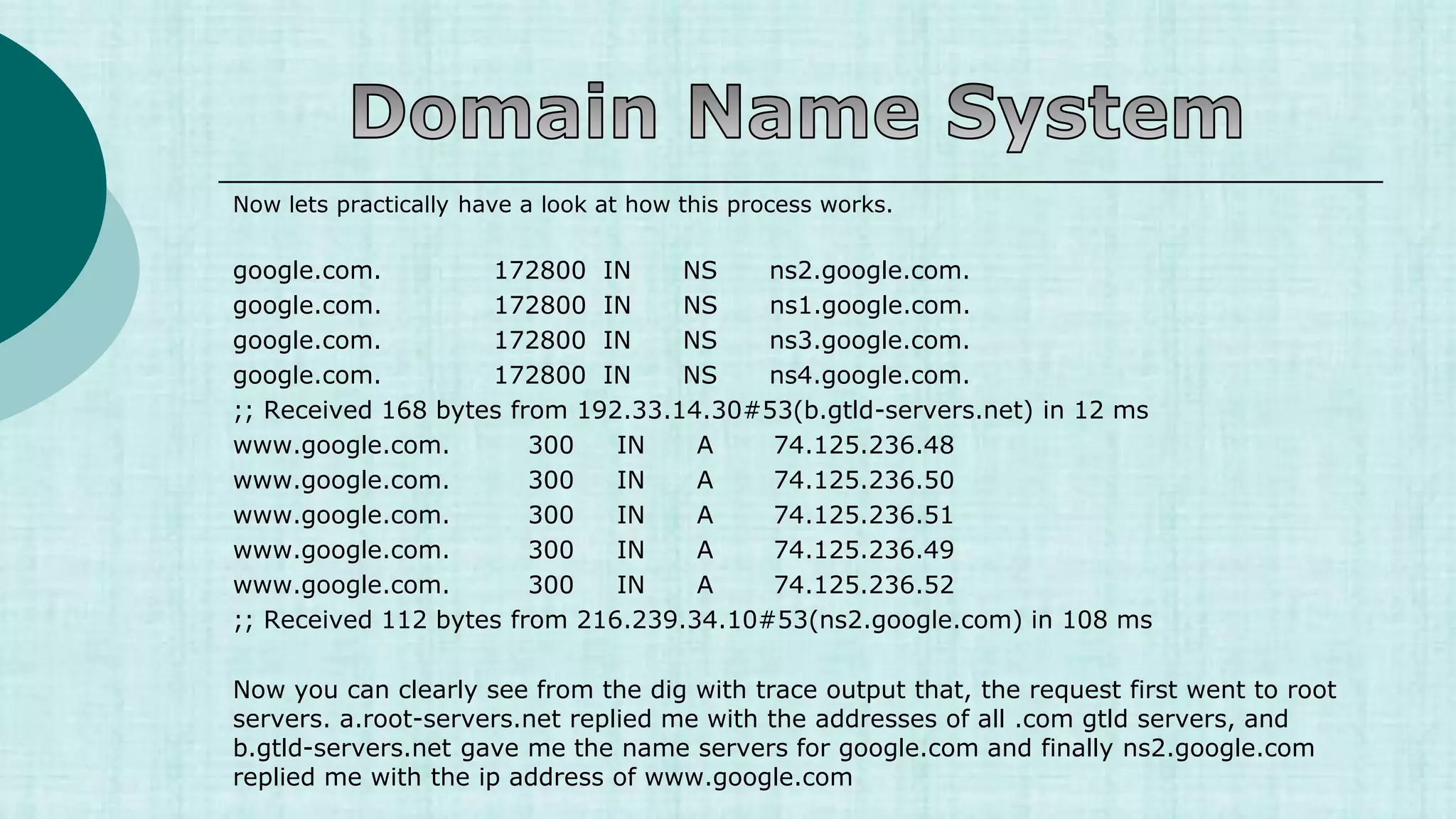
![Now lets practically have a look at how this process works.
[root@myvm1 ~]# dig +trace www.google.com
; <<>> DiG 9.3.4-P1 <<>> +trace www.google.com
;; global options: printcmd
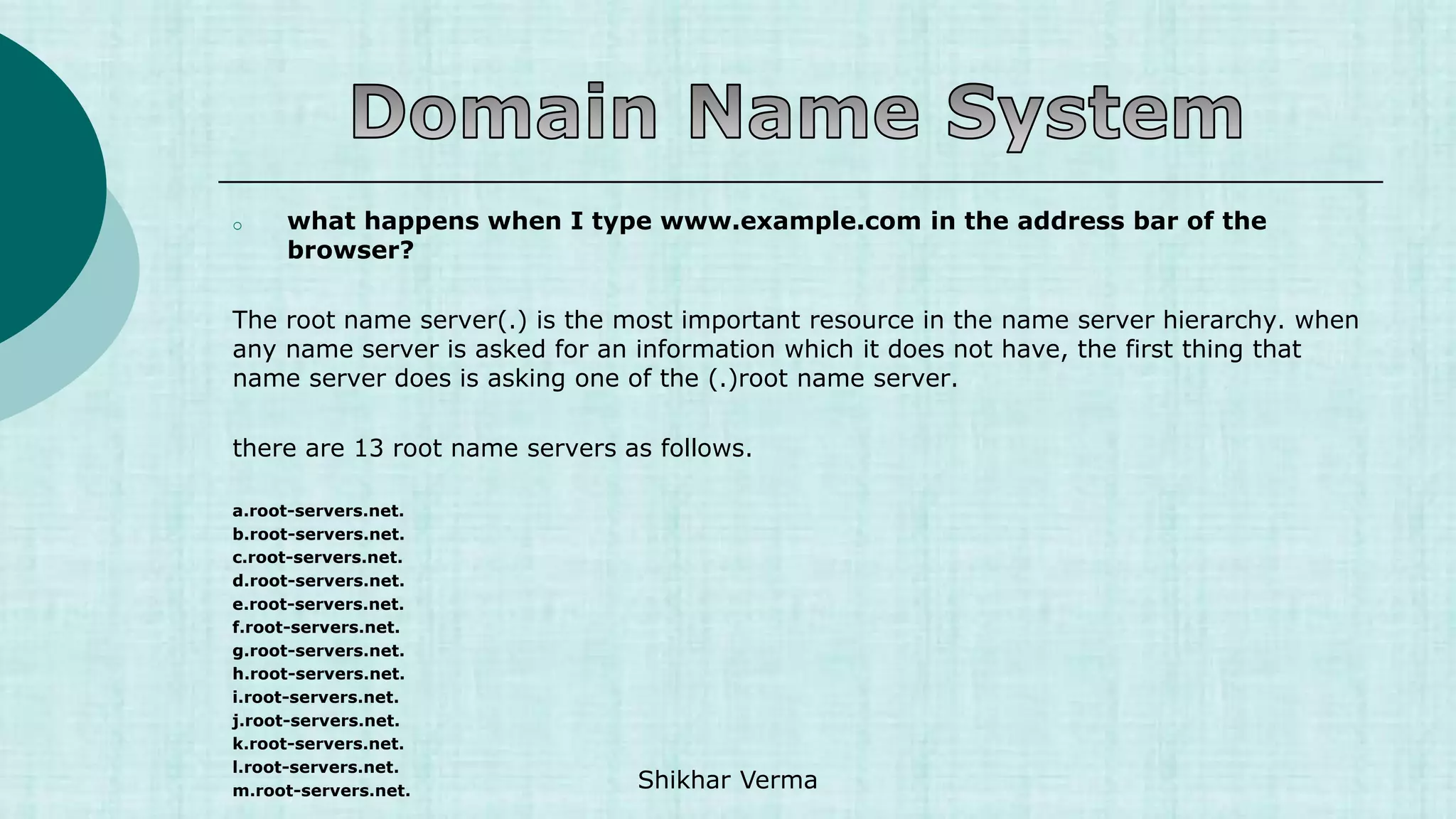
. 5 IN NS a.root-servers.net.
. 5 IN NS b.root-servers.net.
. 5 IN NS c.root-servers.net.
. 5 IN NS d.root-servers.net.
. 5 IN NS e.root-servers.net.
. 5 IN NS f.root-servers.net.
. 5 IN NS g.root-servers.net.
. 5 IN NS h.root-servers.net.
. 5 IN NS i.root-servers.net.
. 5 IN NS j.root-servers.net.
. 5 IN NS k.root-servers.net.
. 5 IN NS l.root-servers.net.
. 5 IN NS m.root-servers.net.
;; Received 228 bytes from 192.168.159.2#53(192.168.159.2) in 49 ms](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-230421052609-ef0fa890/75/1-1-DNS-ppt-ppt-13-2048.jpg)










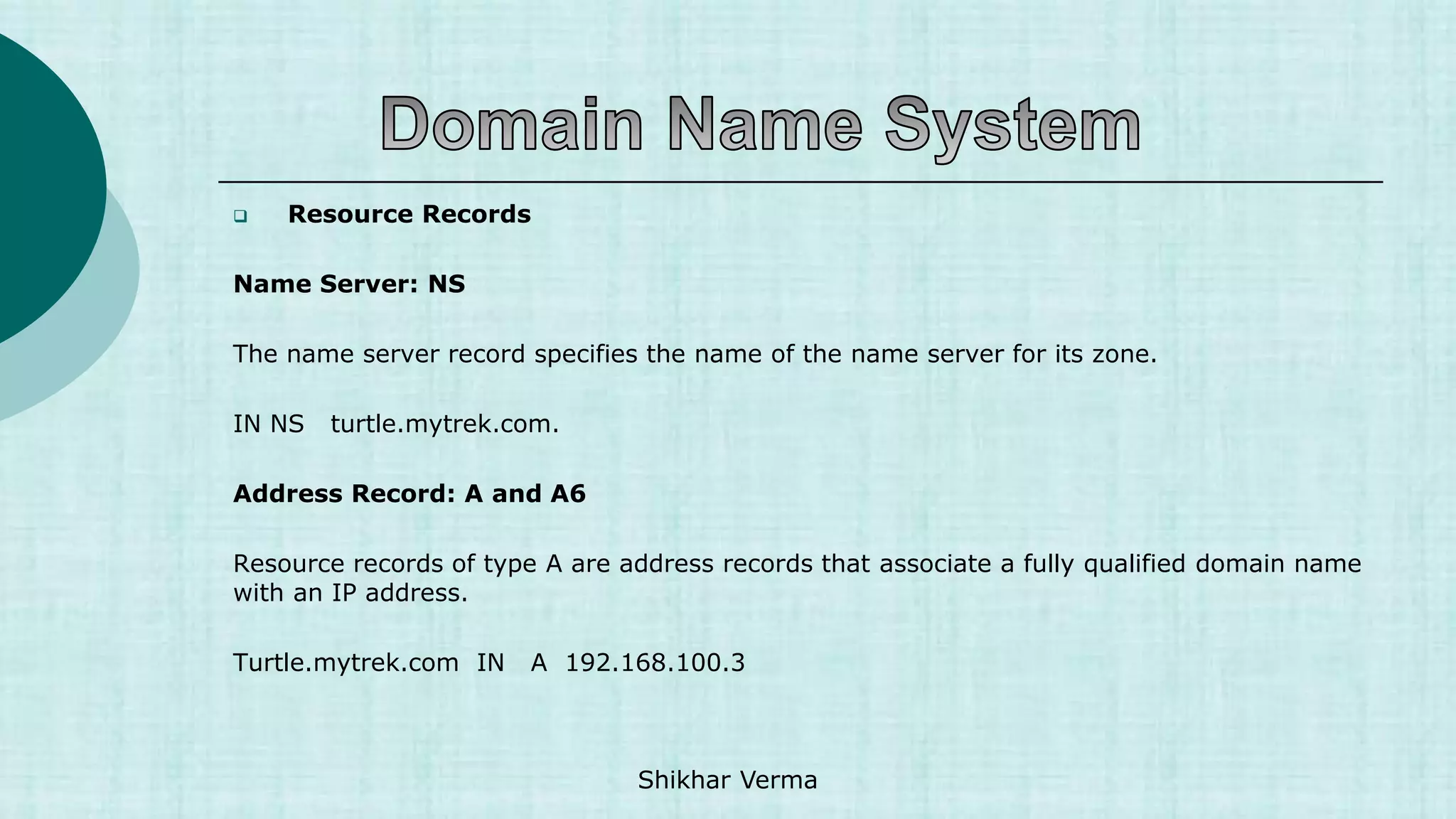
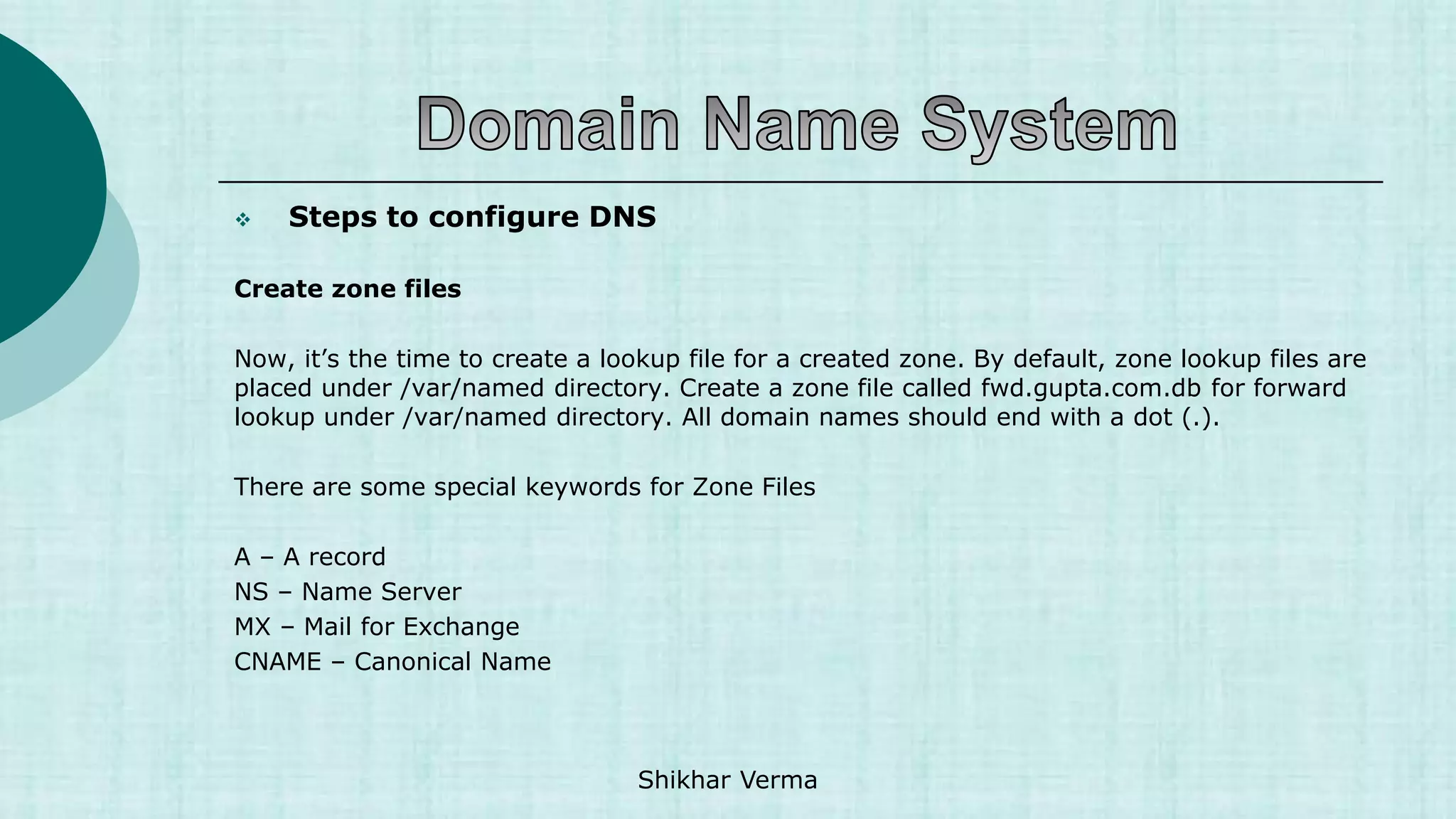
![ Resource Records
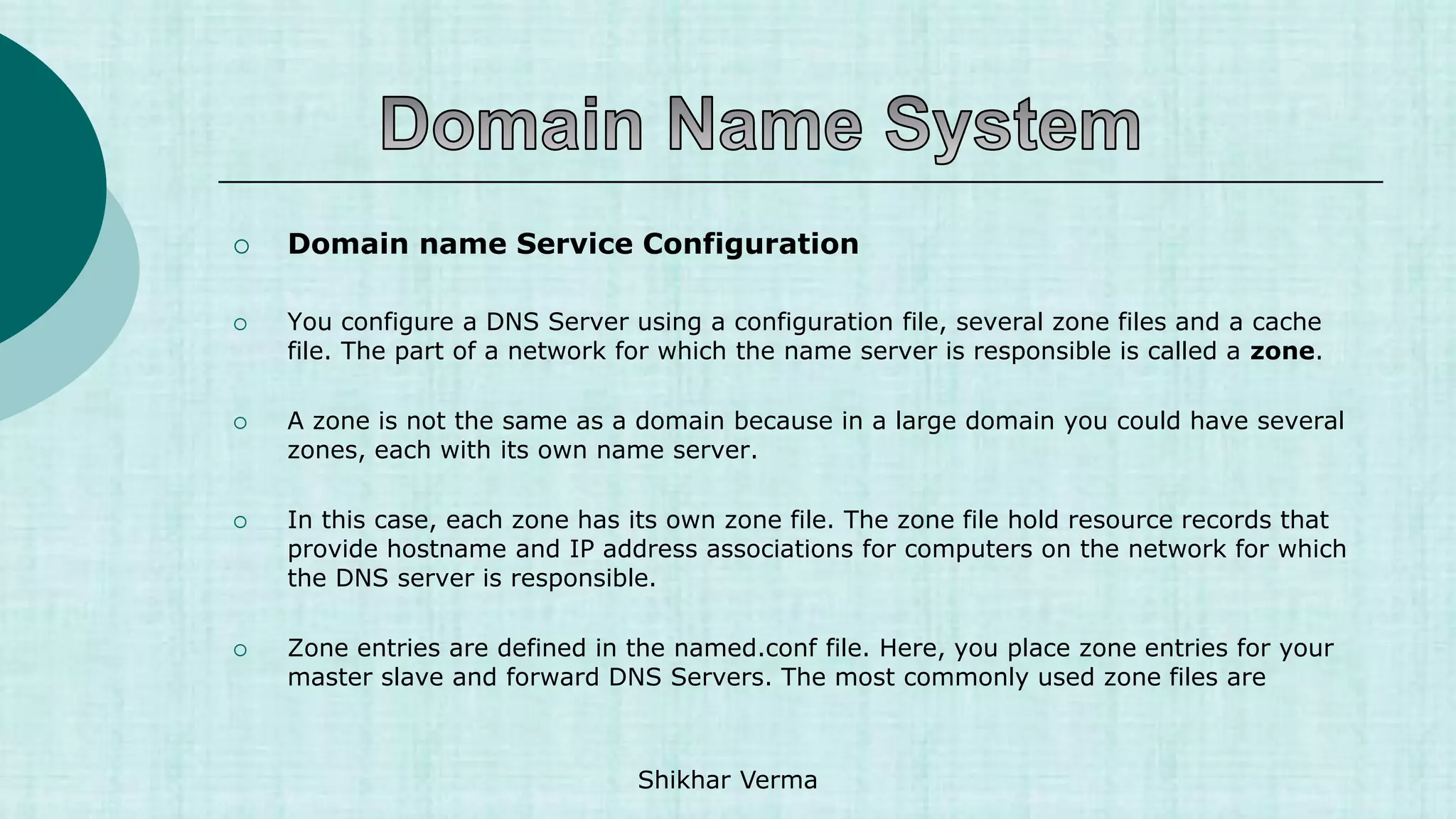
Resource records are used to associate IP Addresses with fully qualified domain names. You
need a record for every computer in the zone.
name [<ttl> [<class>] <type> <rdata> [<comments>]
Each zone files contains a variety of records (SOA, NS,MX,A,PTR and CNAME)
Shikhar Verma](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-230421052609-ef0fa890/75/1-1-DNS-ppt-ppt-30-2048.jpg)





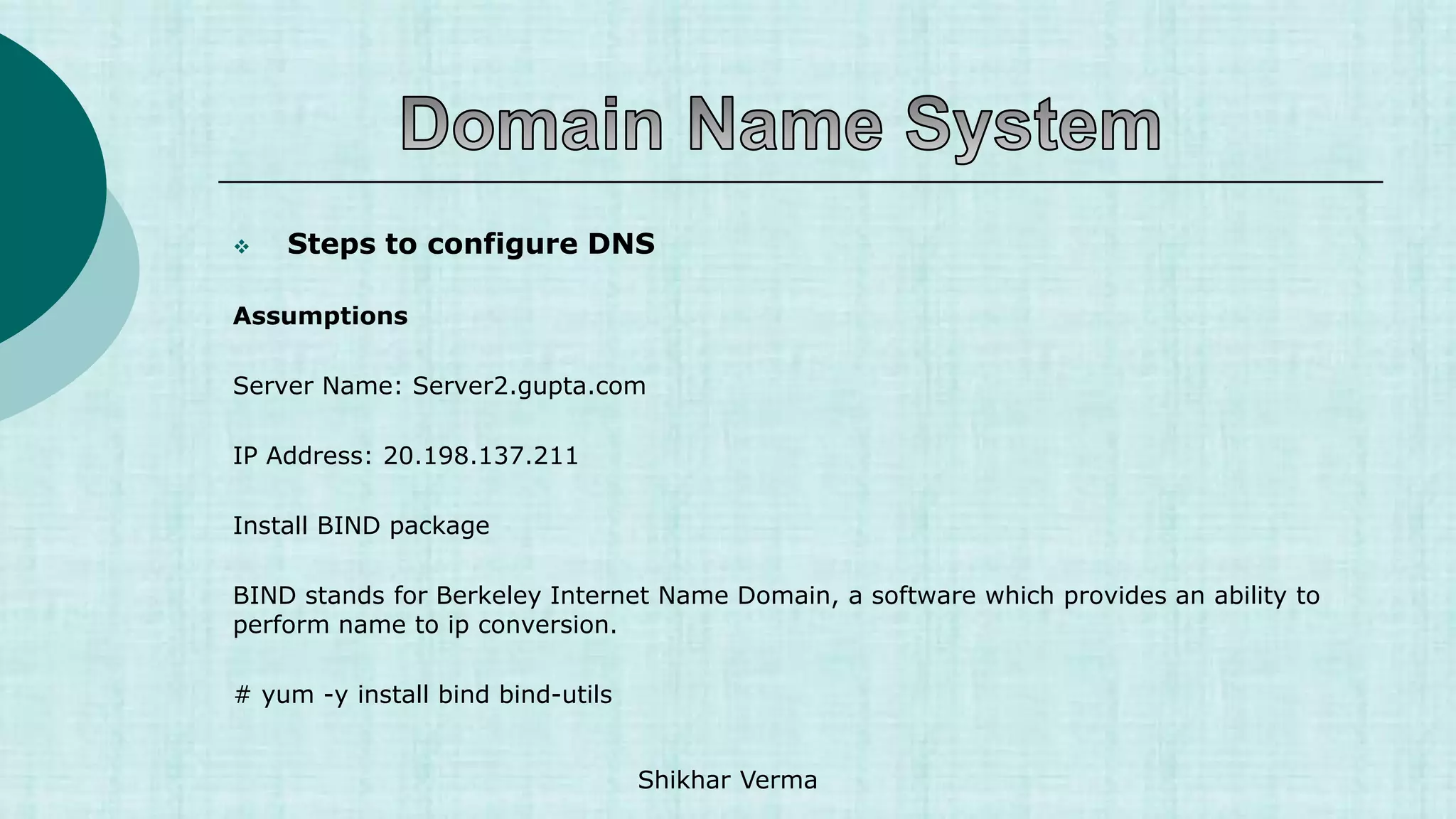
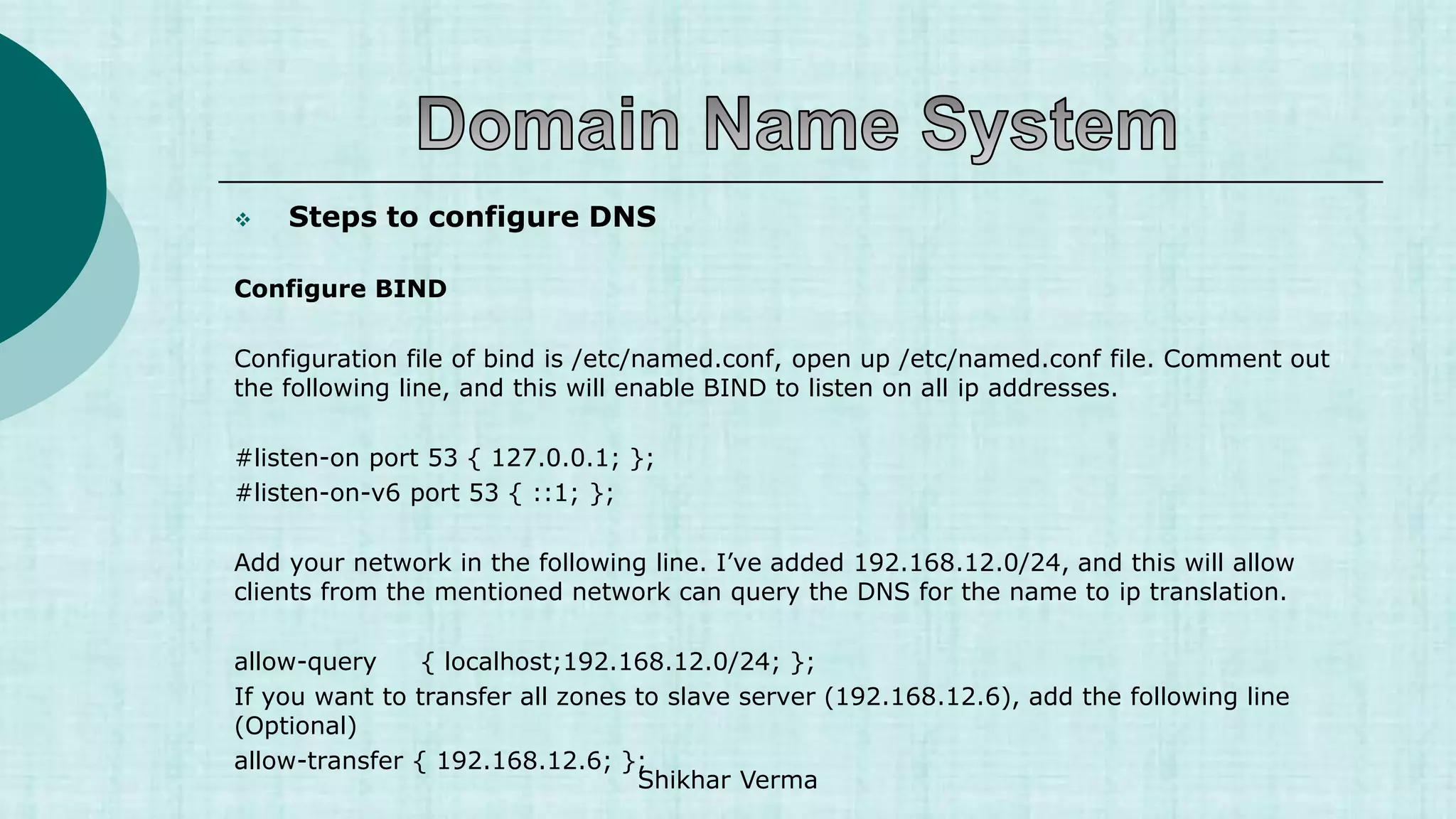
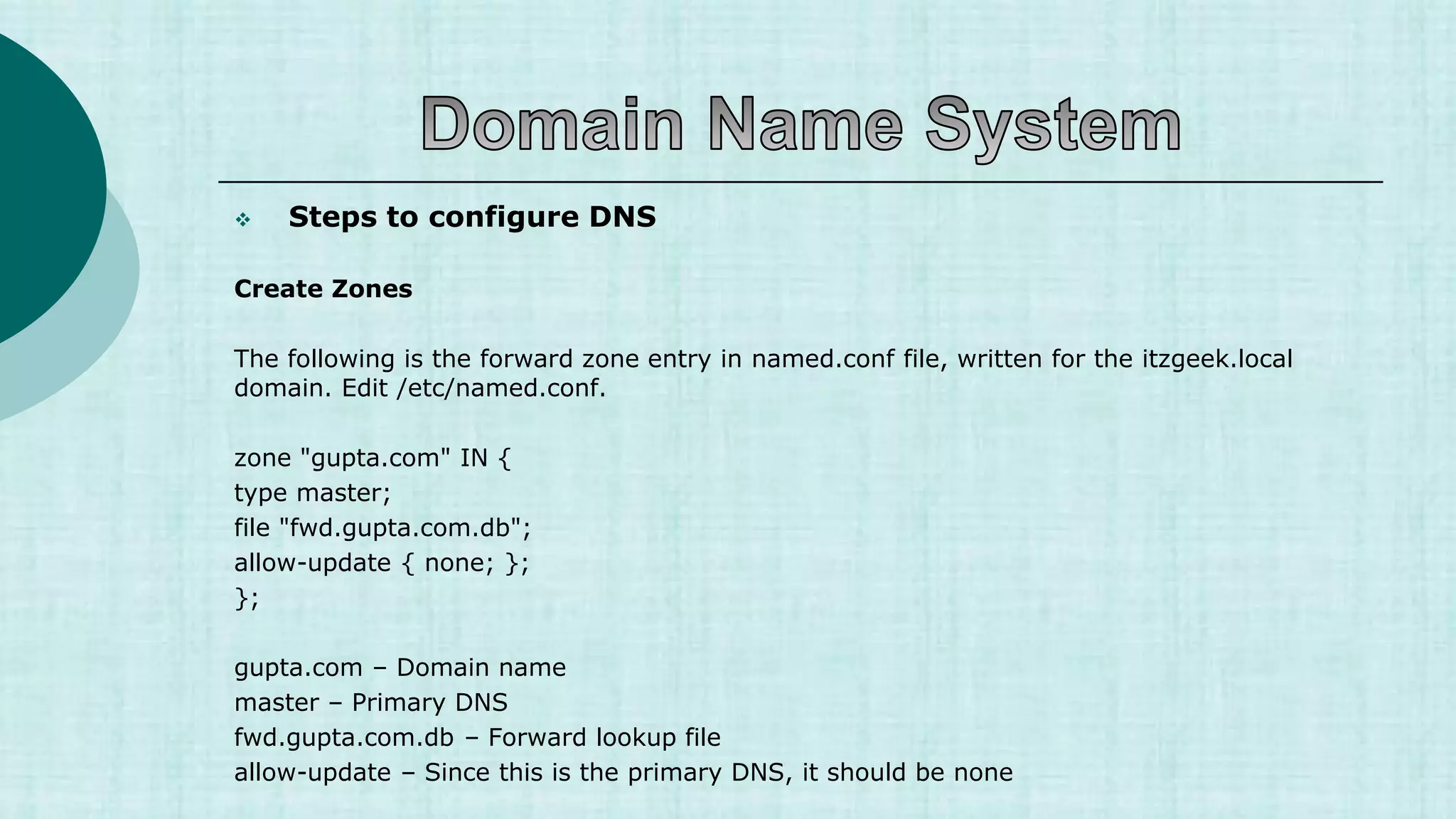

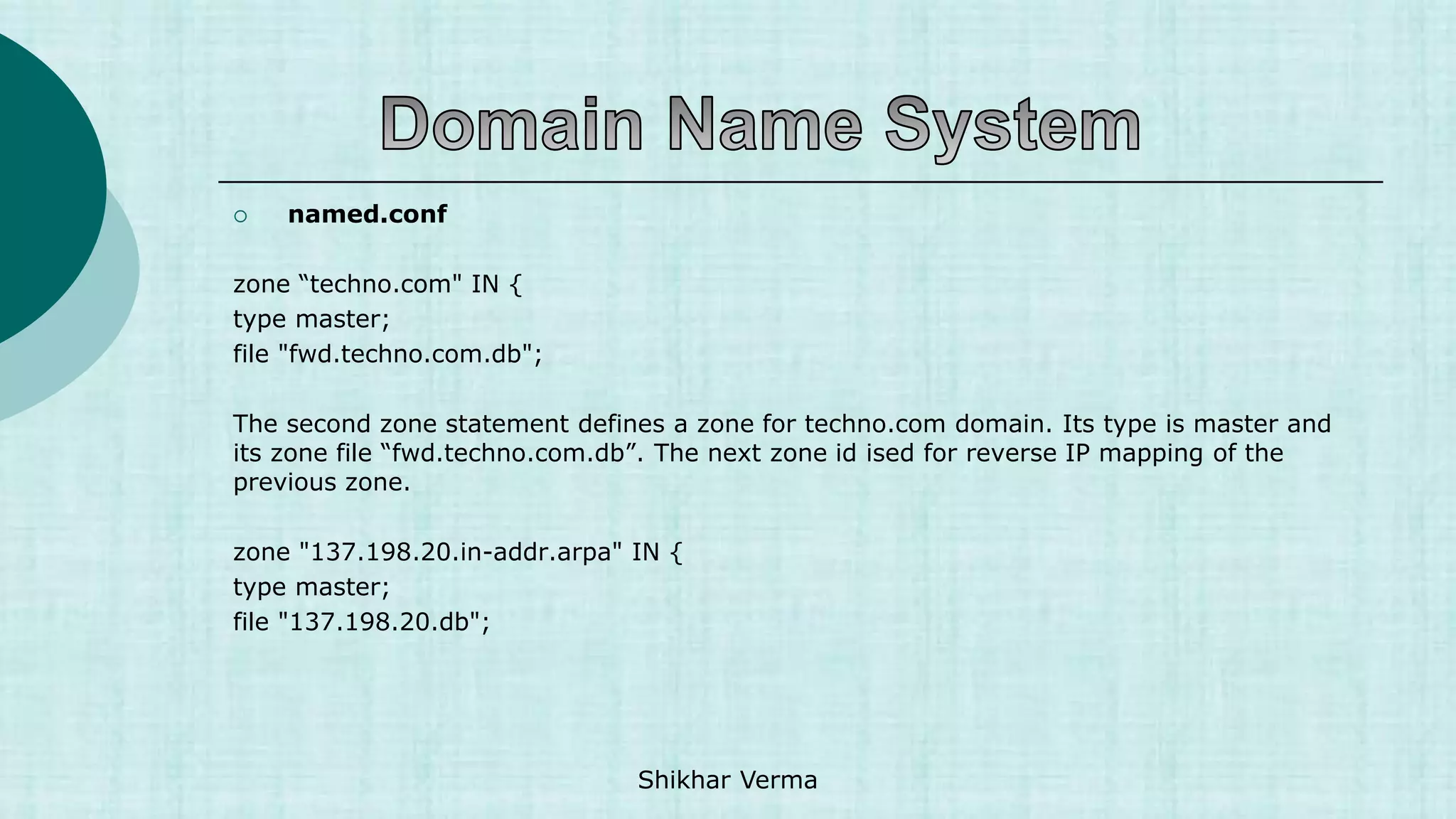
![ Steps to configure DNS
[root@Server2 named]# vi /var/named/fwd.gupta.com.db
$TTL 86400
@ IN SOA Server2.gupta.com. root.gupta.com. (
2017112807 ;Serial
3600 ;Refresh
1800 ;Retry
604800 ;Expire
86400 ;Minimum TTL
)
@ IN NS Server2.gupta.com.
Server2 IN A 20.198.137.211
Server1 IN A 20.198.137.84
gupta.com. IN MX 10 mail.gupta.com.
www IN A 20.198.137.211
mail IN A 20.198.137.211
shikhar IN CNAME Server2.gupta.com. Shikhar Verma](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-230421052609-ef0fa890/75/1-1-DNS-ppt-ppt-42-2048.jpg)
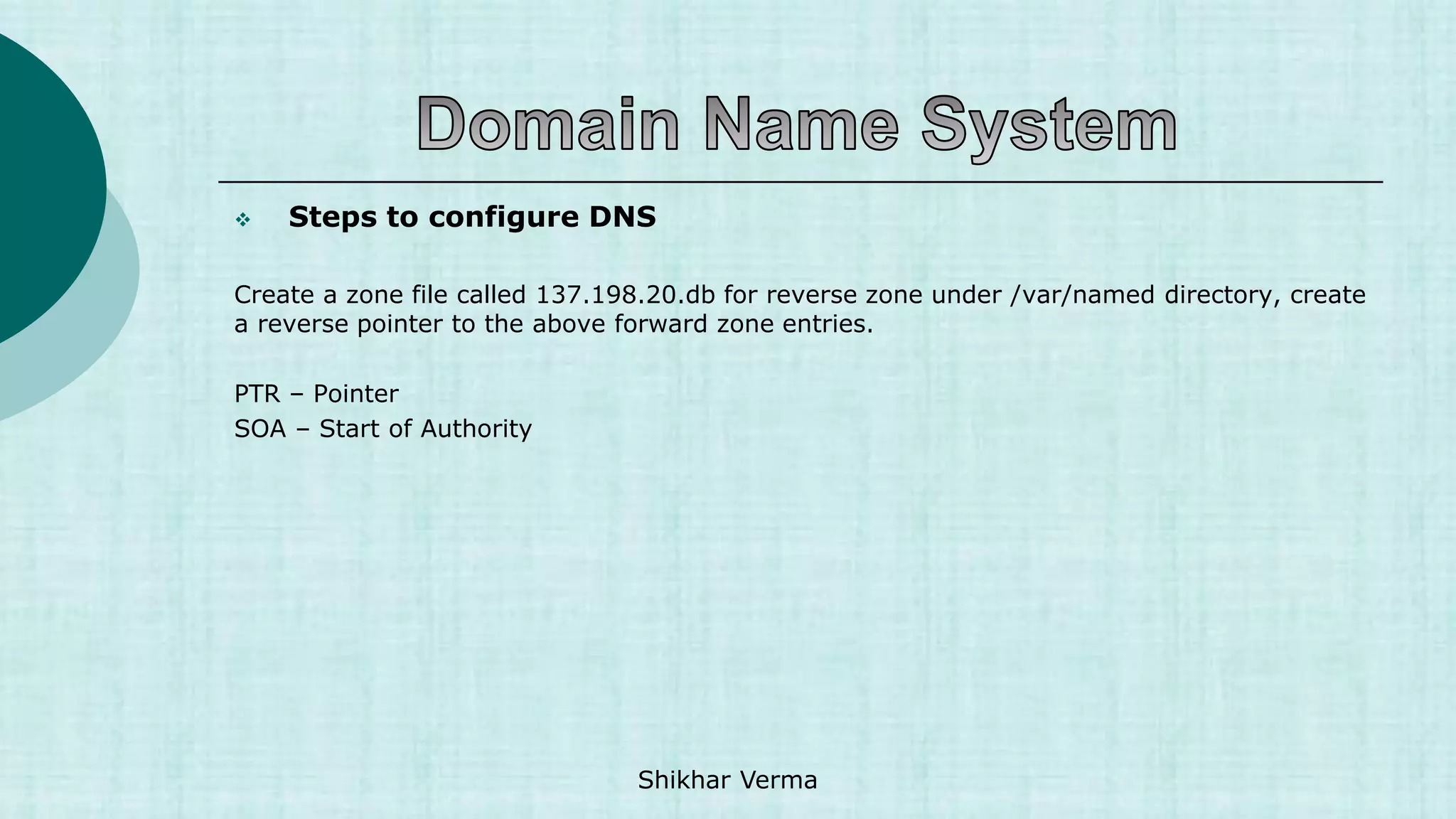
![ Steps to configure DNS
[root@Server2 named]# vi /var/named/137.198.20.db
$TTL 86400
@ IN SOA Server2.gupta.com. root.gupta.com. (
2017112807 ;Serial
3600 ;Refresh
1800 ;Retry
604800 ;Expire
86400 ;Minimum TTL
)
@ IN NS Server2.gupta.com.
211 IN PTR Server2.gupta.com.
211 IN PTR www.gupta.com.
84 IN PTR Server1.gupta.com.
Shikhar Verma](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-230421052609-ef0fa890/75/1-1-DNS-ppt-ppt-44-2048.jpg)