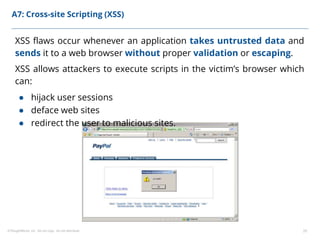
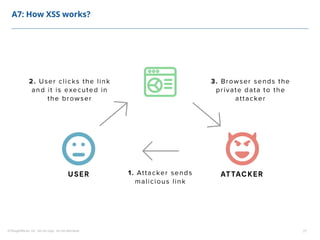
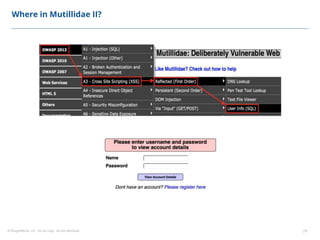
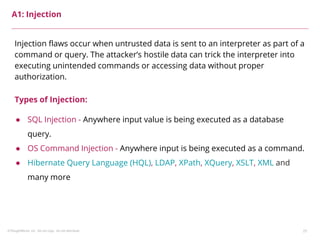
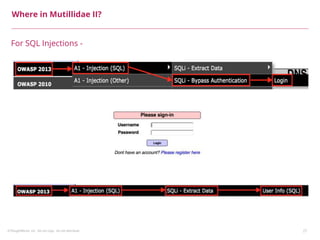
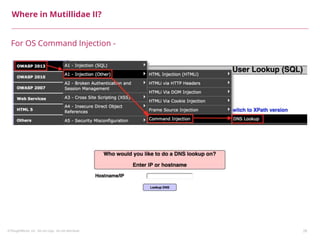
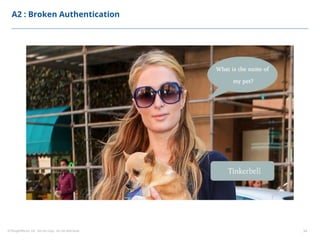
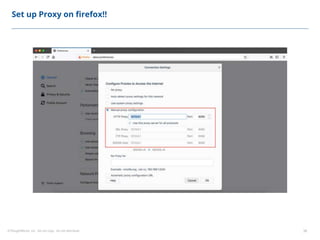
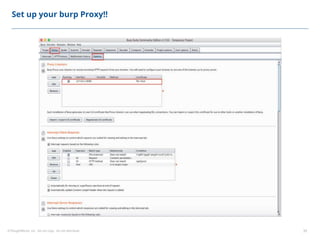
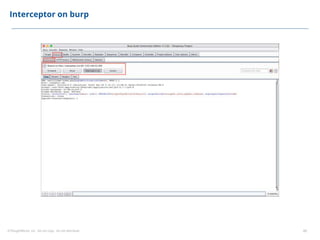
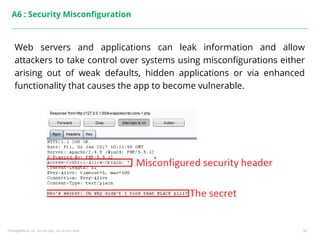
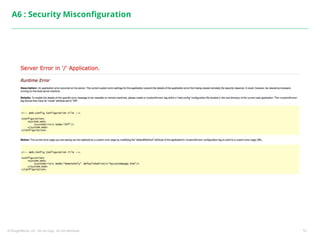
This document summarizes a presentation on security testing by Amit Gundiyal and Nalinikanth from ThoughtWorks. The presentation covered the role of quality analysts in security testing, the OWASP Top 10 security risks, and hands-on examples of vulnerabilities like cross-site scripting, SQL injection, sensitive data exposure, and broken authentication. It emphasized that security testing should be a priority for quality analysts due to their role in testing all parts of a system and helping build more secure products.