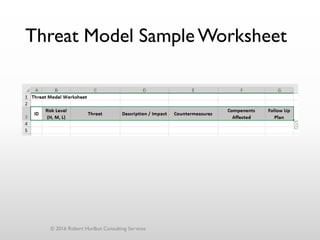
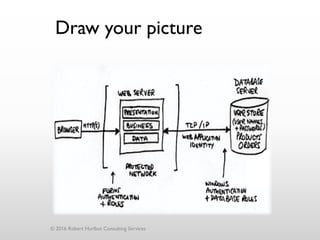
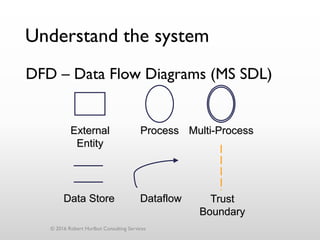
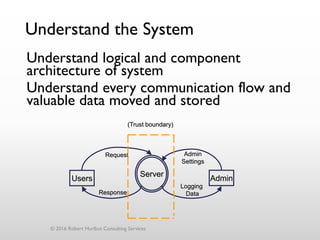
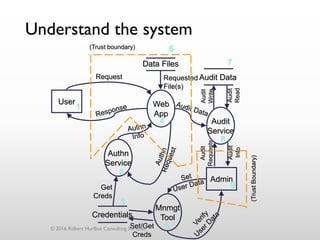
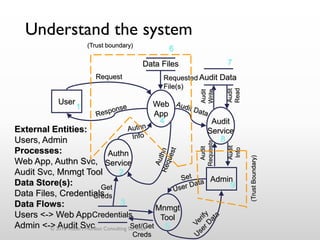
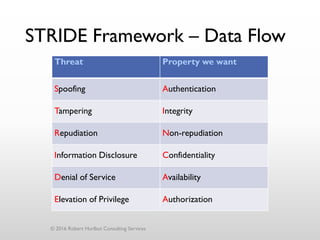
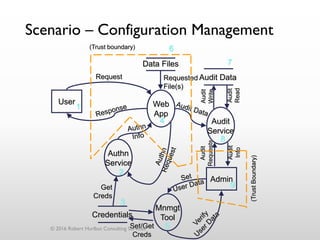
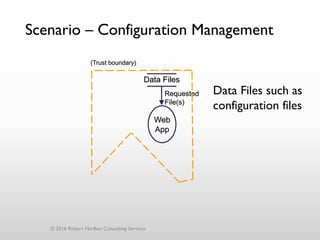
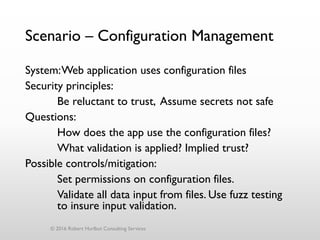
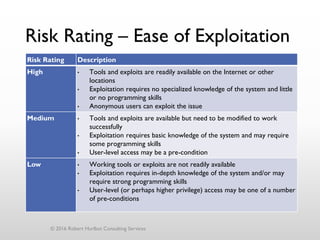
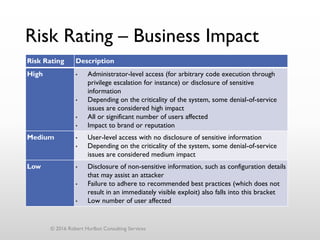
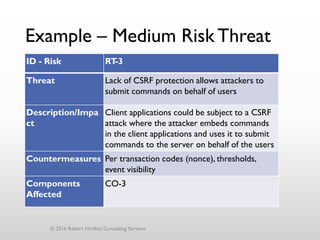
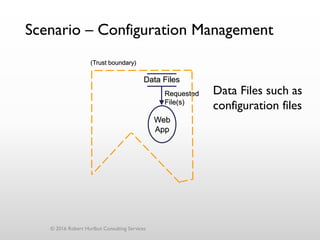
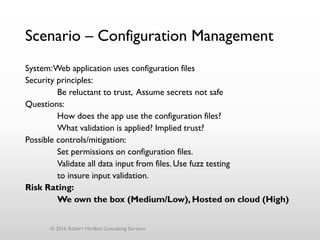
The document discusses threat modeling as a process for secure software design. It begins with an introduction of the speaker, Robert Hurlbut, and his background. The presentation then discusses how threat modeling helps bridge gaps between different security roles and fits within the software development lifecycle. Key aspects of threat modeling covered include understanding the system, identifying potential threats, determining mitigations and risks. The document provides examples and questions to guide the threat modeling process.