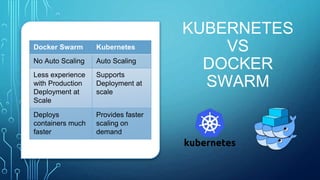
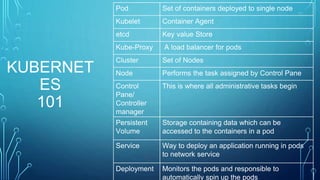
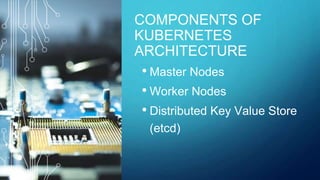
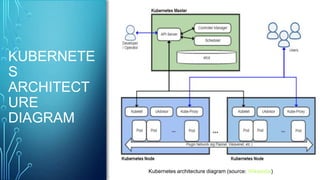
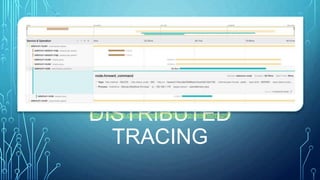
This document discusses testing cloud native applications. It begins with definitions of testing for monolithic vs cloud native applications. It then provides an overview of concepts like Kubernetes, containers, microservices and cloud computing. The rest of the document focuses on how testing has evolved for cloud native applications, including techniques like A/B testing, performance testing, security testing and end-to-end automation testing. It emphasizes measures for cloud native applications like scalability, resiliency, robust deployments and resource utilization. Throughout it emphasizes the importance of observability metrics, tracing and logs for testing cloud native systems.