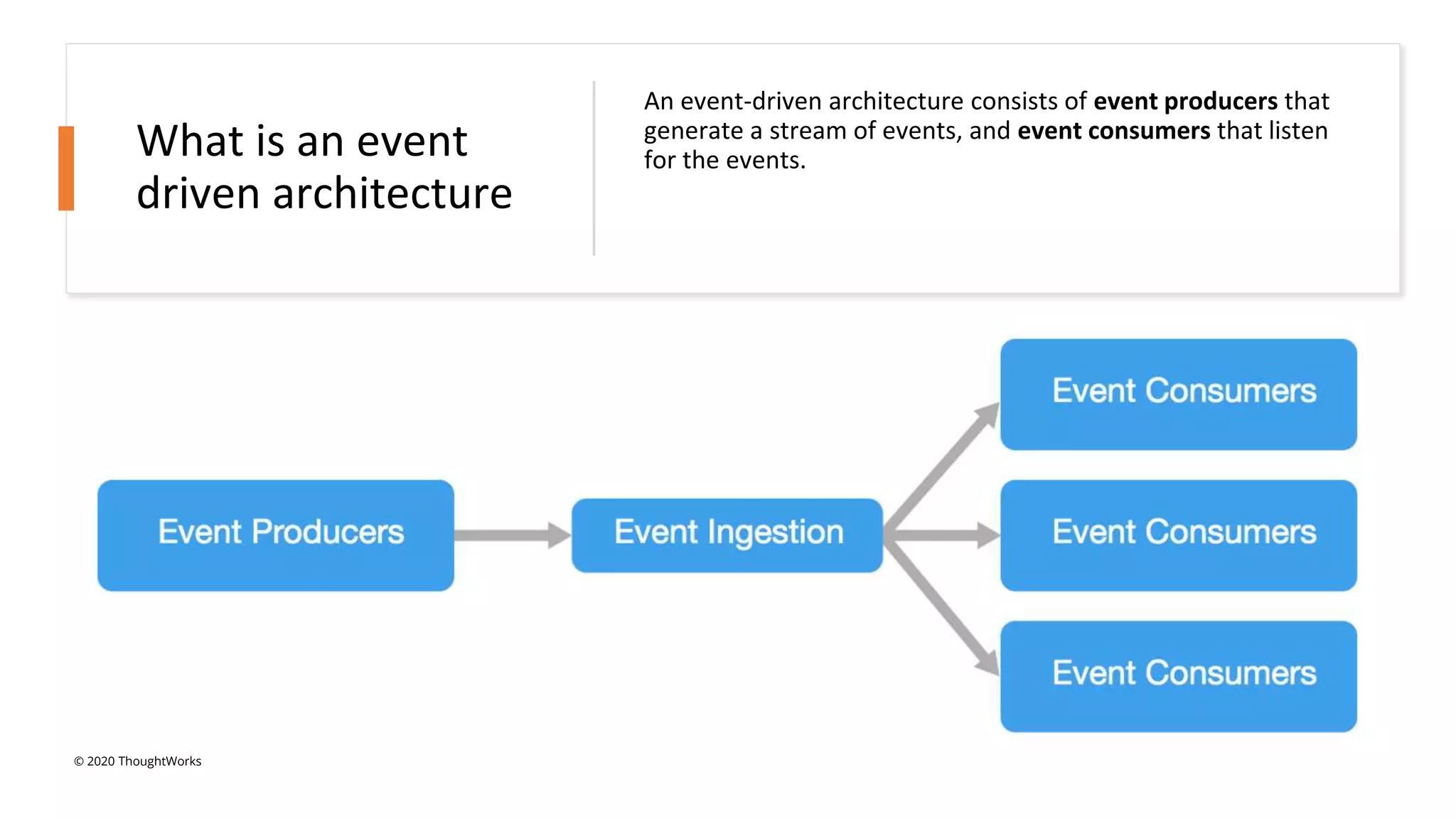
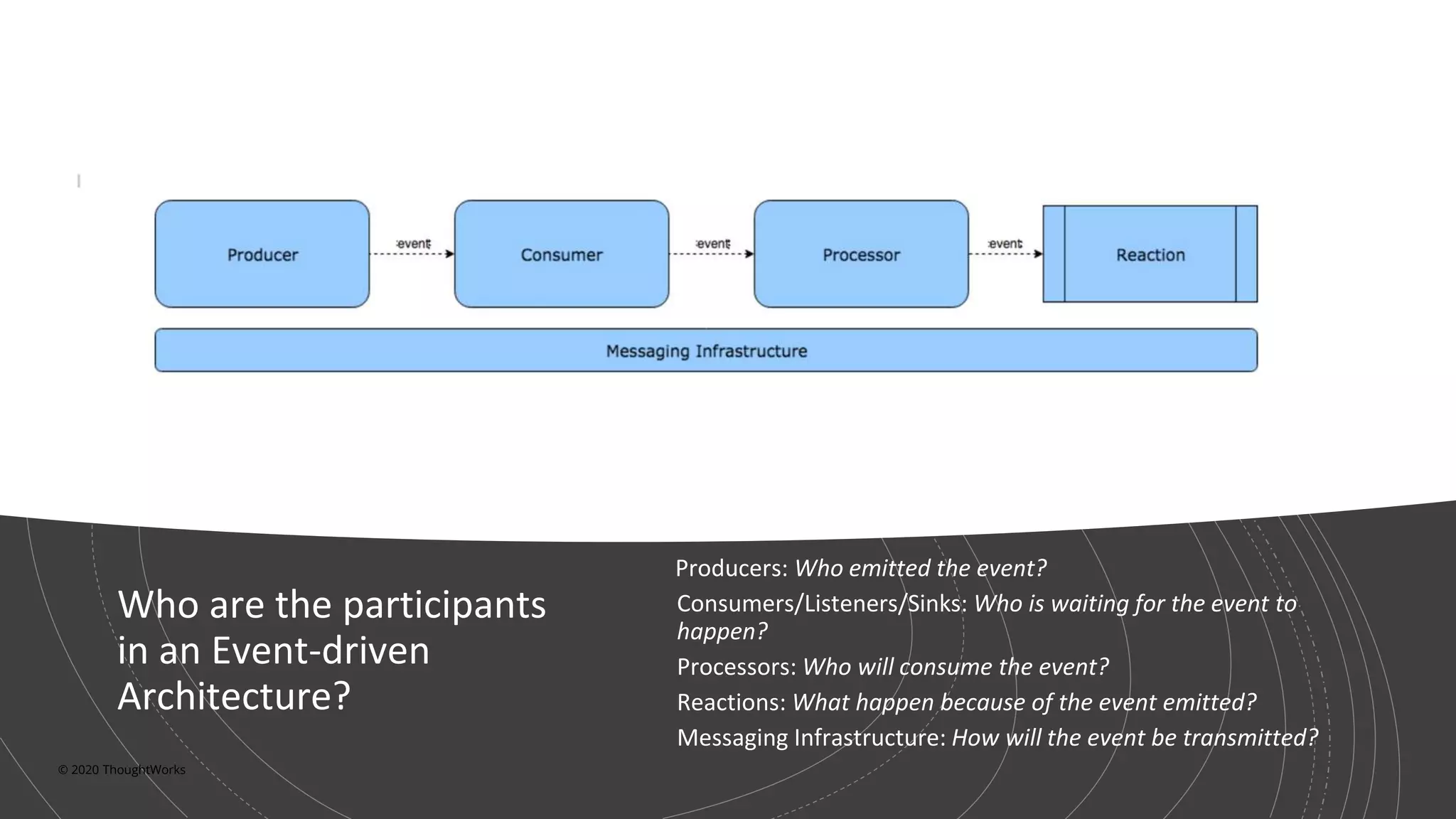
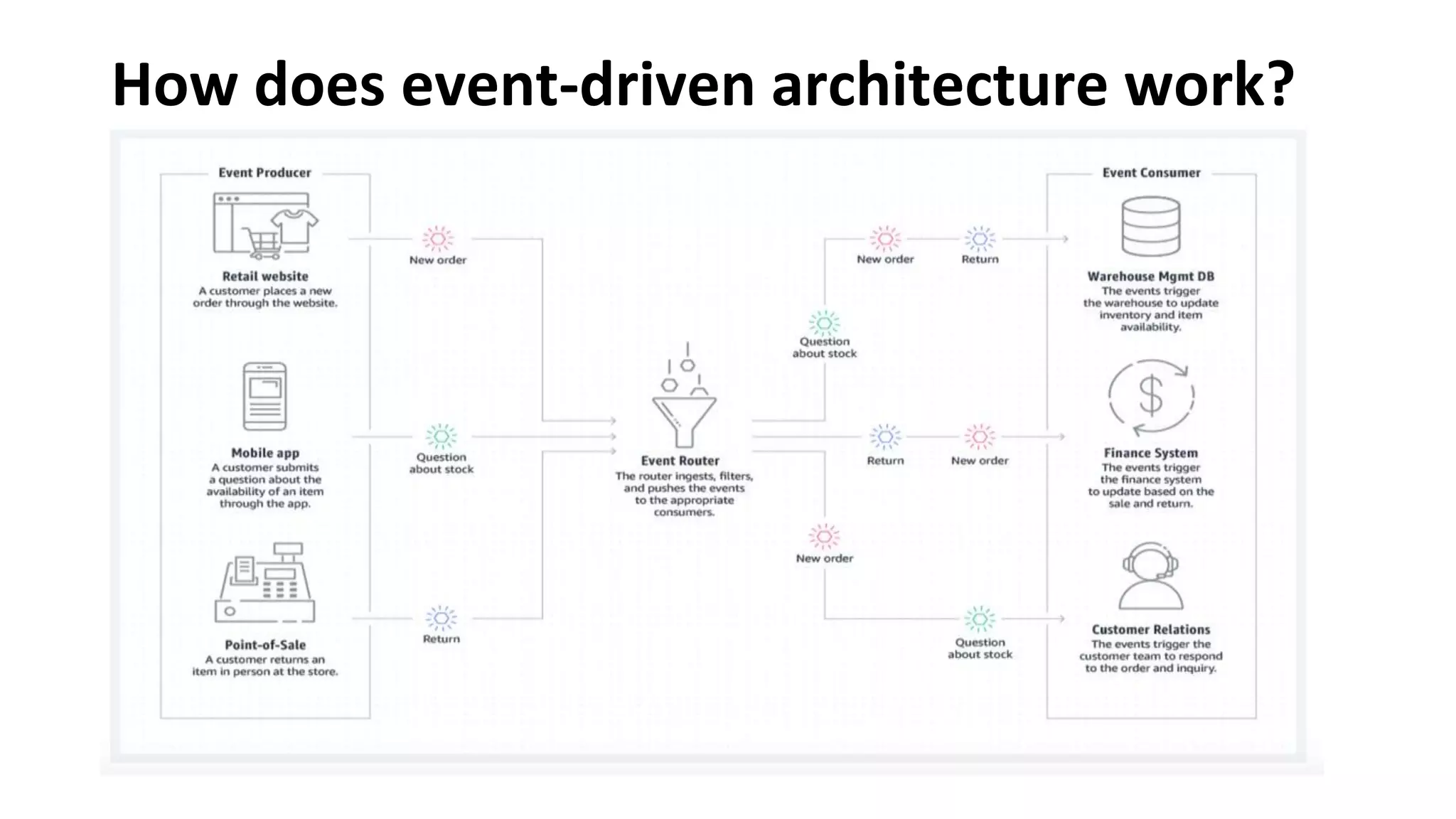
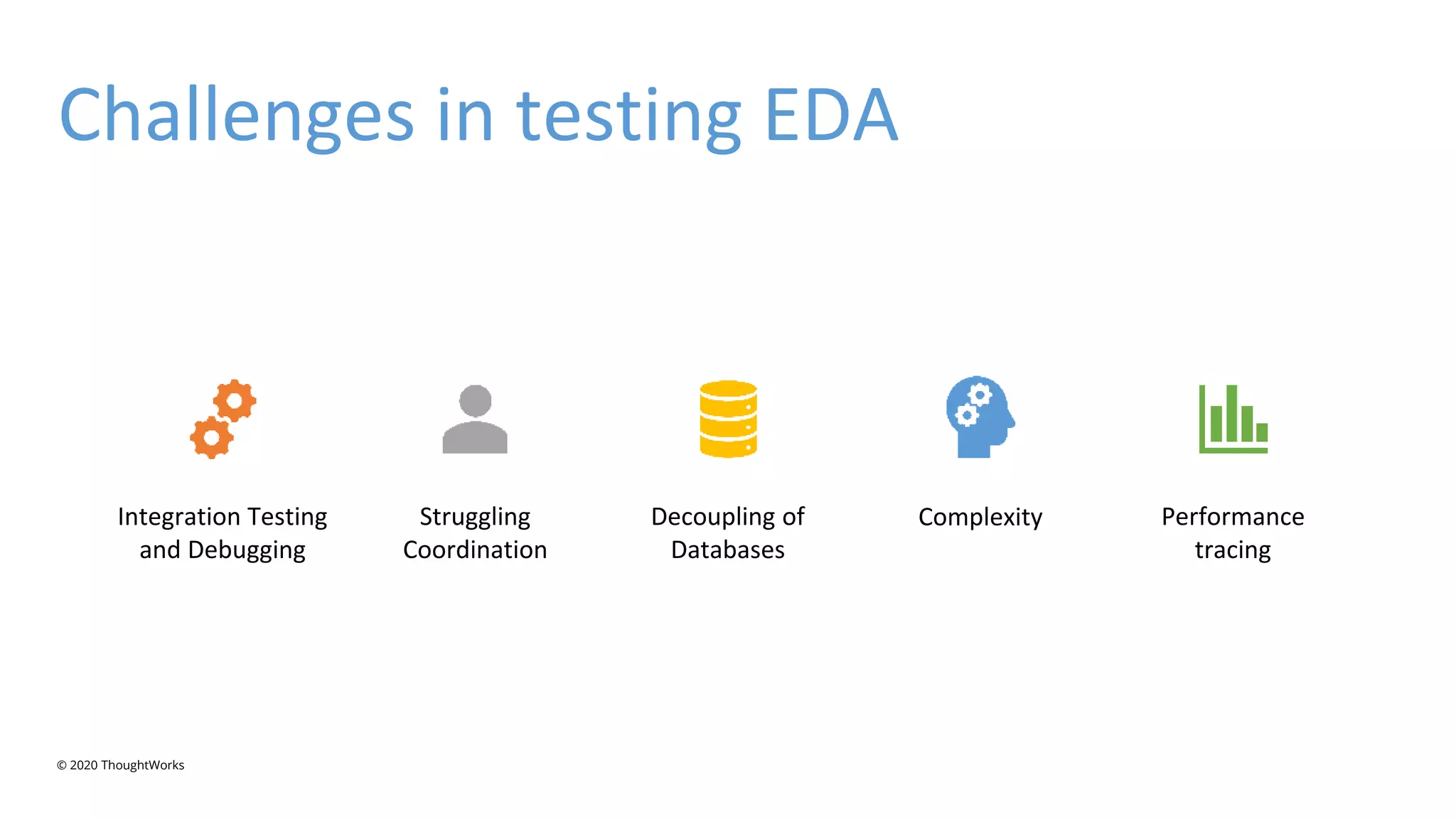
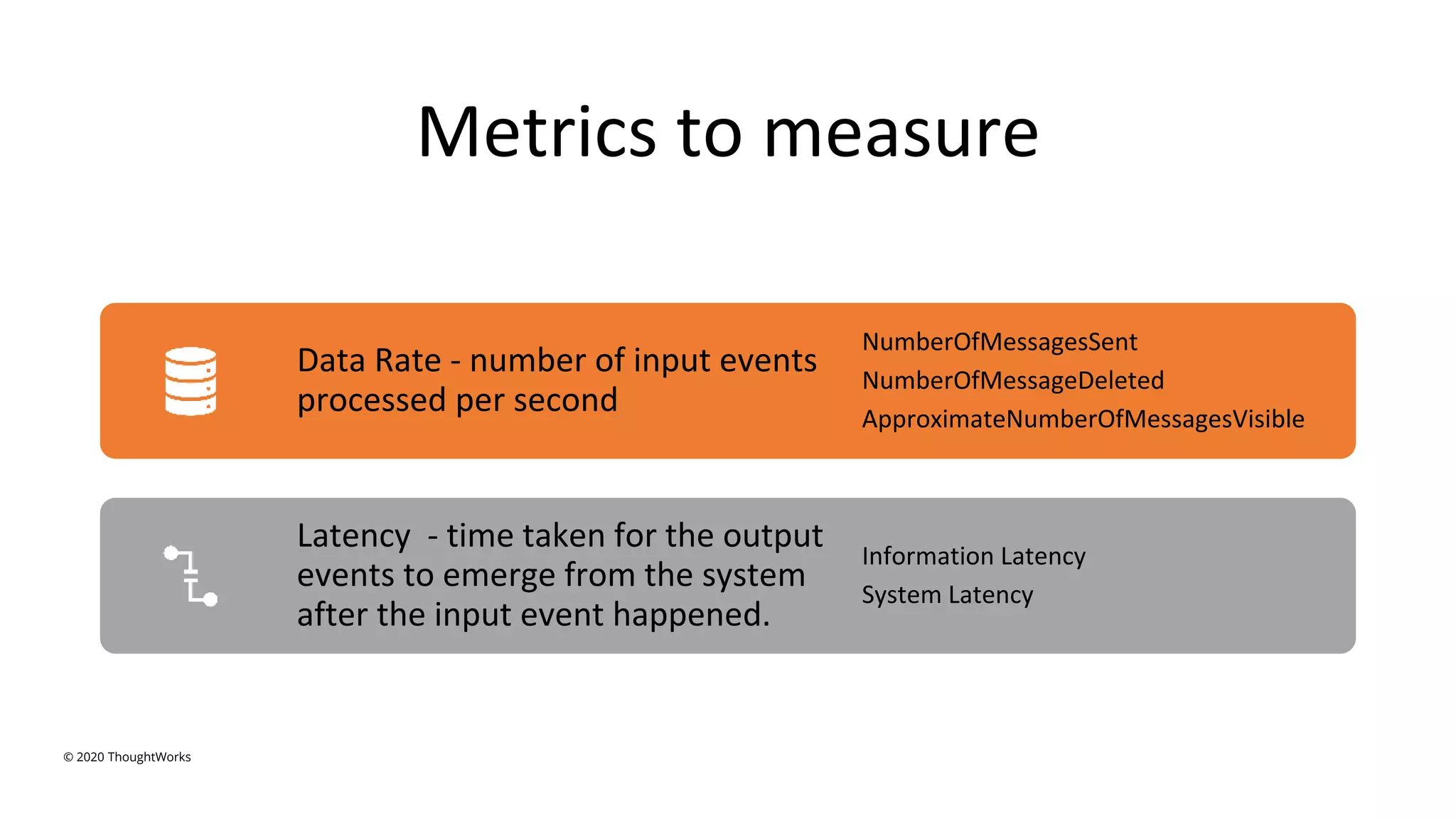
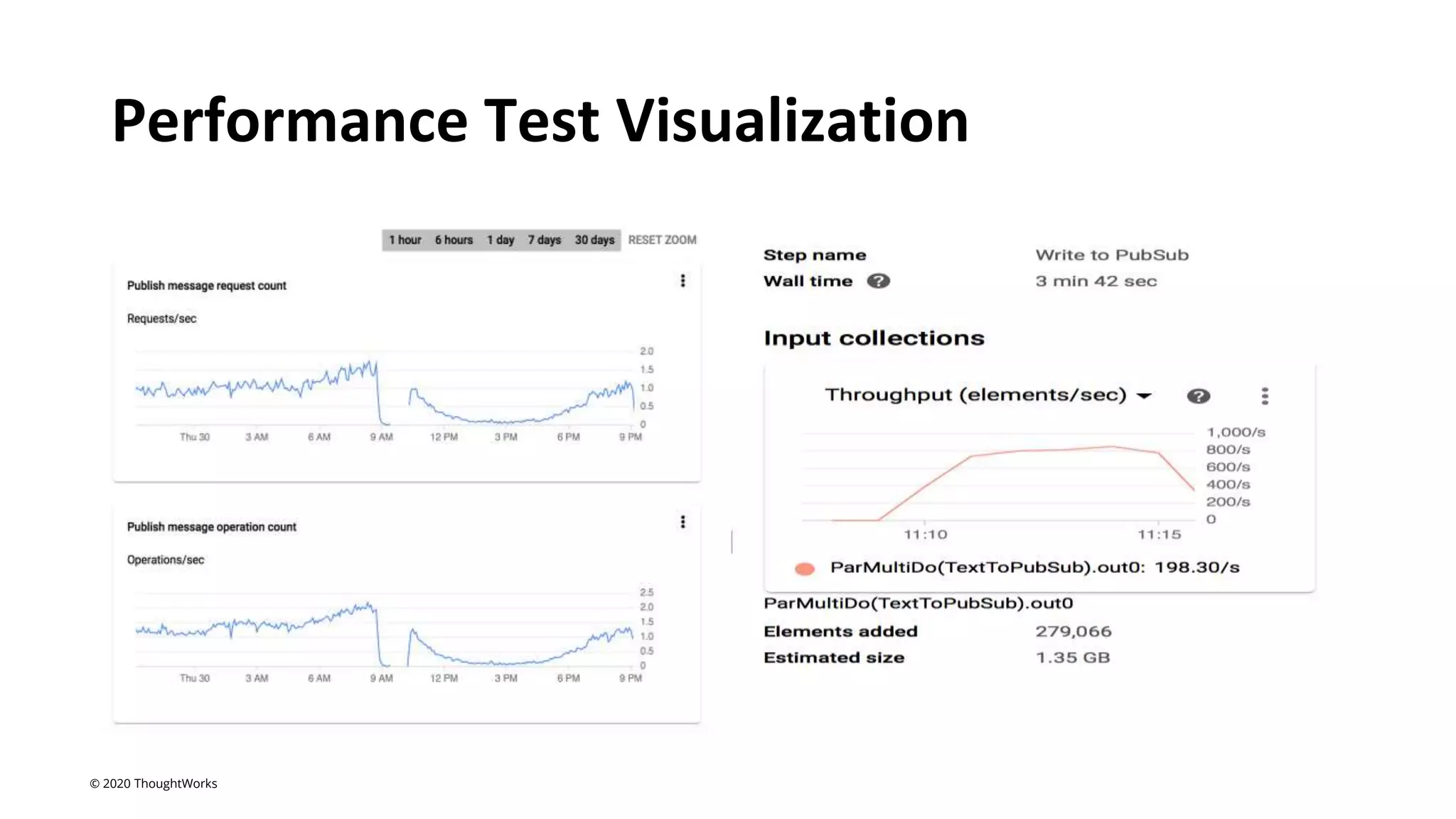
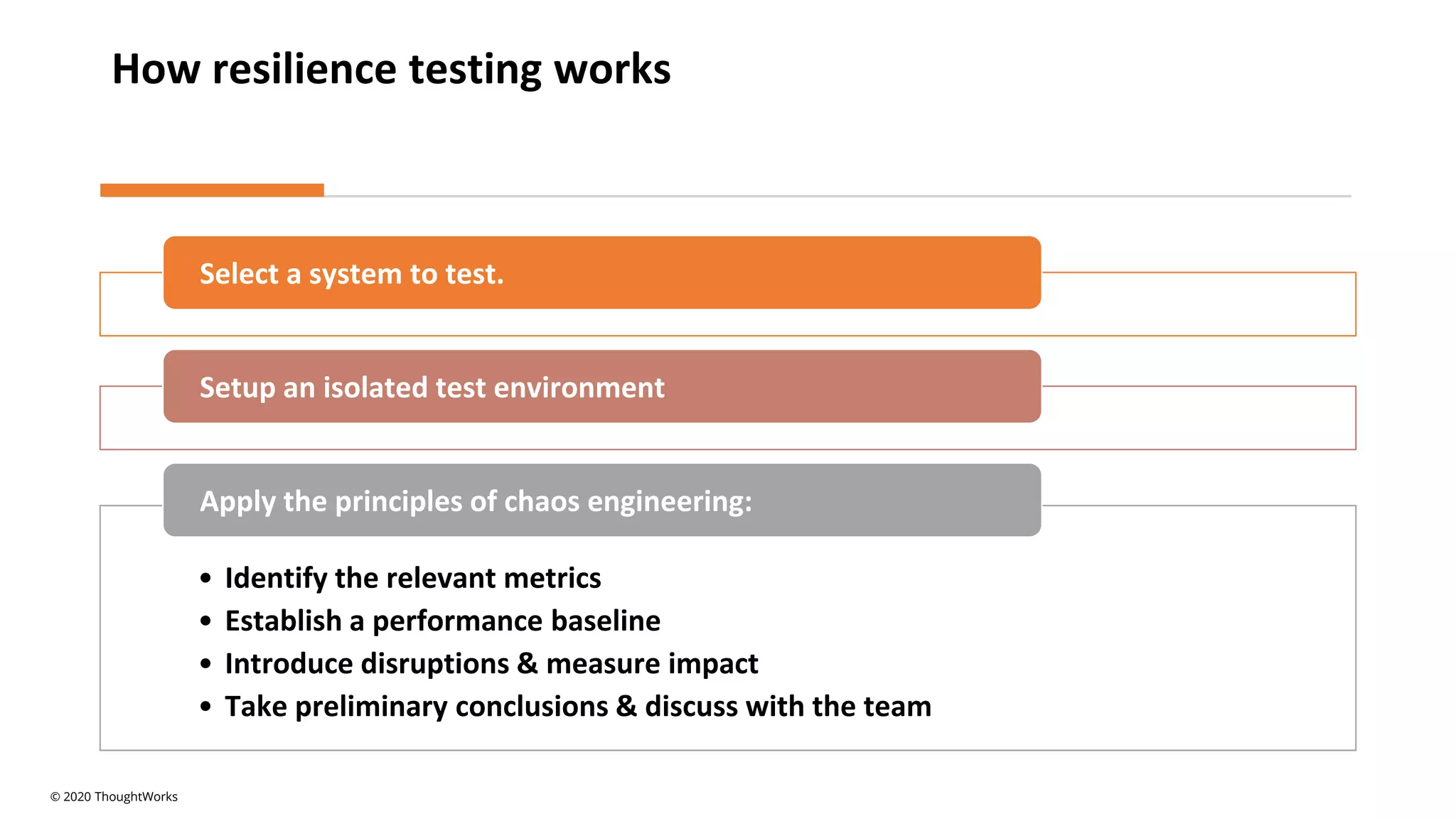
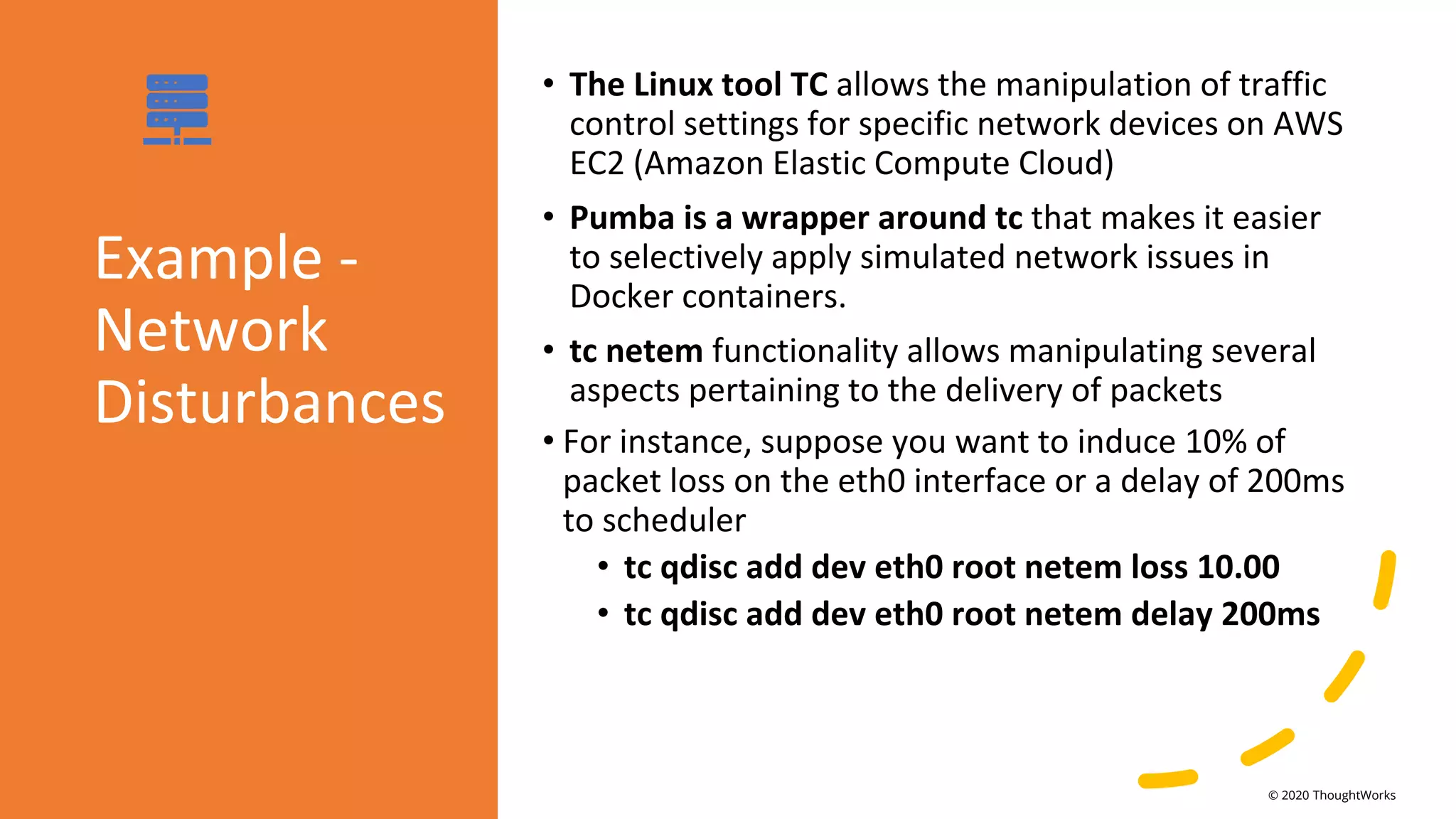
An event-driven architecture consists of event producers that generate a stream of events and event consumers that listen for the events. It includes publishers that emit events and subscribers that process those events. Testing event-driven architectures presents challenges related to integration, coordination, and complexity. Functional testing includes unit, integration, and system testing, while non-functional testing focuses on performance, resilience, and security. Performance is tested by measuring metrics like data rate and latency under various loads. Resilience testing introduces disruptions to identify issues from areas like message queuing or event processing.