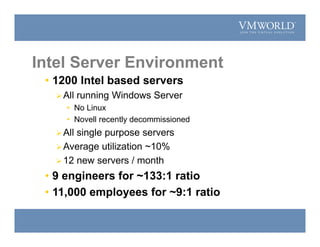
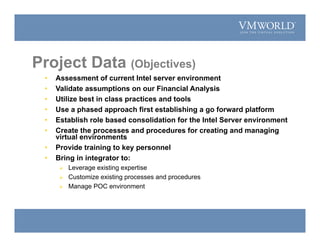
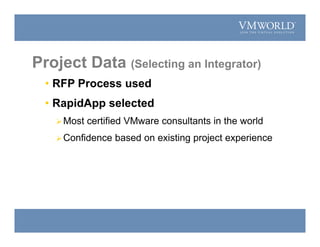
The document summarizes a presentation on justifying the transition from a physical to virtual Intel server environment. It outlines CNA's current physical server environment with low utilization. Implementing VMware virtualization could save over $2 million over 5 years by reducing TCO by 66% through server consolidation and faster provisioning. A proof of concept showed 22 applications could run virtually. Future phases would virtualize 350 NT4 servers, standardize images, and potentially move UNIX workloads to a Windows virtual environment for even greater cost savings.