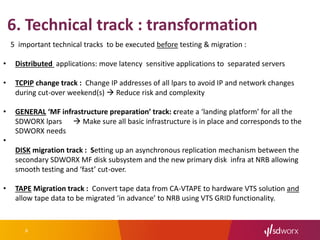
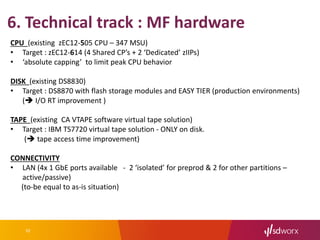
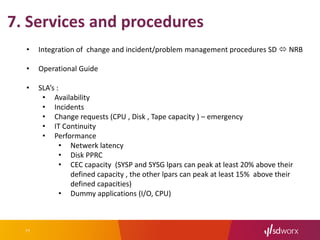
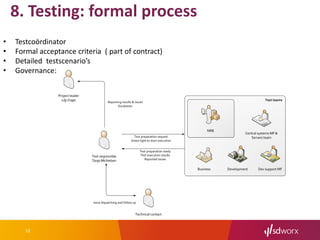
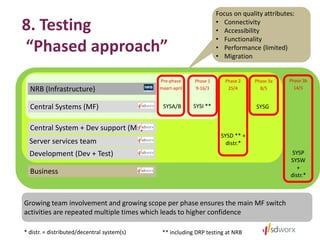
The document outlines SD Worx's project for outsourcing its mainframe environment to NRB, highlighting the goals of achieving cost efficiencies and improved service through shared resources. It details the project timeline, selection criteria for NRB, technical transformation requirements, and integration of management processes. The conclusion emphasizes the project's focus on maintaining performance and availability while reducing costs under an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) model.