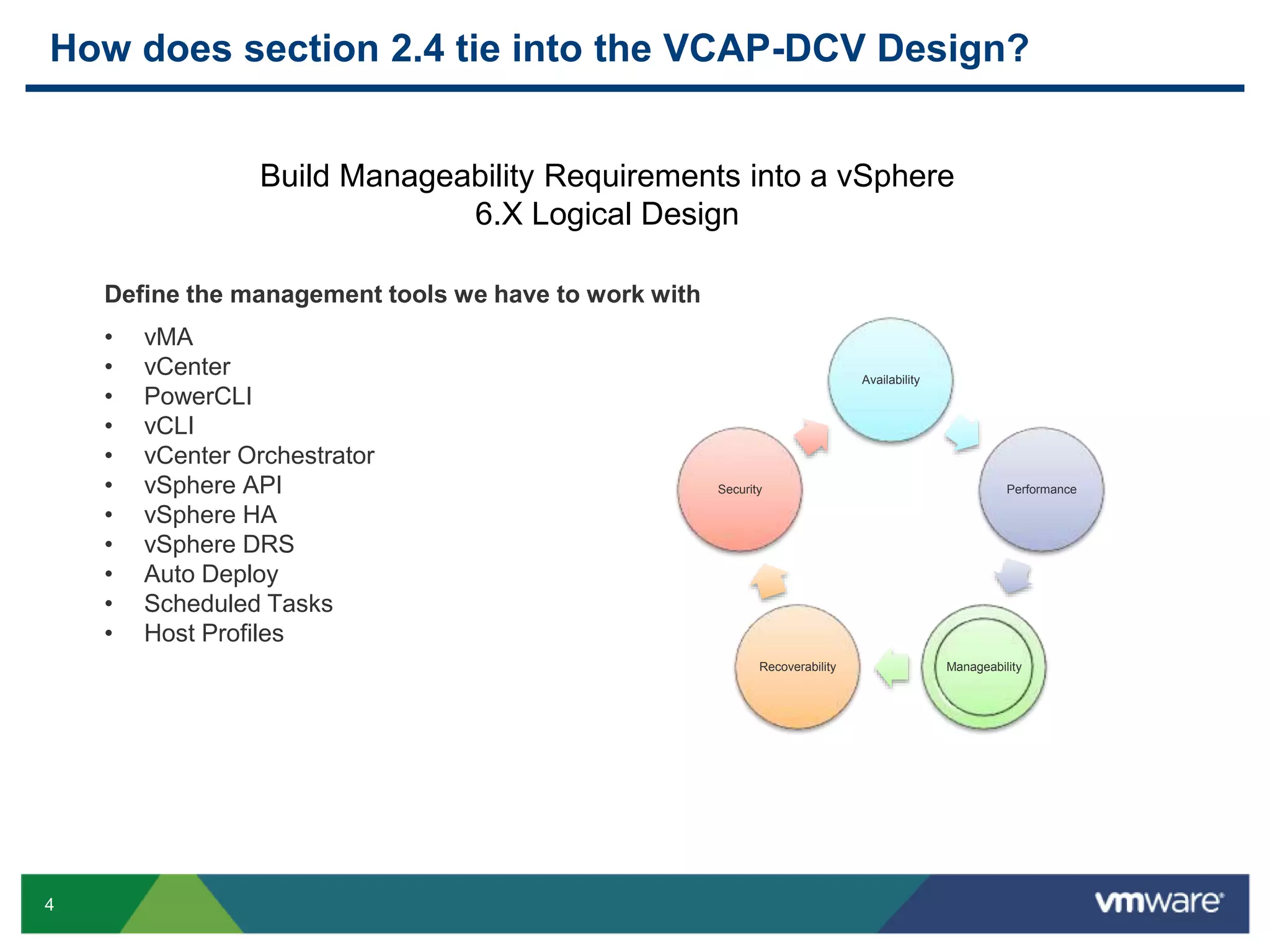
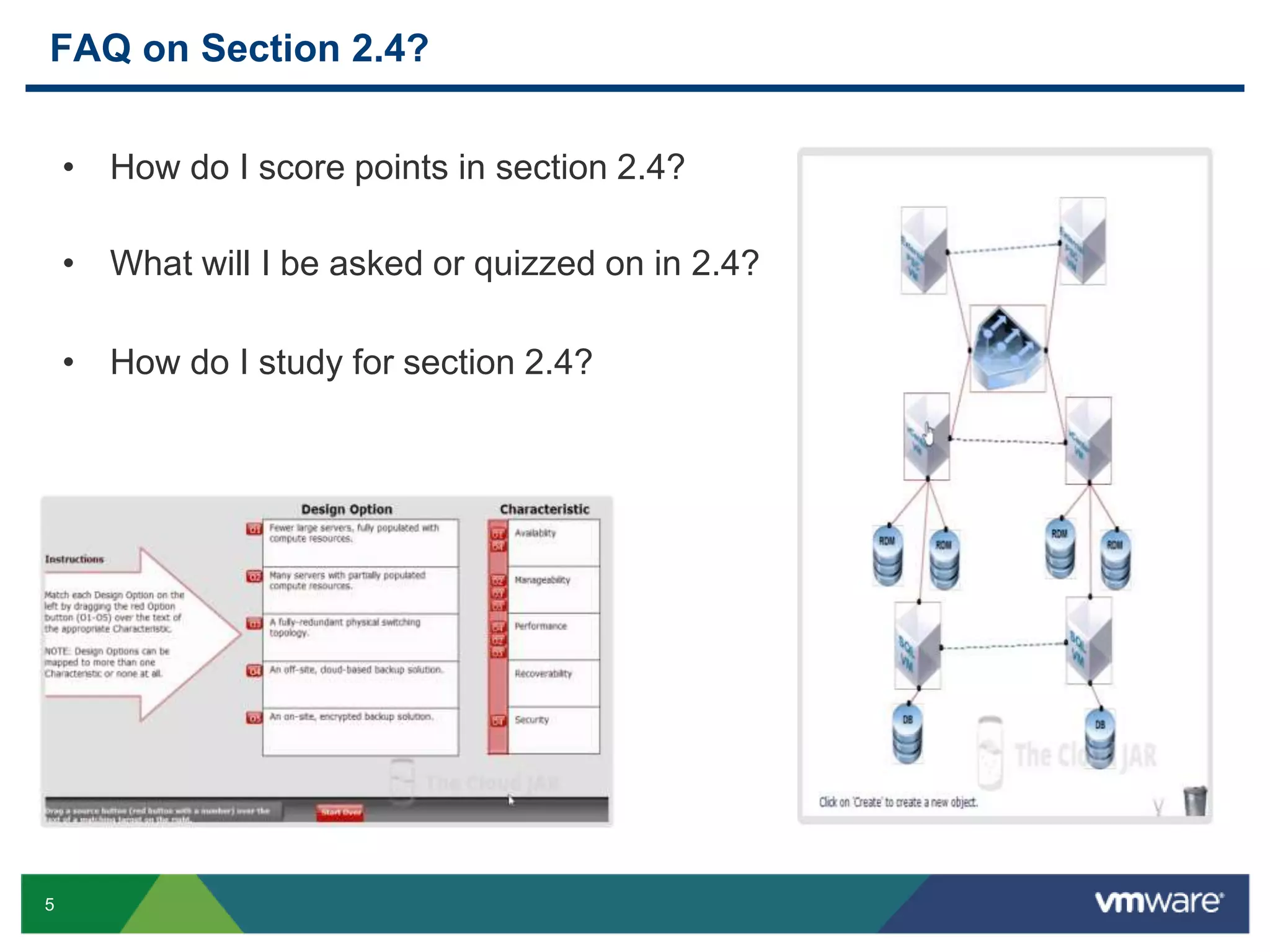
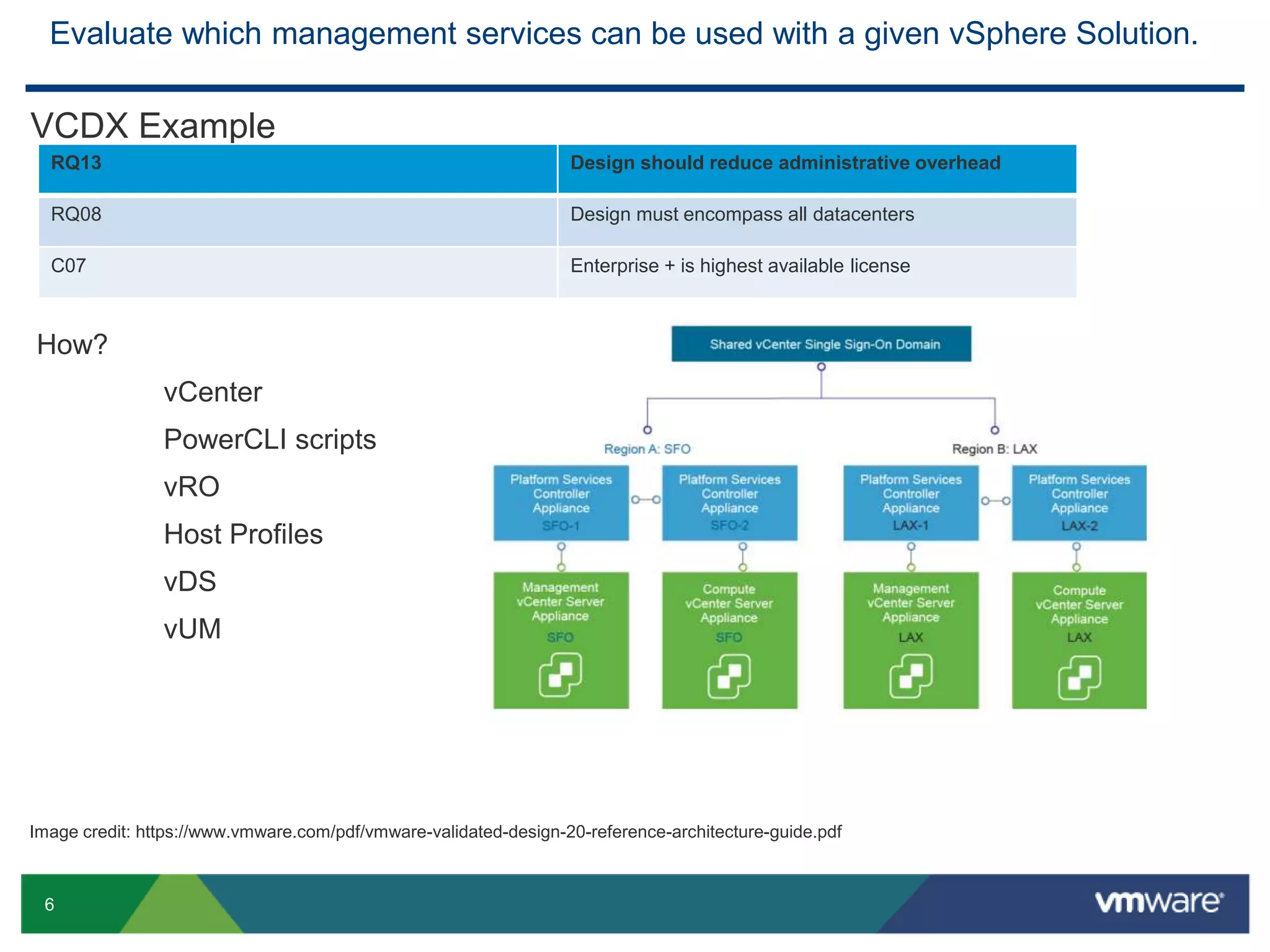
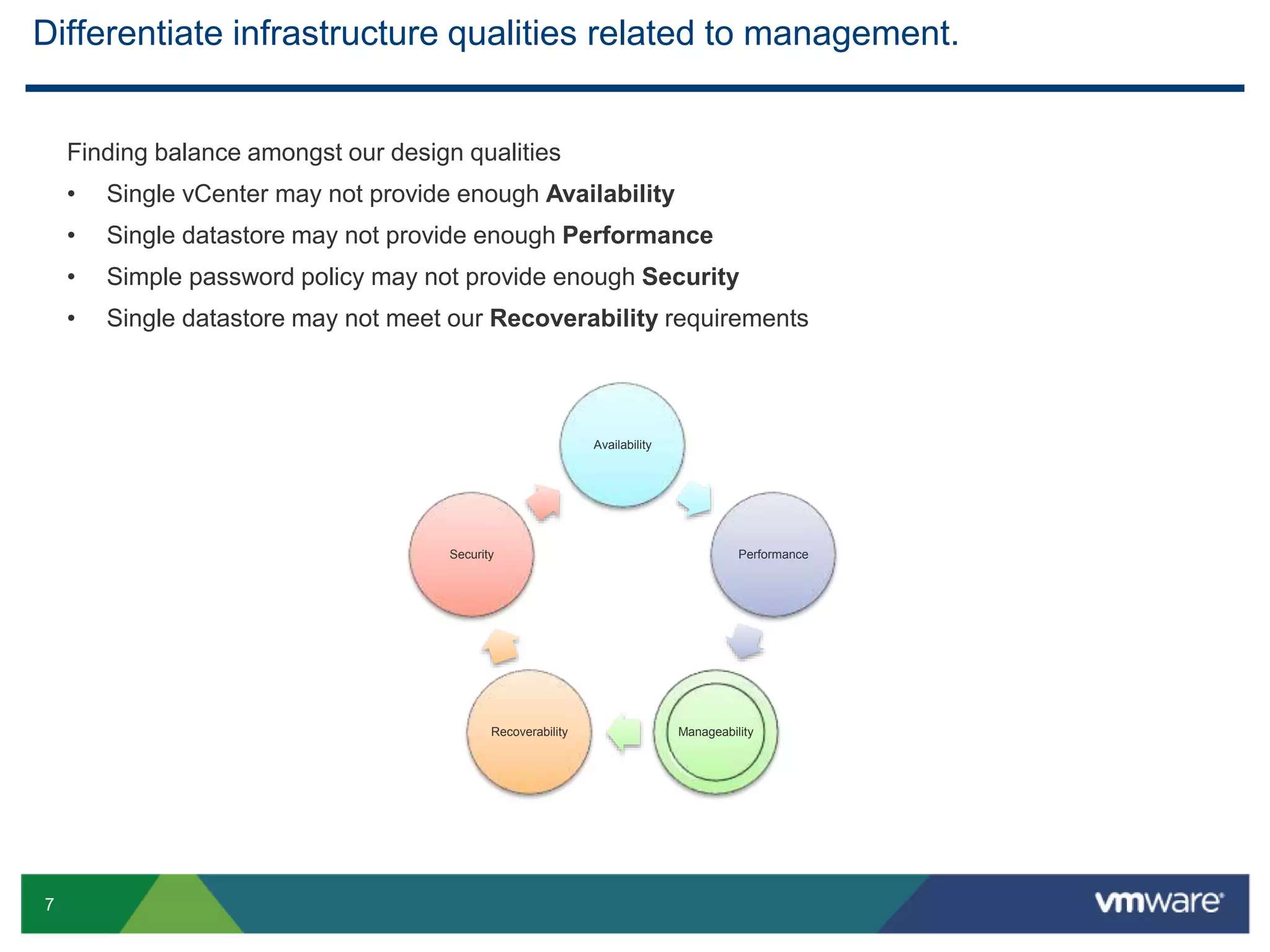
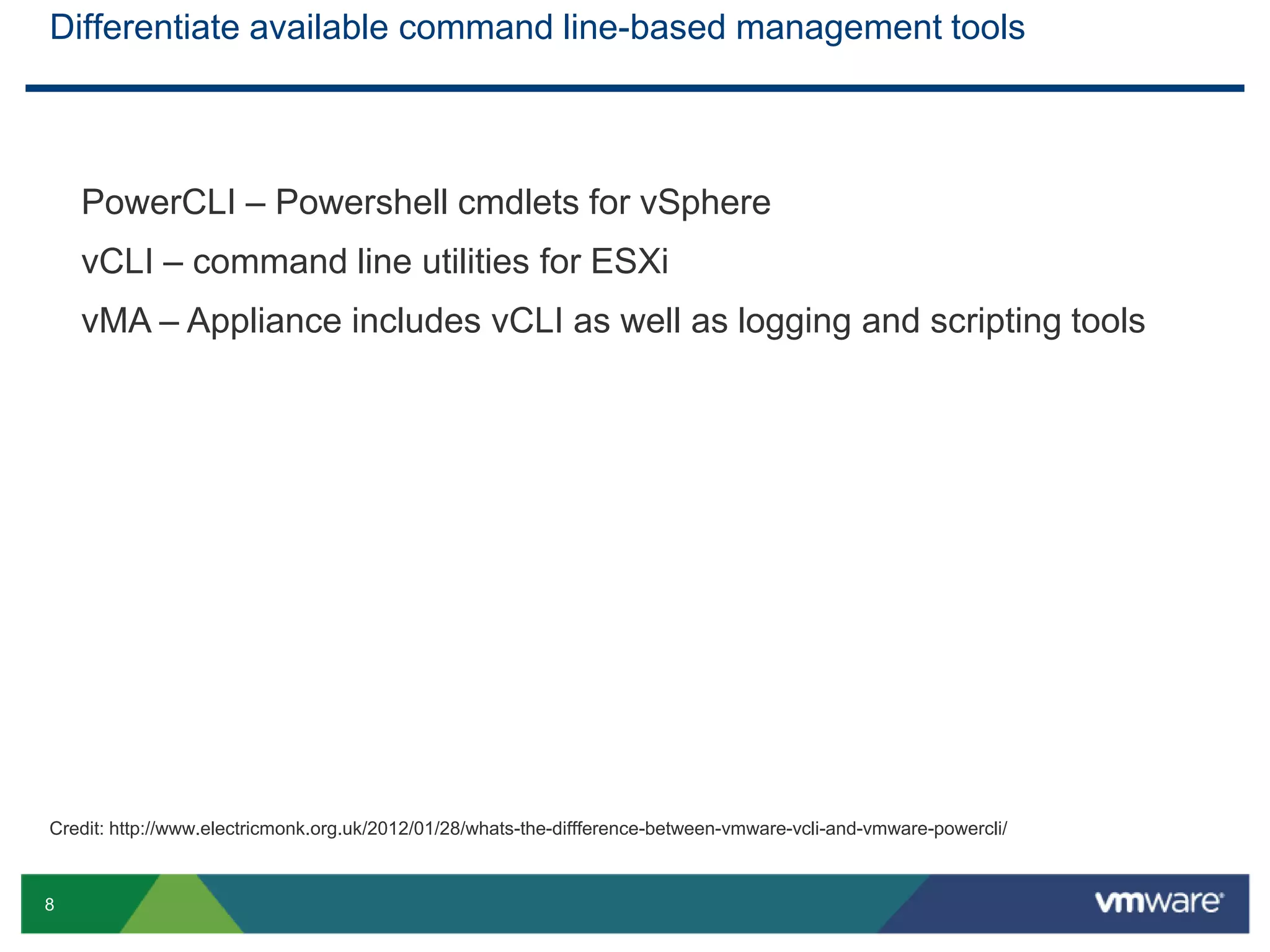
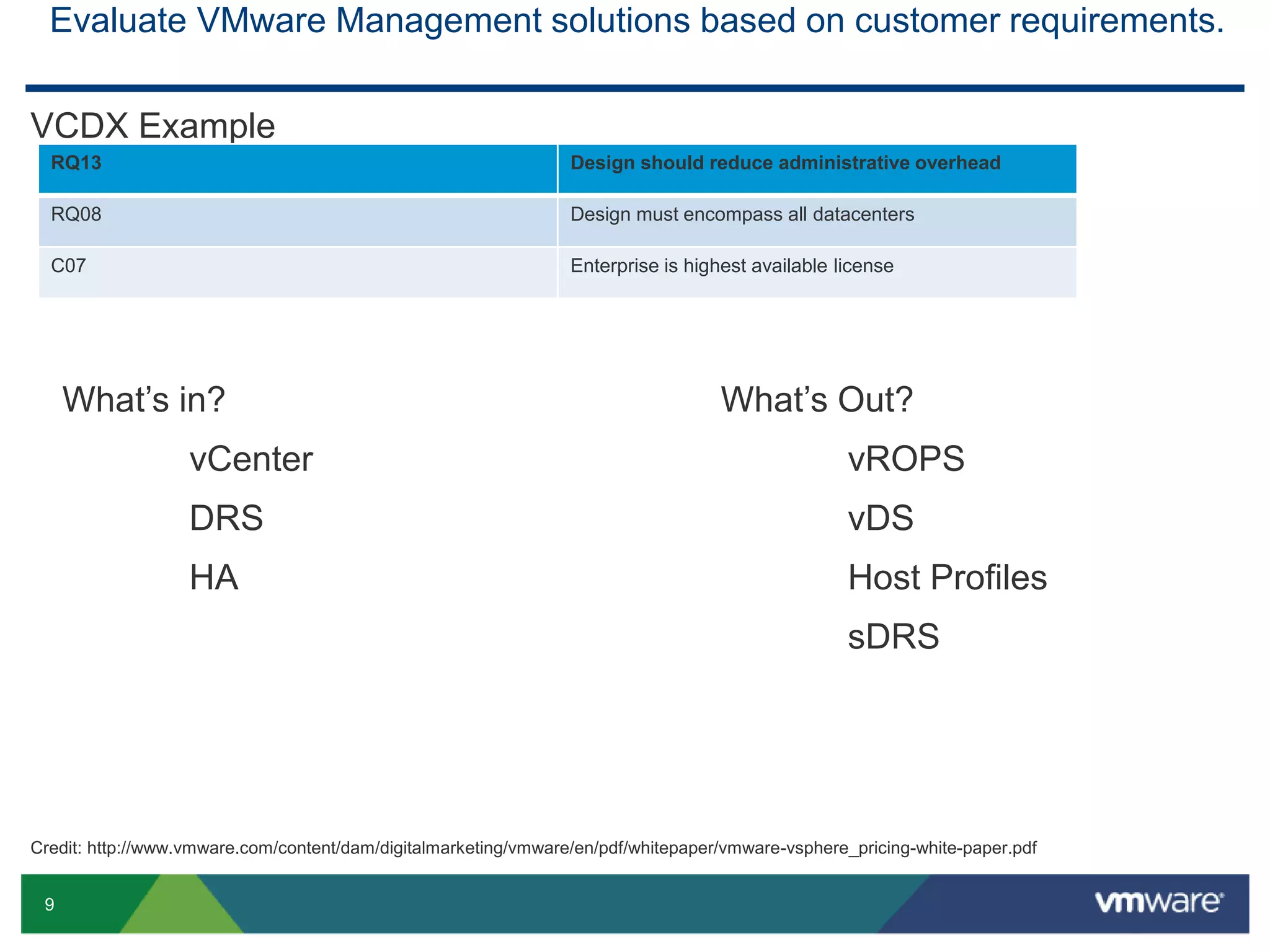
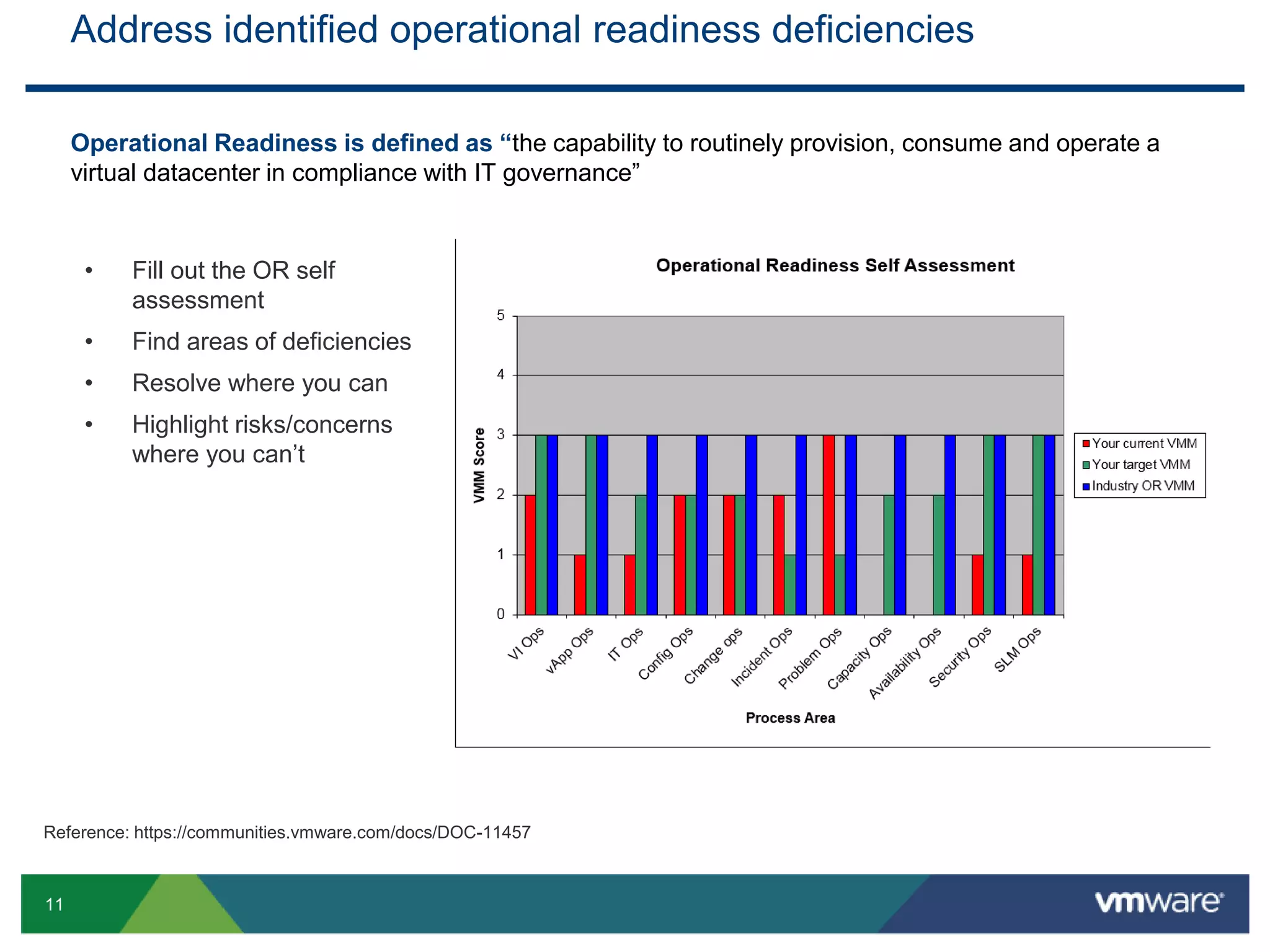
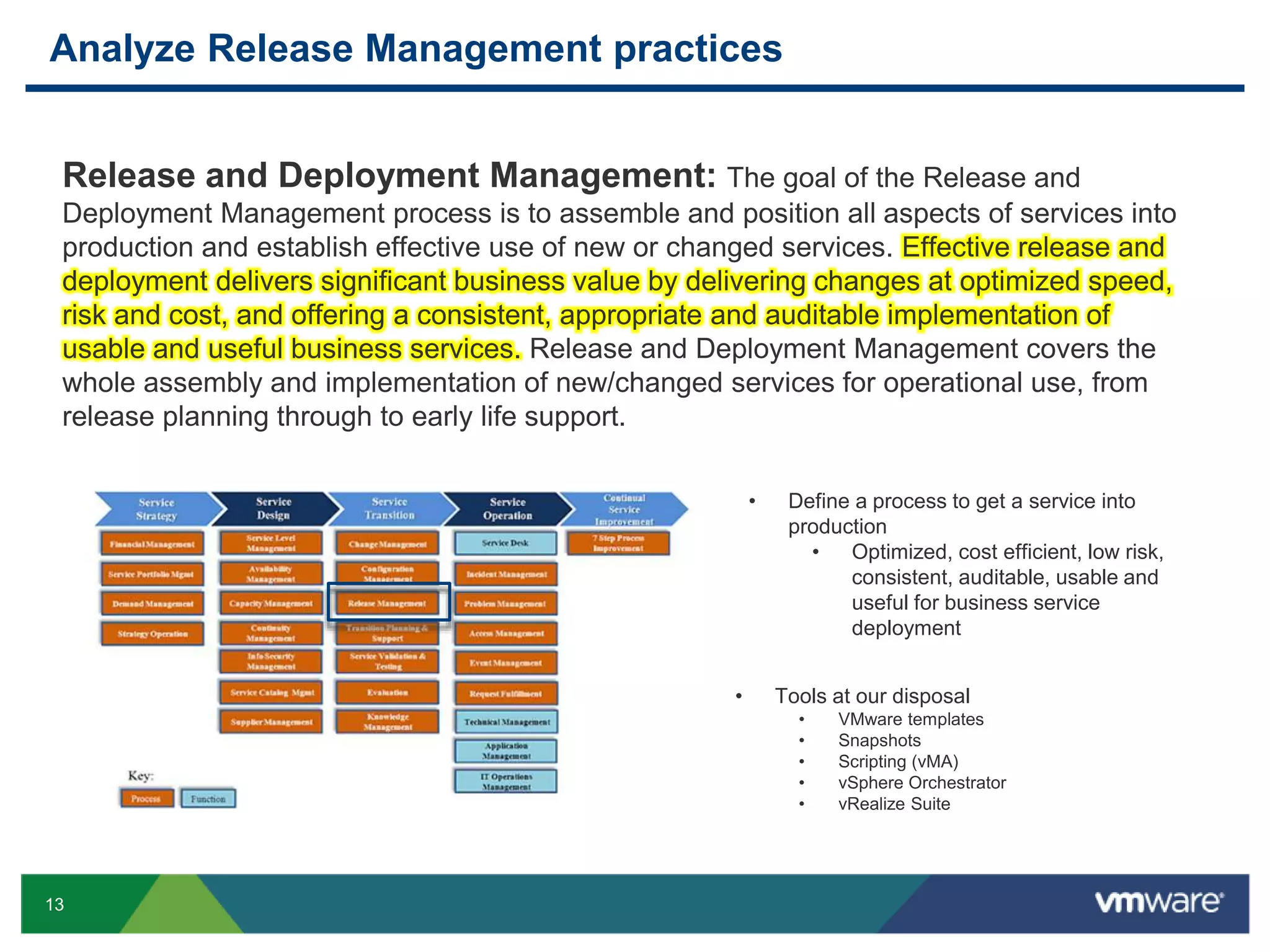
The document outlines the agenda for Objective 2.4 of the VCAP6-DCV Design exam, which involves building manageability requirements into a vSphere 6.x logical design. It discusses evaluating management services, tools, and solutions based on customer requirements and defining processes for configuration, change, event, incident, problem and release management to integrate manageability into the logical design.