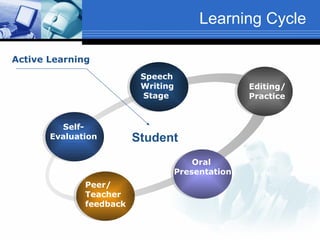
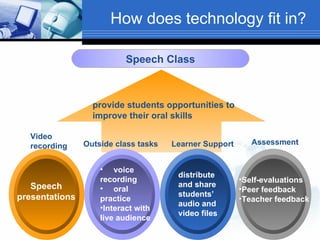
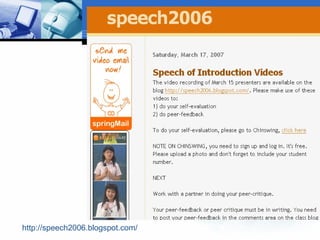
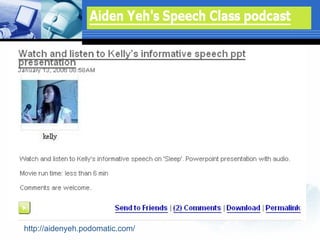
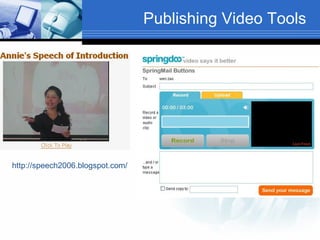
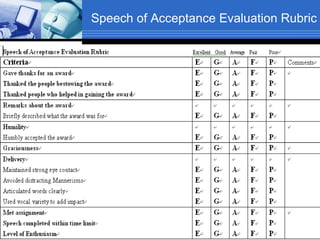
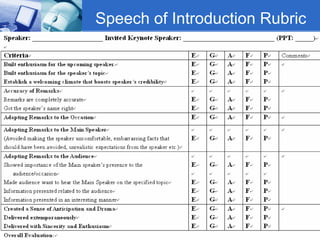
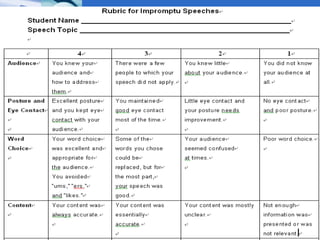
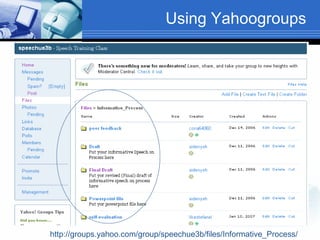
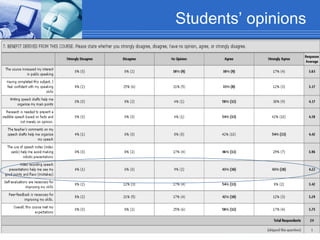
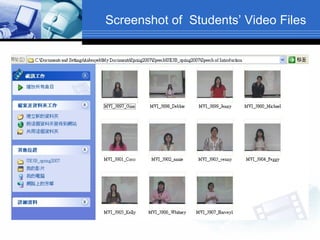
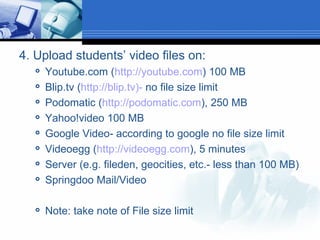
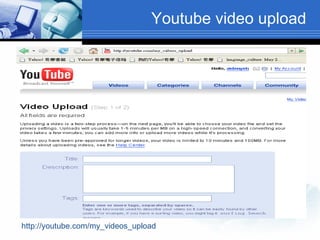
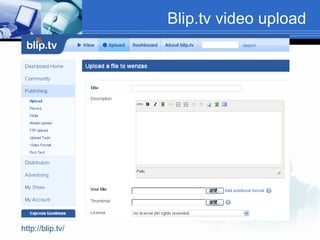
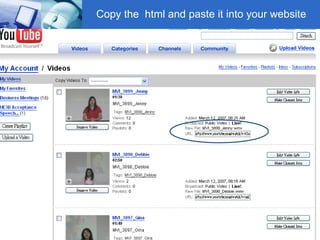
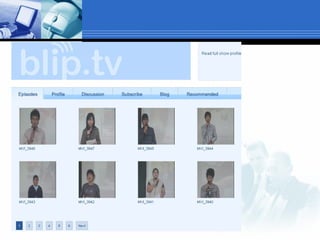
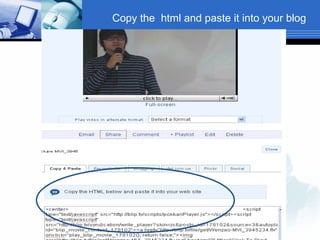
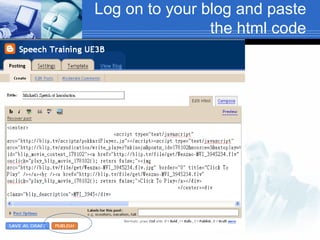
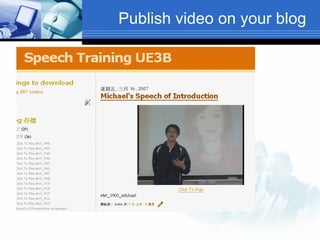
The document discusses using video recording and blogs to assess students' oral presentation skills in an English speech training class. Students give speeches that are recorded and uploaded to blogs for self-evaluation and feedback from peers and teachers. This blended learning approach allows students more opportunities to improve by watching their performances and learning from others.