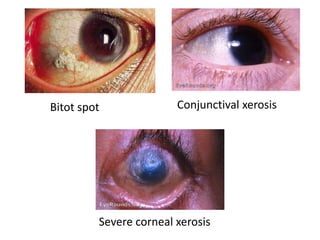
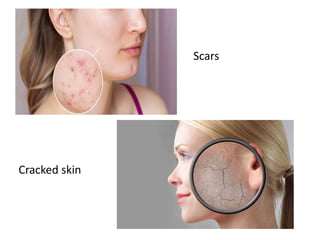
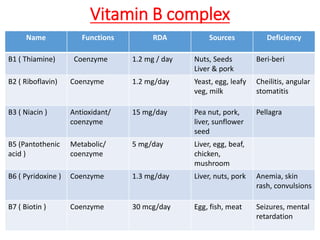
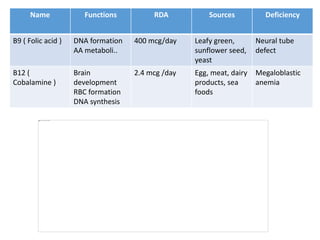
Vitamins are essential nutrients required by the body that must be obtained through foods or supplements. They are classified as either fat-soluble or water-soluble. Fat-soluble vitamins include A, D, E, and K and are stored in the liver, while water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and the B vitamins have limited storage and are excreted in urine. Each vitamin serves important functions, and deficiencies can lead to diseases like rickets, scurvy, or neural tube defects. Sources of vitamins include plants, animals, and exposure to sunlight.