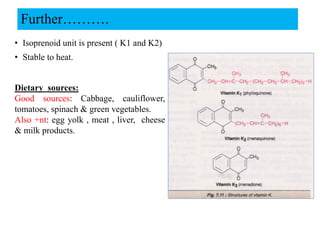
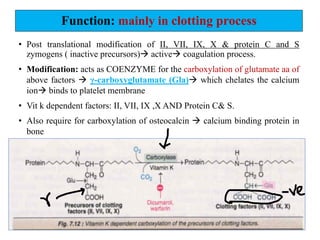
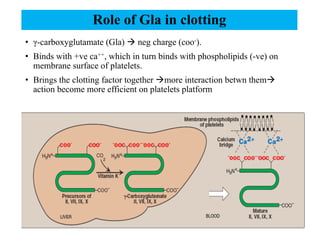
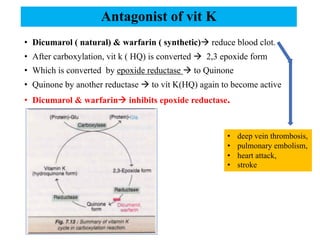
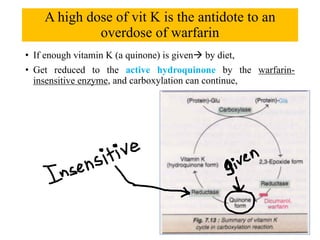
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin that acts as a coenzyme in the coagulation process. It exists in three forms: K1 from plants, K2 from intestinal bacteria and animals, and K3 which is synthetic. Vitamin K is important for the carboxylation of clotting factors II, VII, IX, X and proteins C and S in the liver. This carboxylation adds a negative charge that allows the clotting factors to bind to platelet membranes and interact efficiently to form blood clots. Vitamin K deficiency can result from fat malabsorption, broad-spectrum antibiotics that kill gut bacteria, or excessive loss of vitamin K in the feces, leading to bleeding disorders