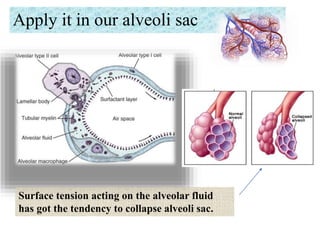
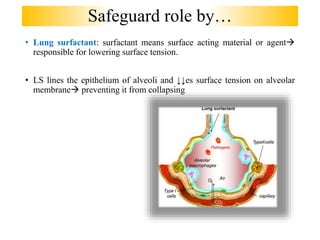
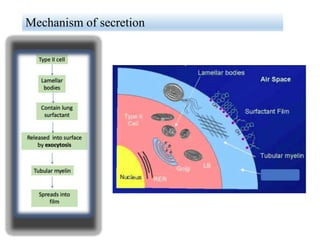
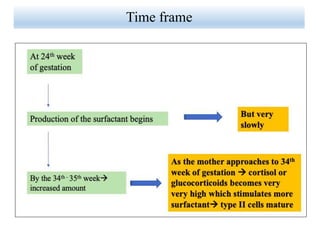
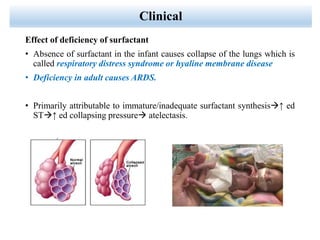
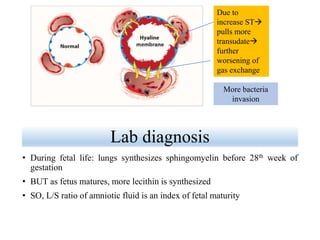
Lung surfactant is crucial for lowering surface tension in alveoli, preventing their collapse during respiration. It is primarily produced by type II pneumocytes and consists of a mix of lipids and proteins, with production increasing significantly in the later stages of gestation. Deficiencies in surfactant can lead to respiratory distress syndrome in infants and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in adults.