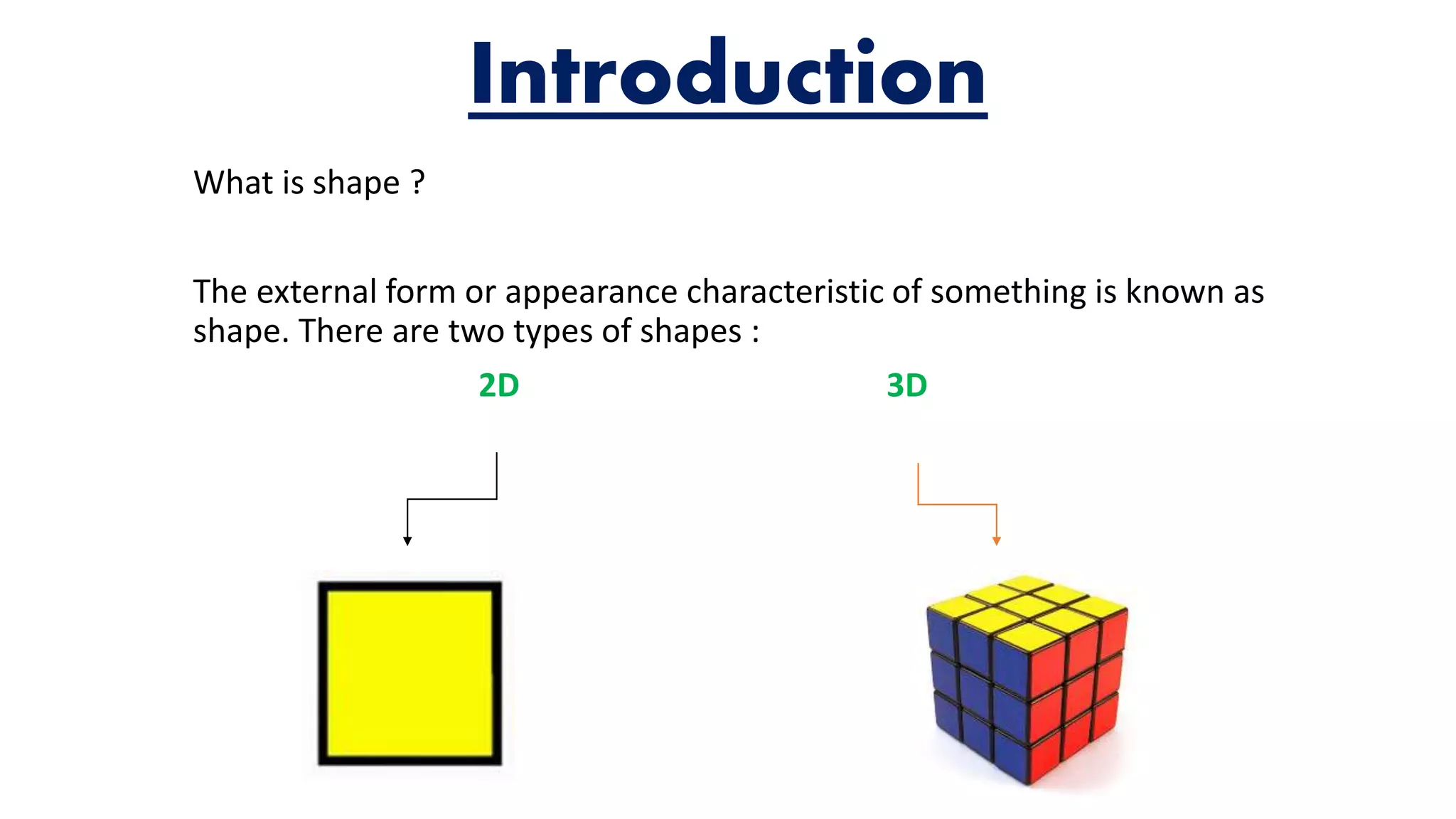
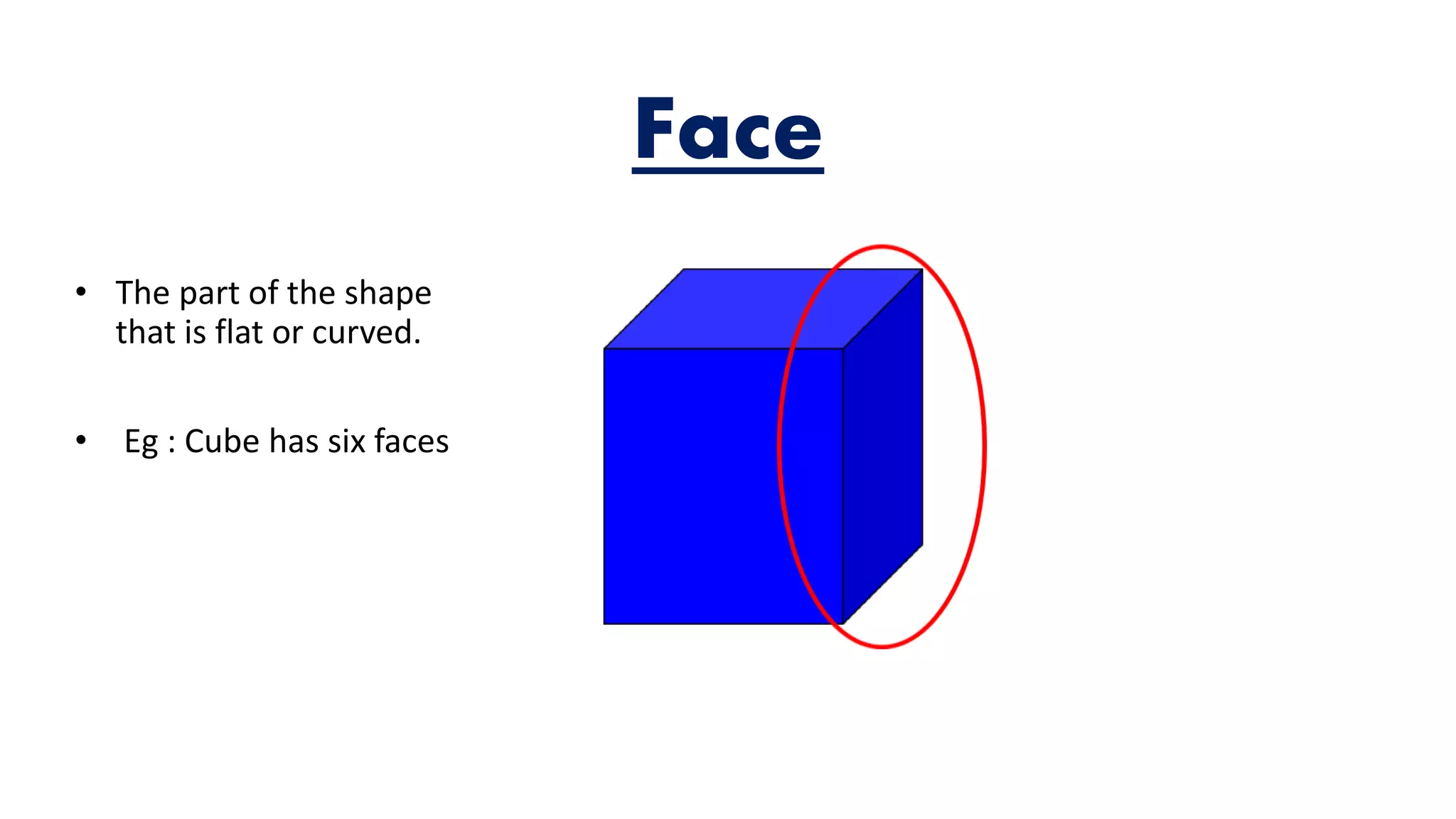
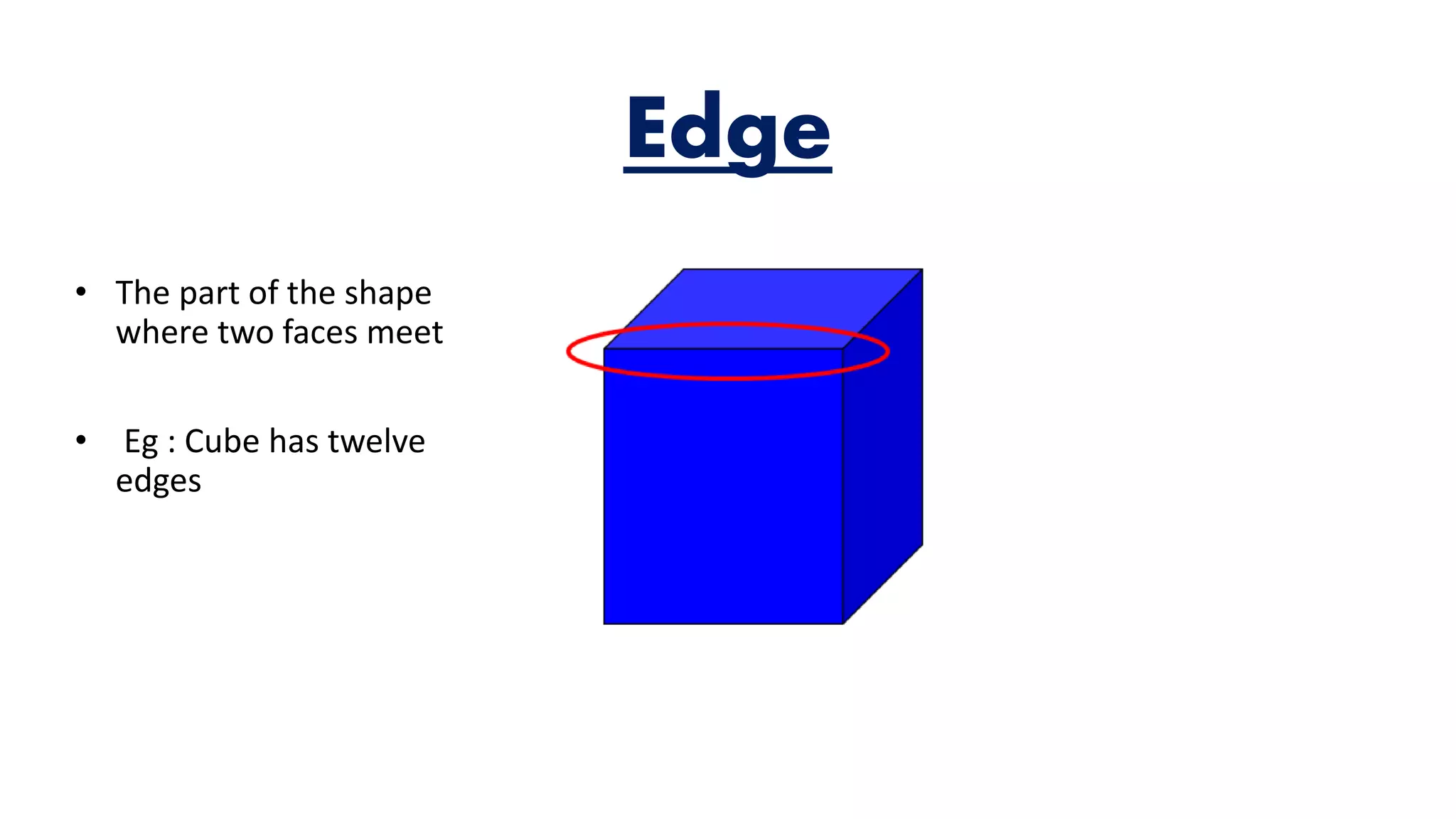
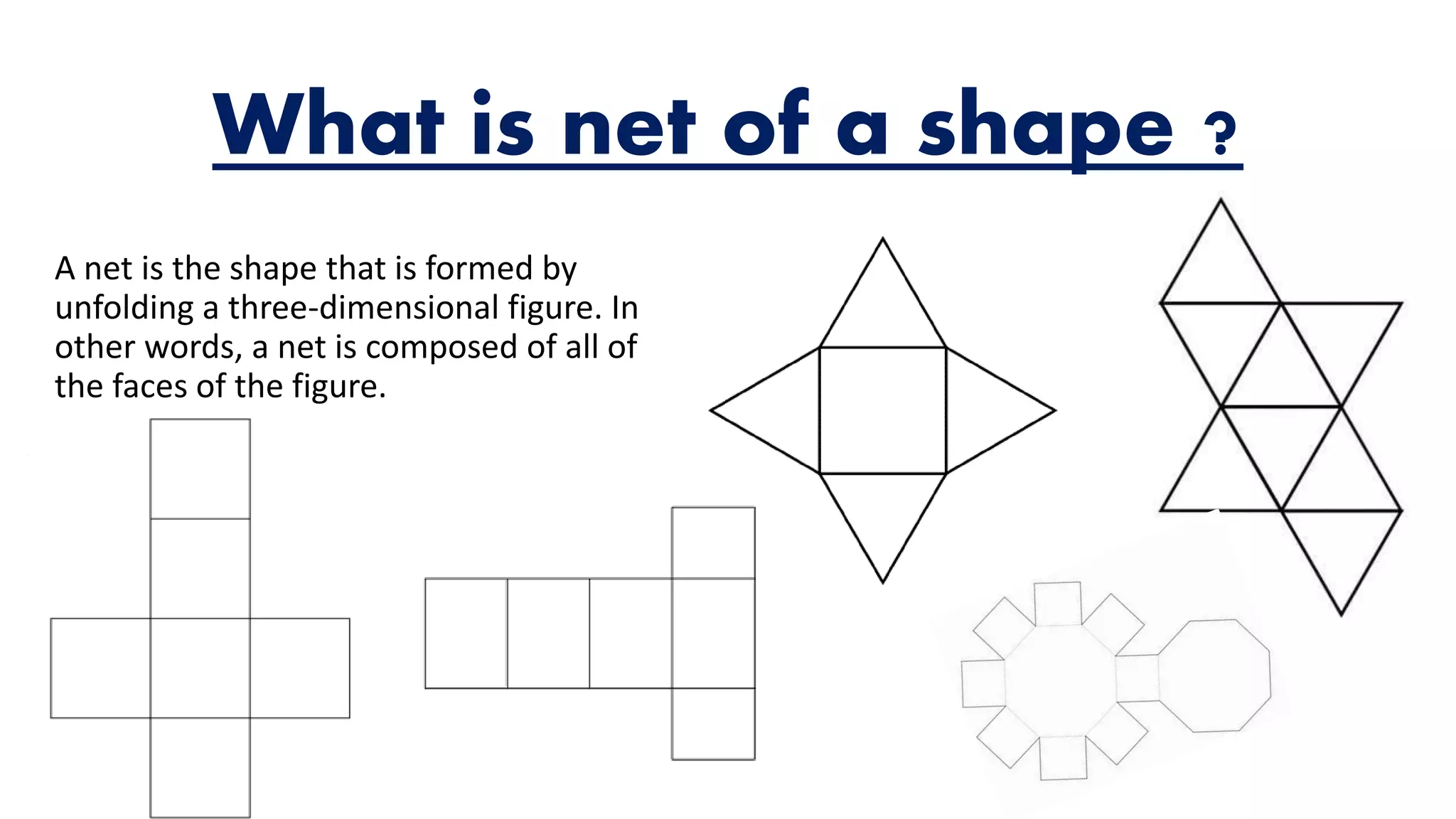
The document provides an overview of solid shapes, distinguishing between two-dimensional and three-dimensional forms, and explains properties such as faces, edges, and vertices. It also covers the concept of nets for three-dimensional figures and offers examples of polyhedrons versus non-polyhedrons. Additionally, the document discusses map representation, including color coding for features and the importance of scales for accurate interpretation of distances.