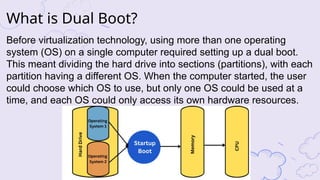
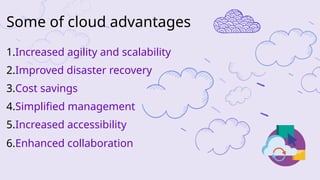
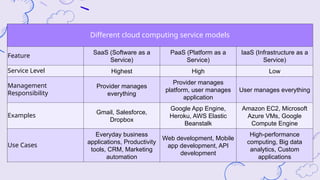
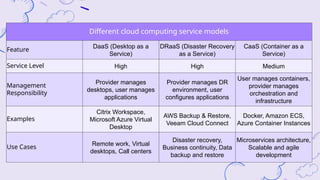
The document explains virtualization as the logical division of resources, primarily applied through software to create virtual servers, and distinguishes between type 1 and type 2 hypervisors. It discusses cloud computing as utilizing internet-based services that offer scalability, pay-per-use, and shared resources, highlighting its benefits like improved agility, cost savings, and simplified management. Additionally, it emphasizes how server virtualization and cloud models contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing energy consumption and e-waste.