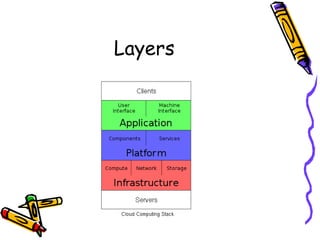
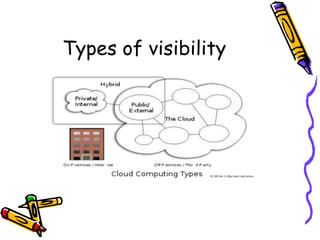
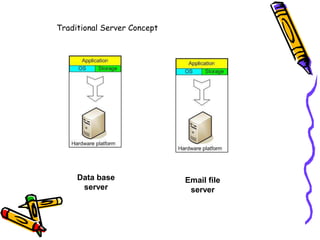
Virtualization allows multiple virtual servers to run on the same physical hardware by encapsulating the server software. In cloud computing, virtualization is extended by allowing users to rent hardware resources from cloud providers on demand, without having to purchase and manage their own physical servers. This enables rapid deployment of applications and scaling of resources. Key benefits include avoiding upfront capital costs, paying only for resources used, and gaining location and device independence through virtual servers that can be accessed from anywhere.