Embed presentation
Downloaded 16 times
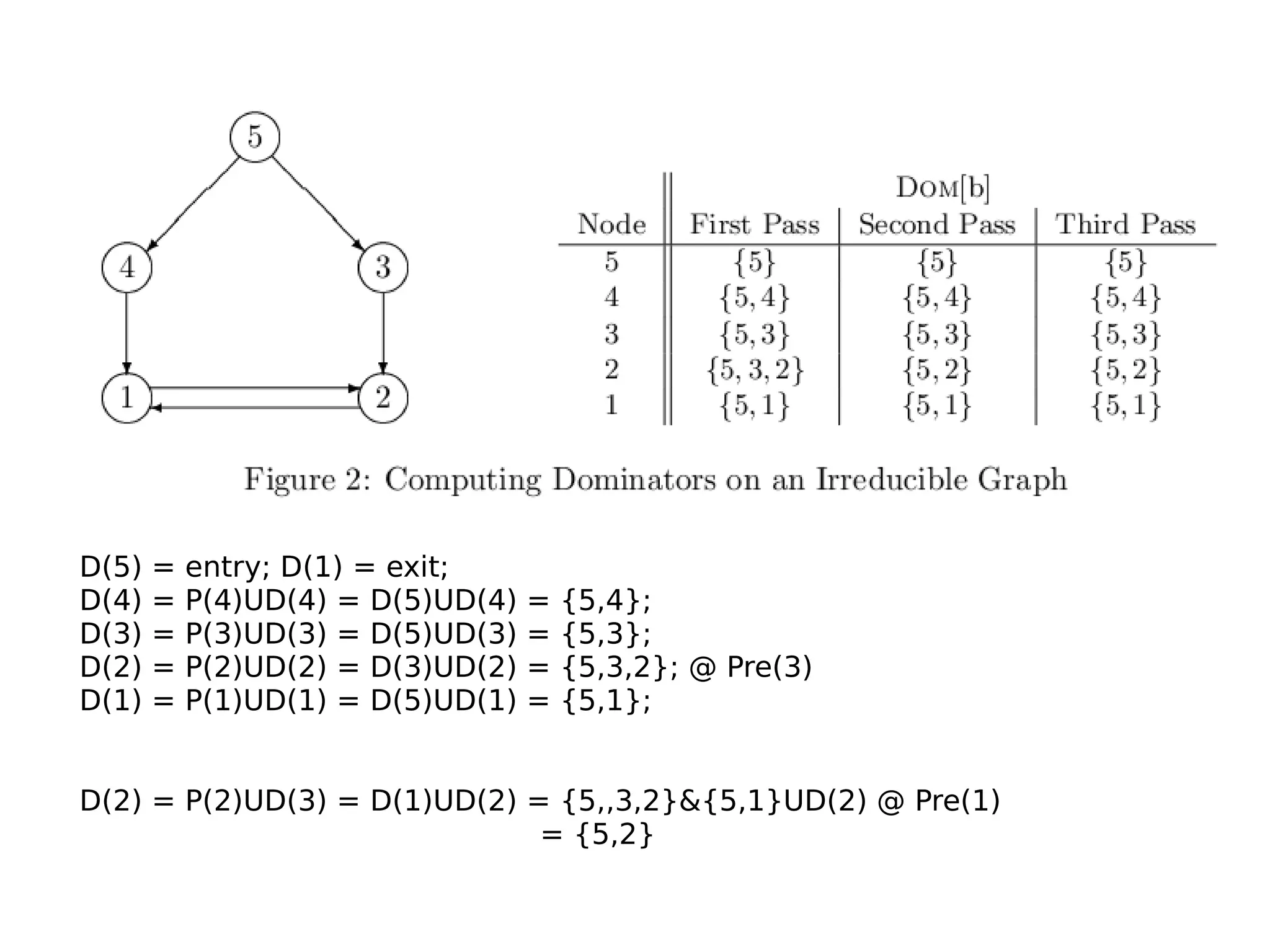
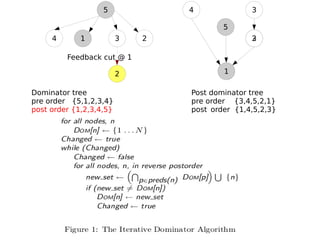

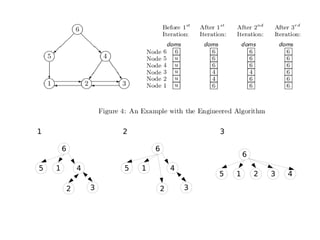


1) The document discusses dominator trees and feedback cuts for a graph. 2) It provides the pre-order and post-order traversals for the dominator tree and post dominator tree of the graph. 3) The document also presents the total time complexity of O(N+E*D) for an algorithm to compute dominator sets, where N is the graph size, E is the number of edges, and D is the size of the largest dominator set.




