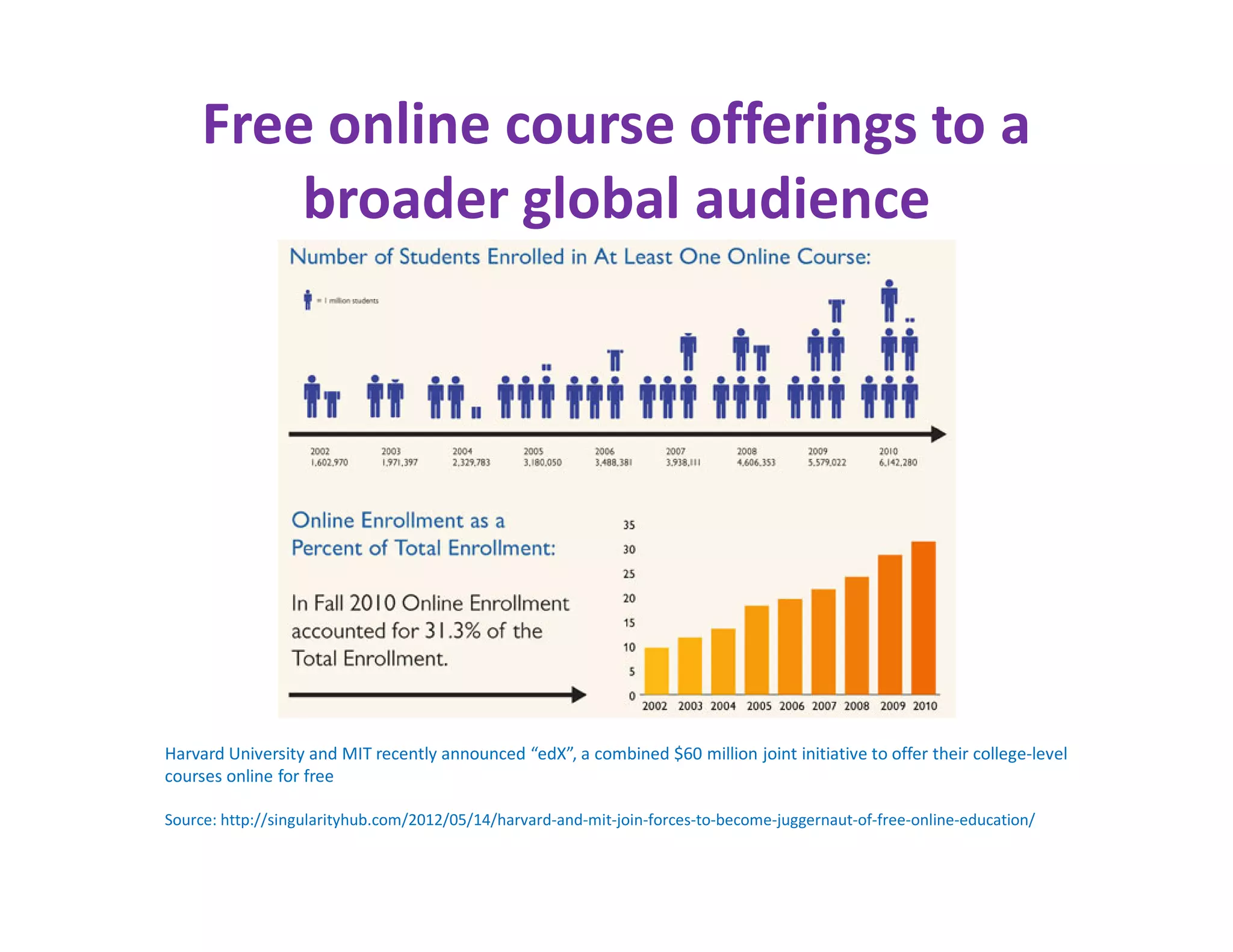
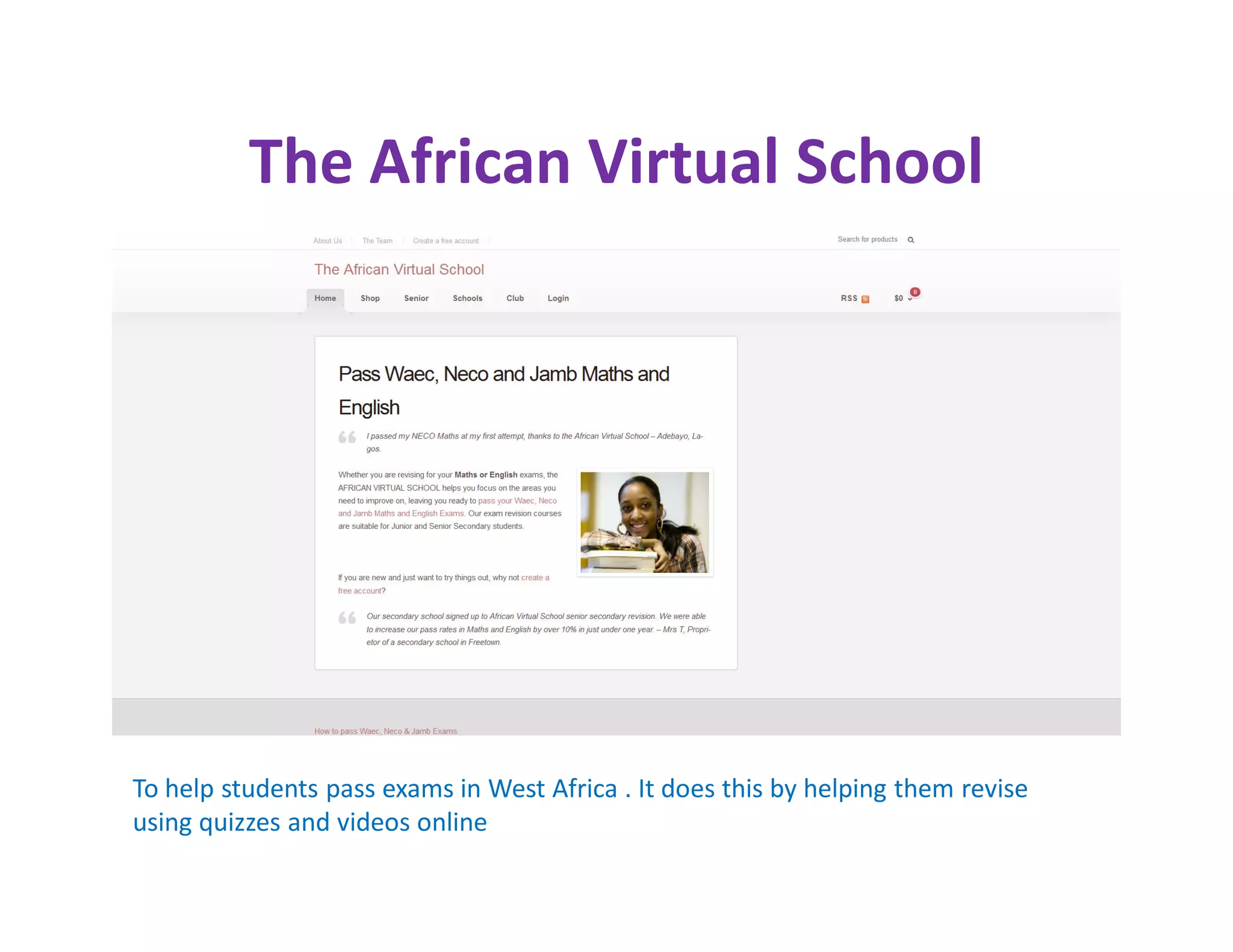
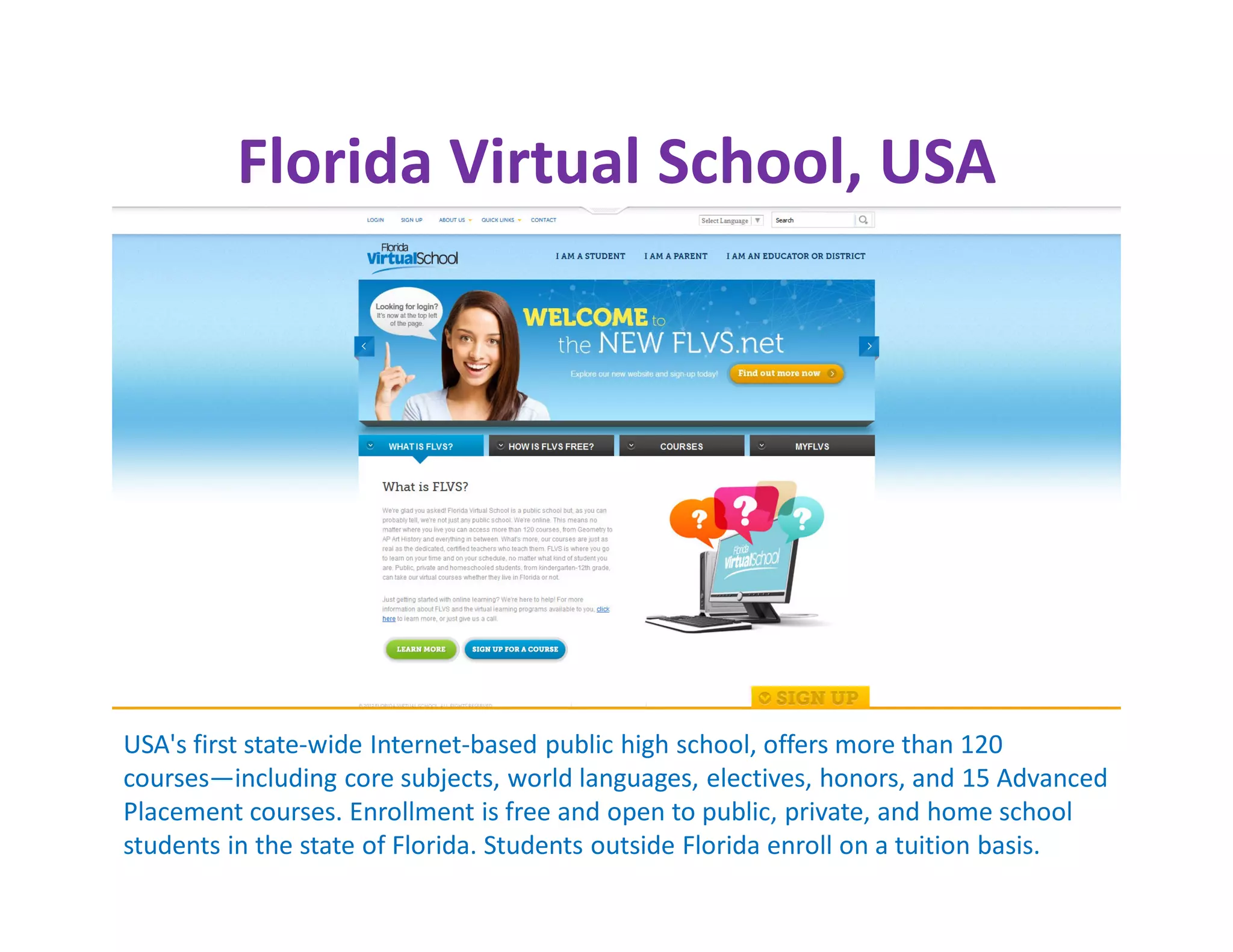
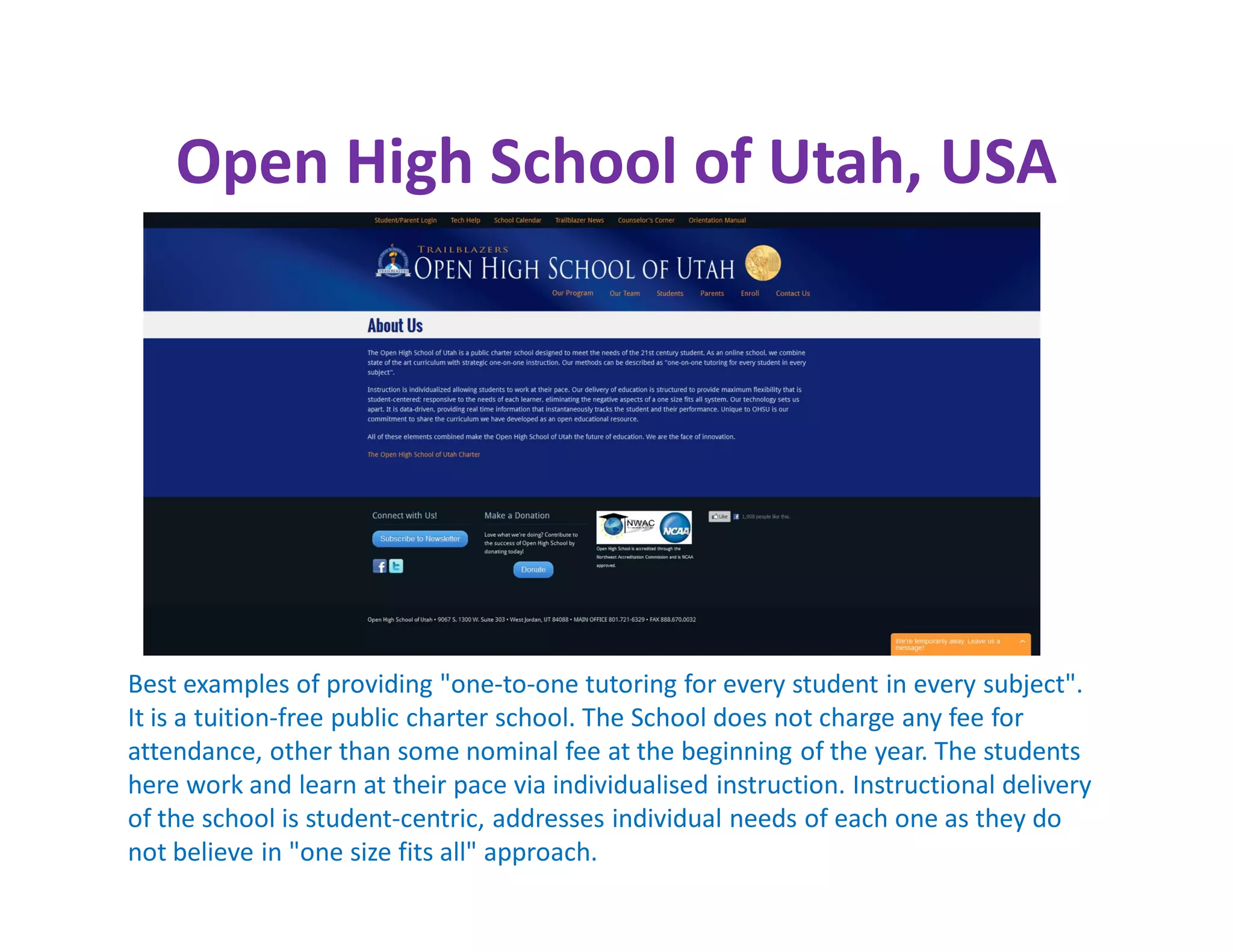
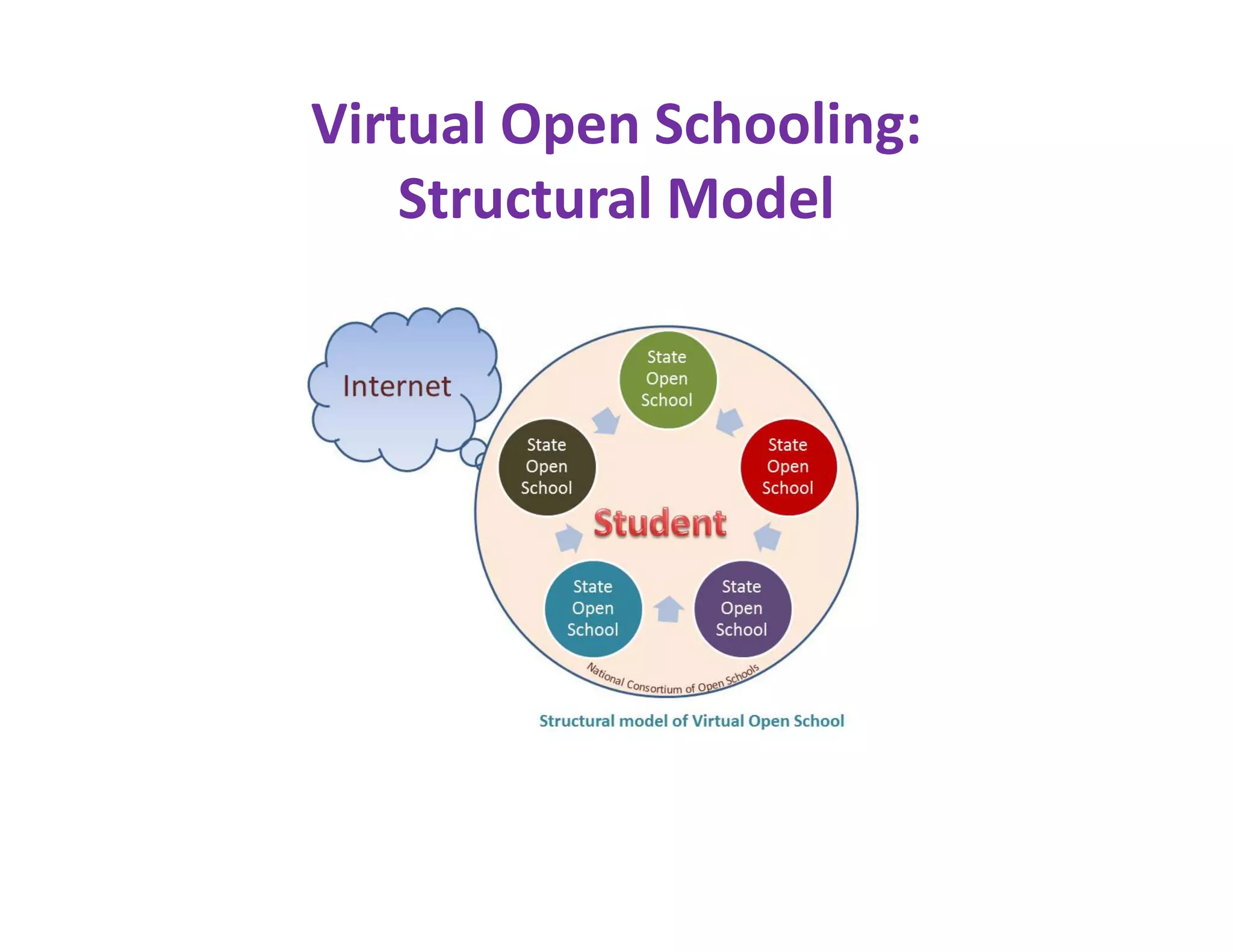
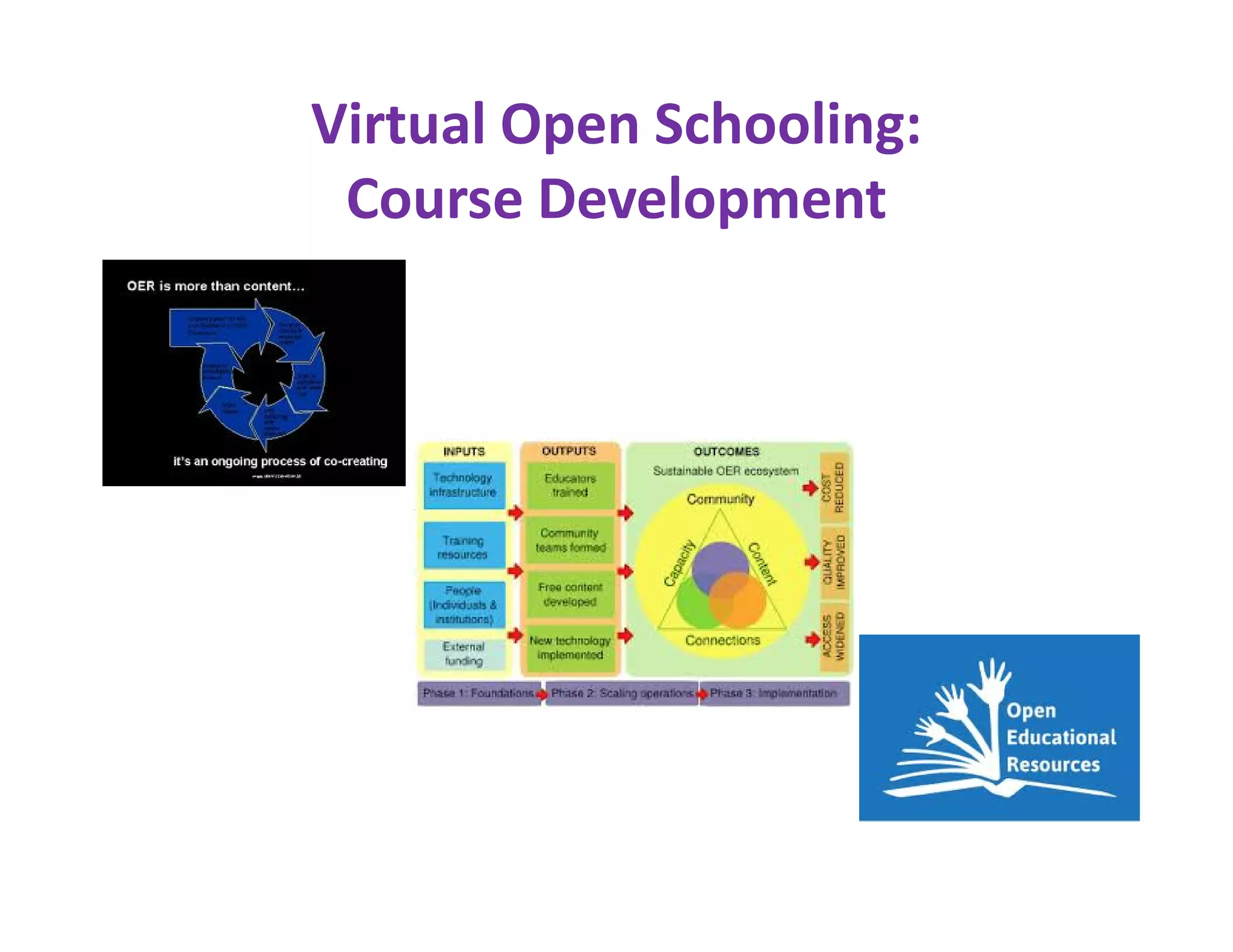
The document discusses the national consultative workshop on virtual open schooling in India, emphasizing the shift towards online and hybrid learning models that cater to the needs of diverse learners. It highlights various global examples of virtual schooling, their benefits, and structural models, while addressing challenges such as quality assurance and teacher skepticism. The Indian model promotes flexibility, digital integration, and student-centric learning modalities, aiming to enhance educational access and efficiency.