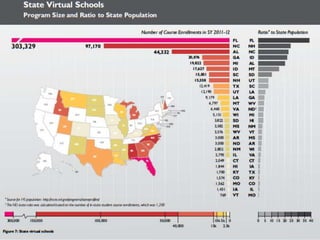
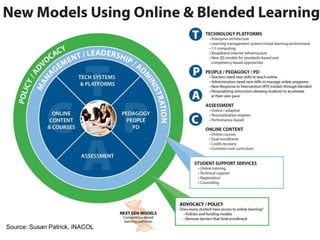
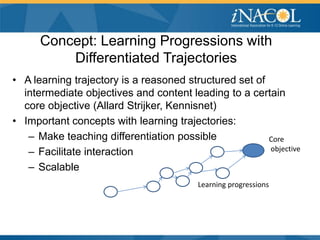
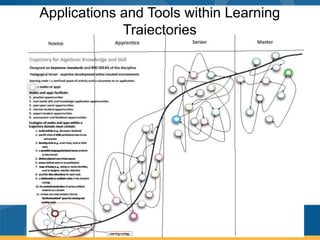
The document outlines the vision for next generation learning and competency education, emphasizing personalized and blended learning environments that leverage technology to enhance education accessibility and quality. It highlights global trends and initiatives in online learning, including efforts in countries like India, China, and South Korea, and the importance of competency-based approaches. Additionally, it discusses the need for policy changes to support innovative educational practices and ensure equitable access for all students.