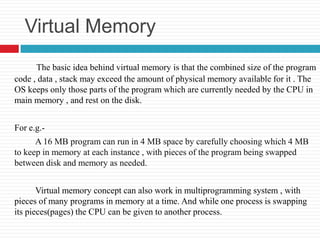
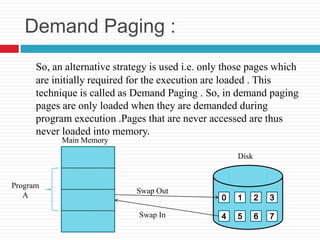
Virtual memory is a technique that allows processes to execute as if they have more memory than is physically installed. It works by swapping pages of memory between RAM and disk as needed. With demand paging, only pages actively being used are loaded into memory, avoiding loading unnecessary pages. This allows programs to be larger than physical memory and improves efficiency by not loading parts that may never be used.

![Virtual Memory
In a computer system, virtual memory is something that
appears to be exist, but actually does not exist. Virtual memory is a
technique , which allows execution of the process , that are not
completely present in the memory.
Advantages:
1] The program can be larger than physical memory.
2] This frees programmers from the concerns of memory limitations.
3] Virtual memory provides efficient mechanism for discontinuous
memory allocation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virtualmemory-120626221808-phpapp01/85/Virtual-memory-2-320.jpg)