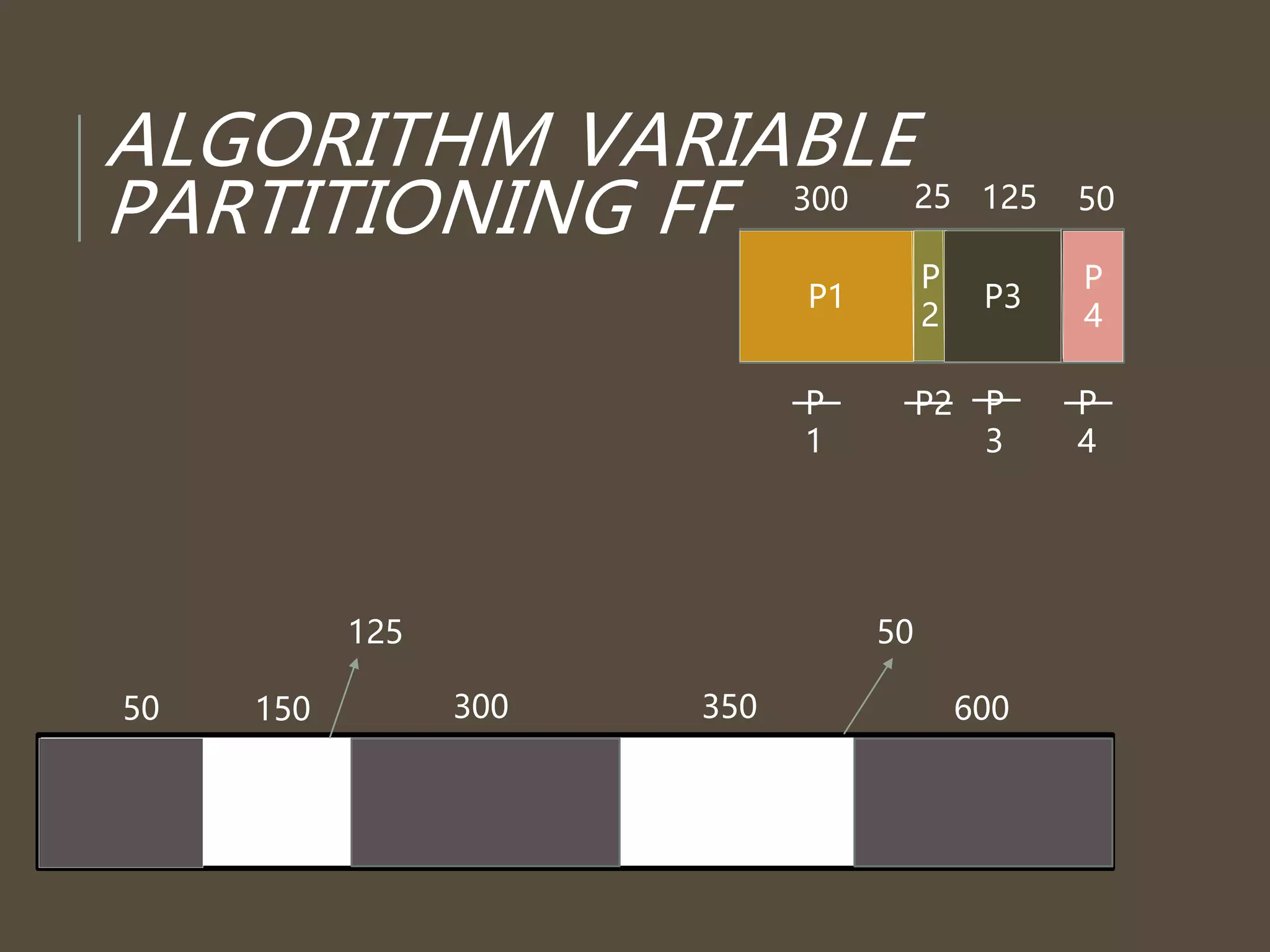
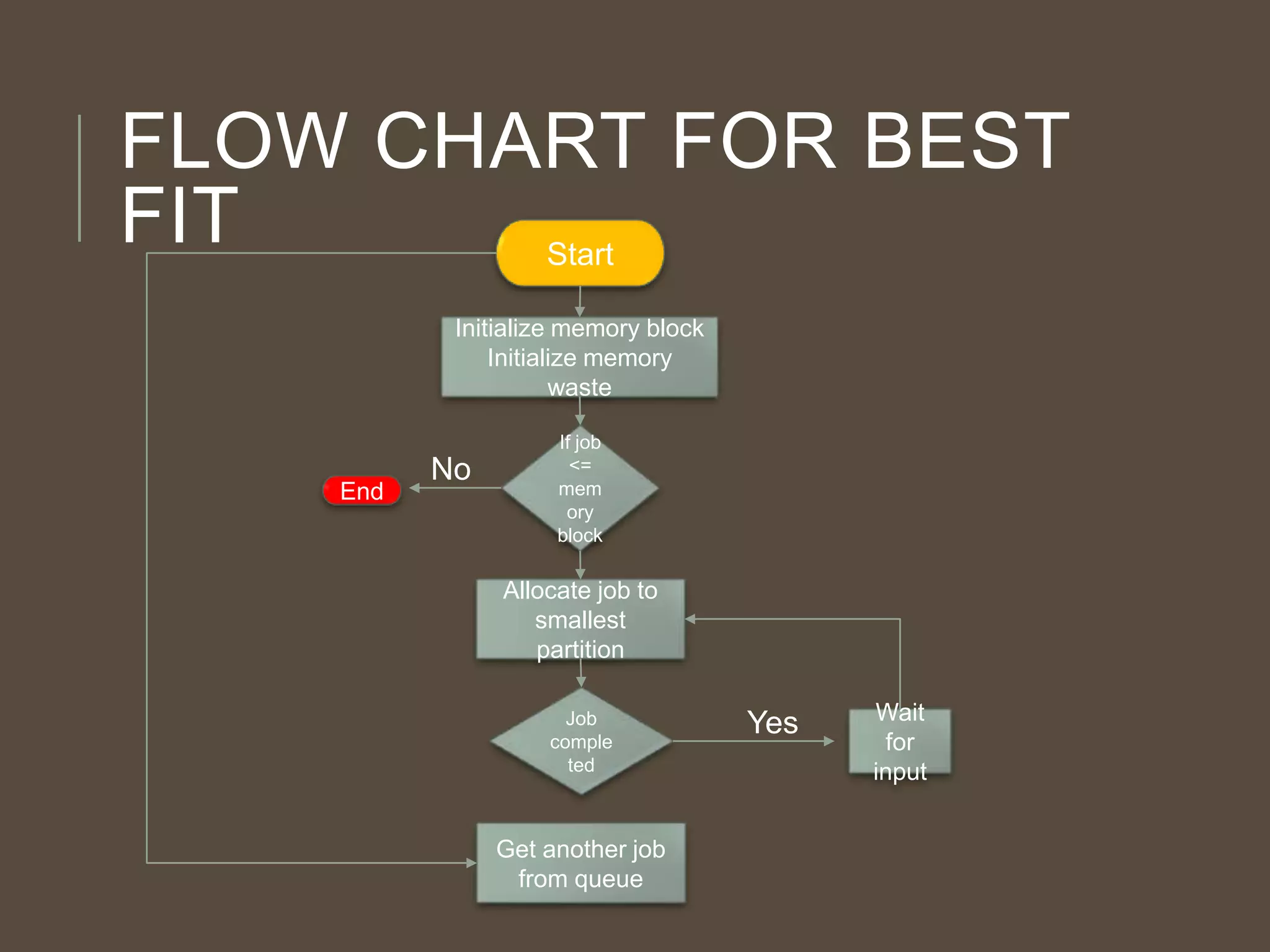
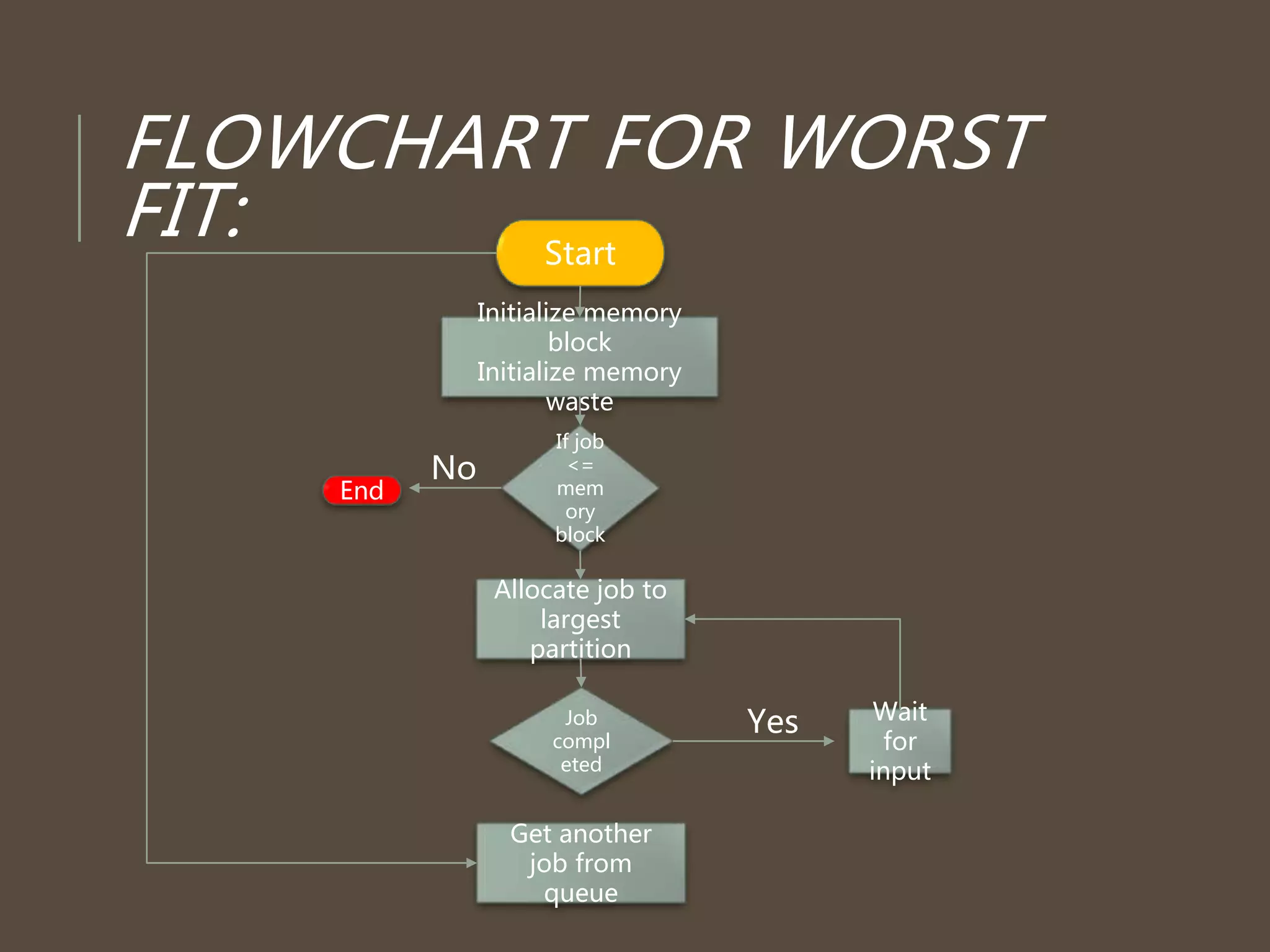
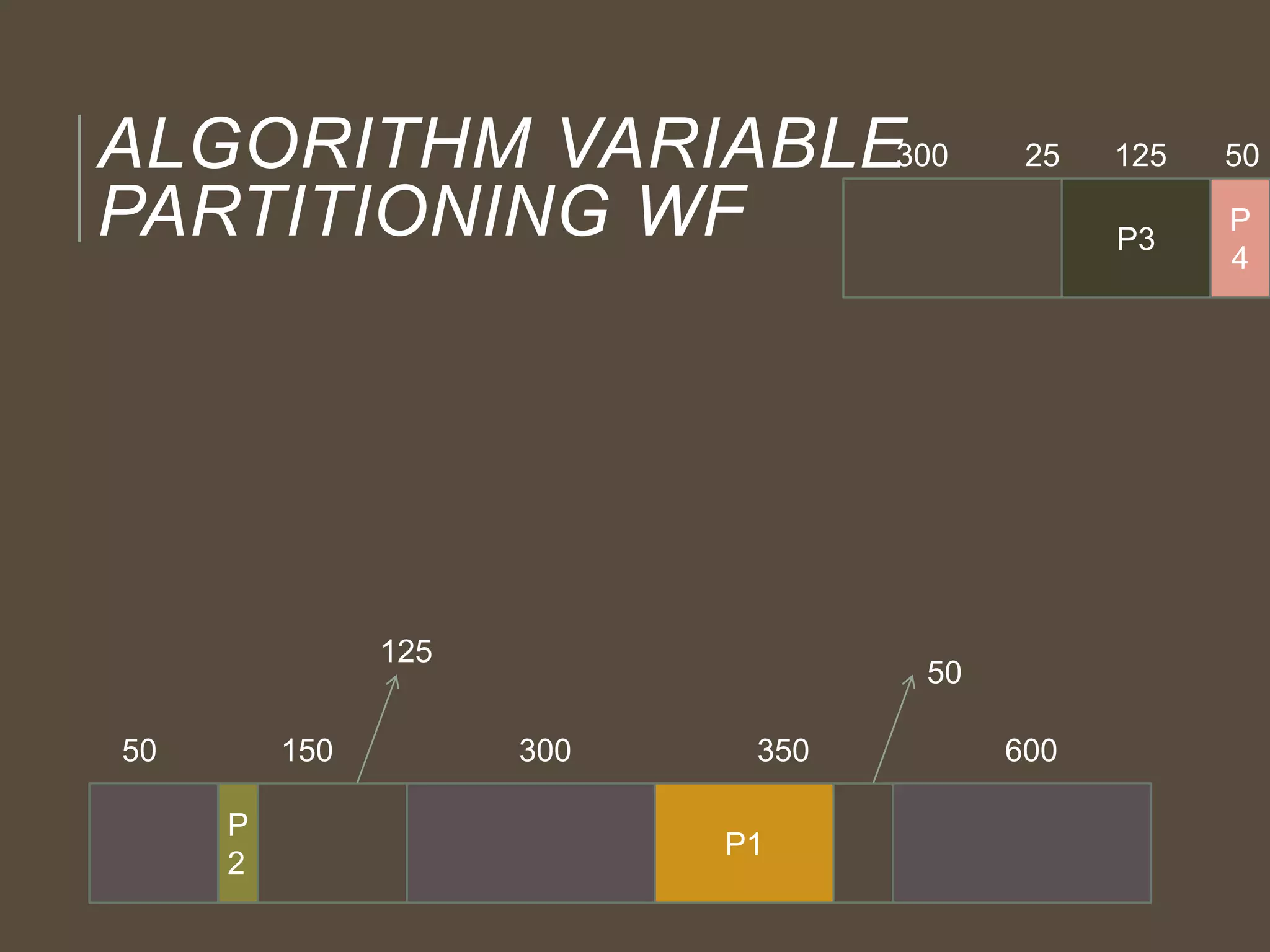
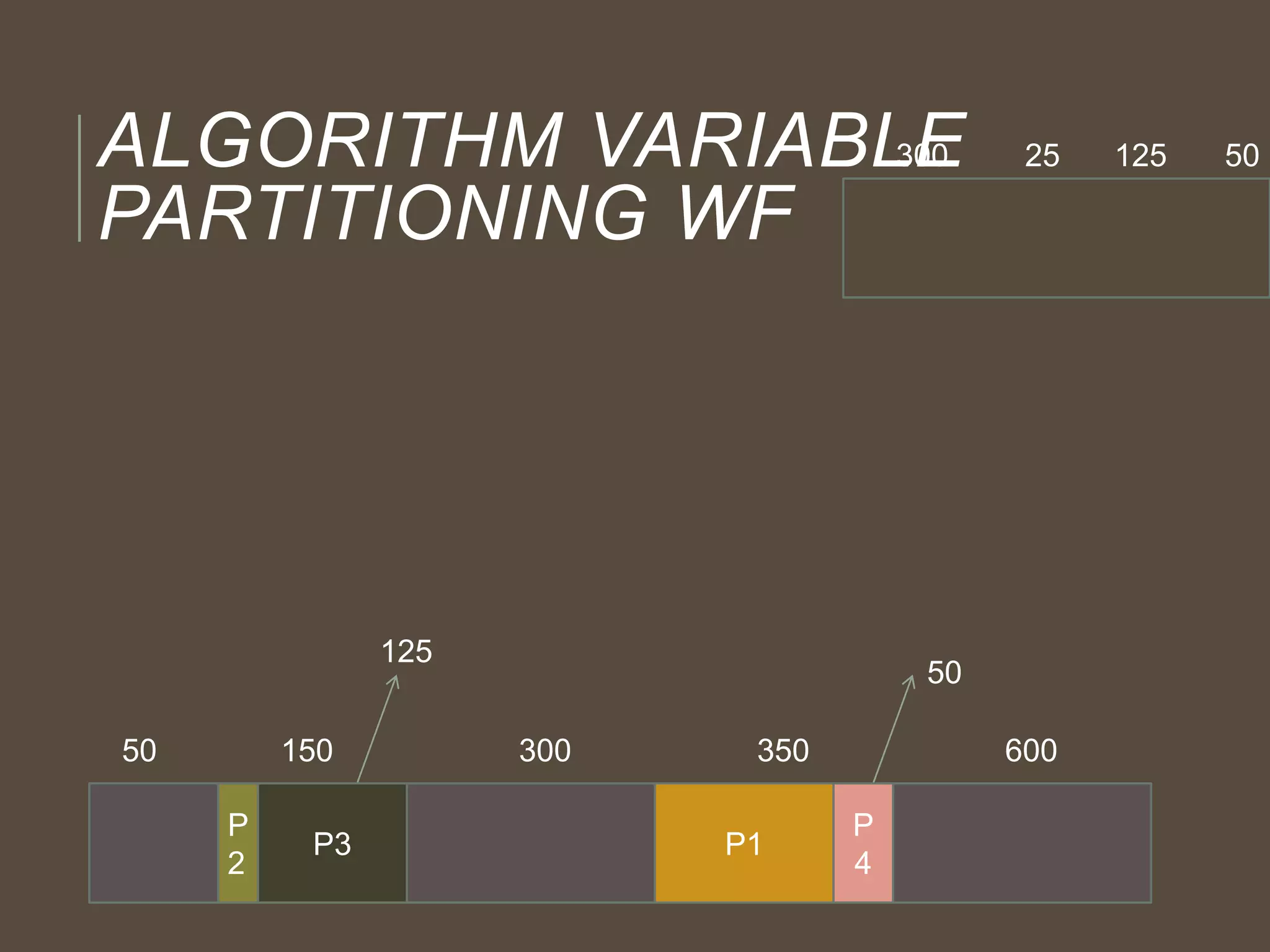
The document discusses three memory allocation algorithms: First Fit (FF), Best Fit (BF), and Worst Fit (WF). FF allocates memory by finding the first suitable free space, leading to potential external fragmentation, while BF searches for the smallest adequate partition, which can result in tiny fragments. WF, conversely, looks for the largest available space to store data, but risks breaking large free blocks and is suited for medium allocations.