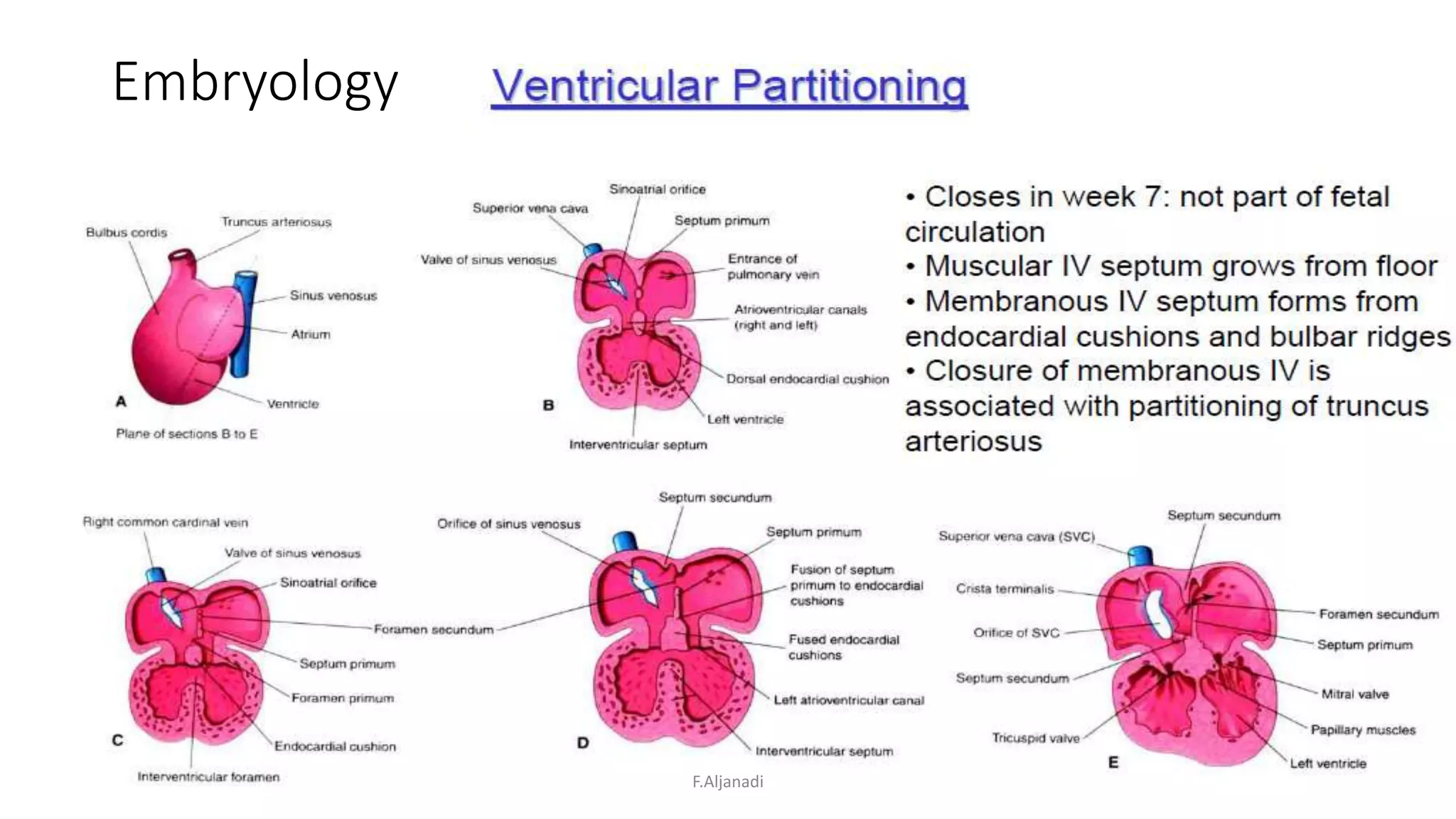
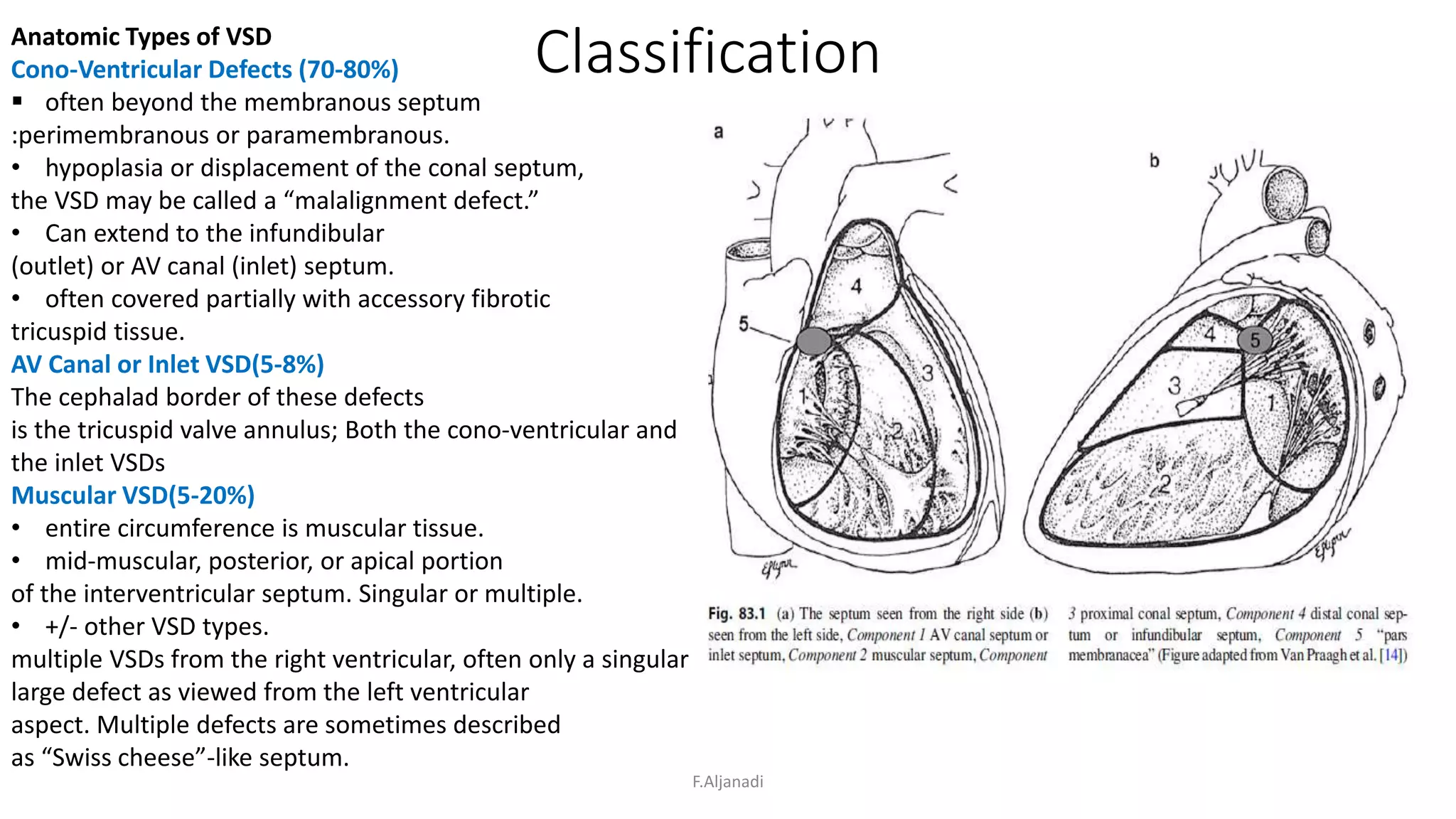
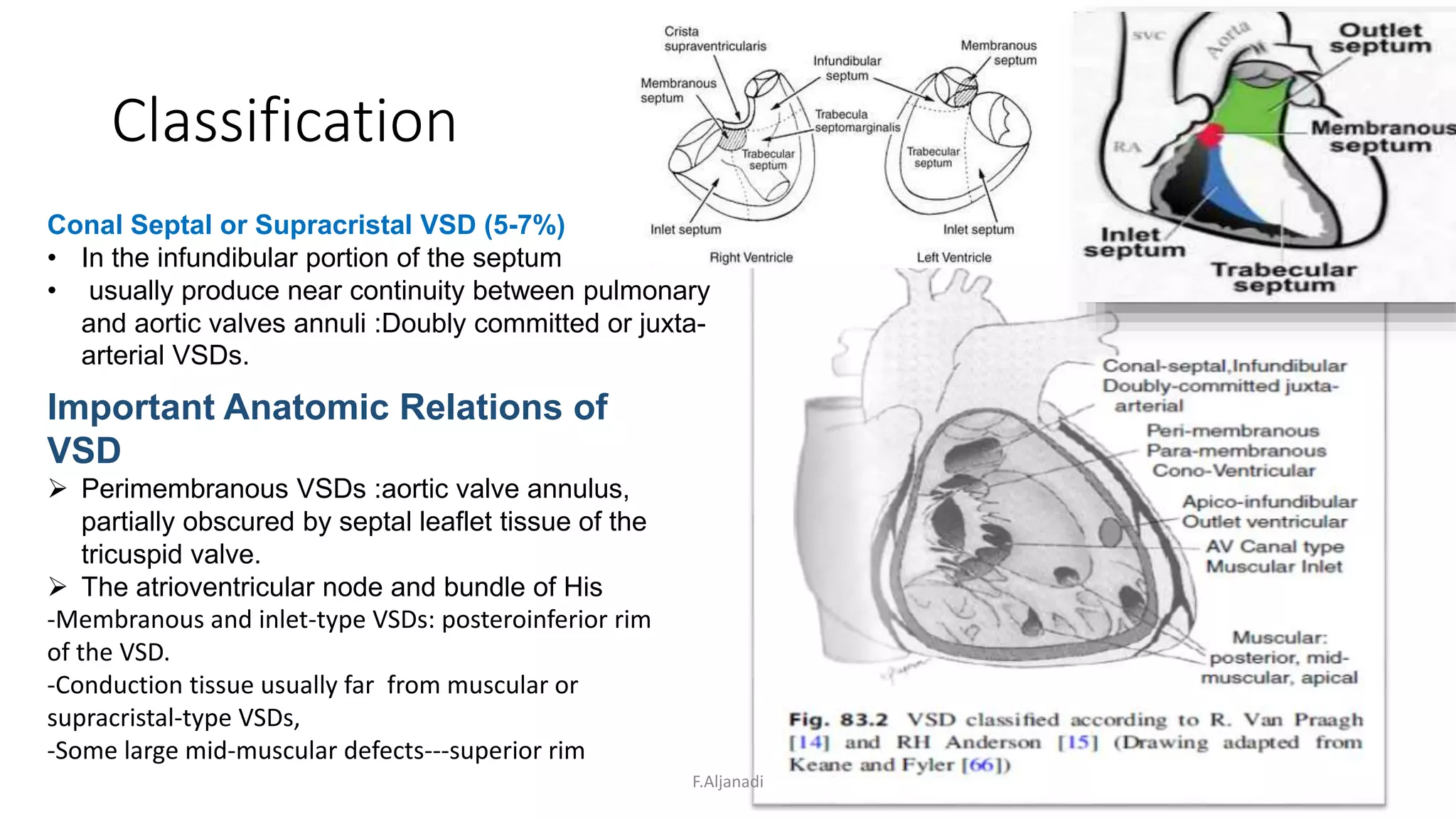
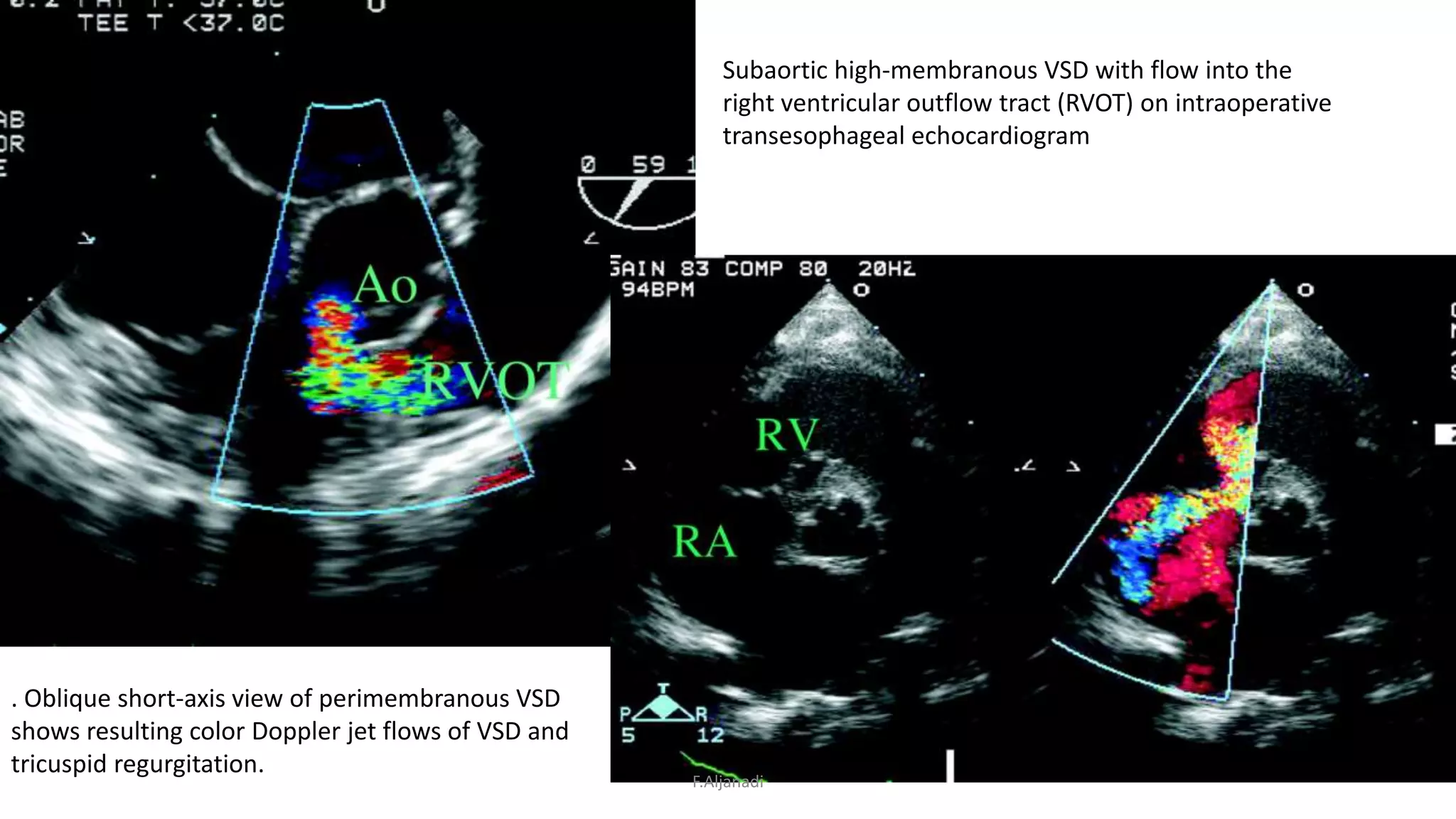
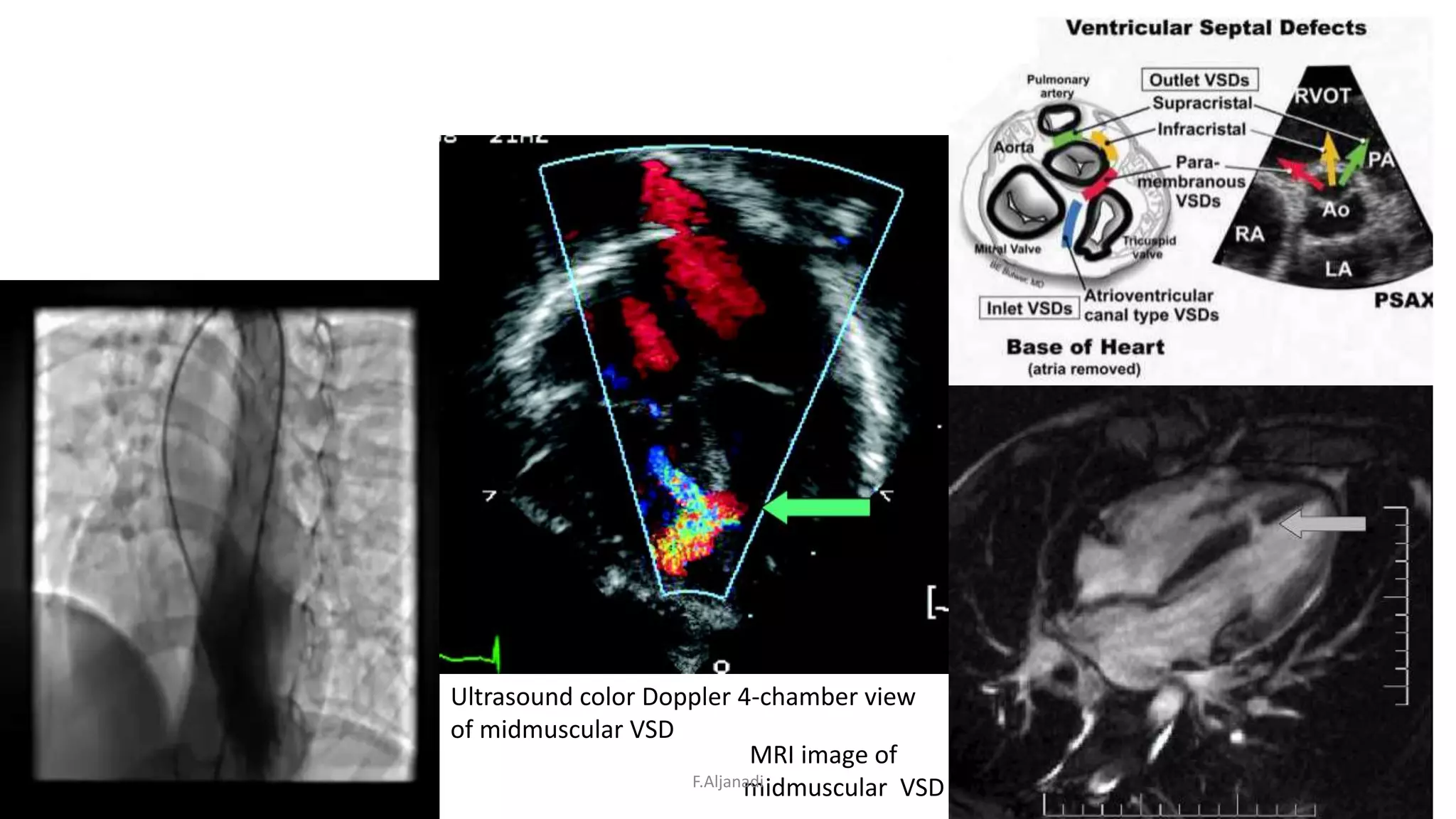
Ventricular septal defect (VSD) is the most common congenital heart defect, accounting for 40% of cardiac anomalies with an incidence of 1 in 500 infants. The underlying causes are unclear, but genetic factors, including various chromosomal conditions, are implicated. Management includes medical and surgical interventions, with a focus on monitoring potential complications such as heart failure and pulmonary vascular disease.