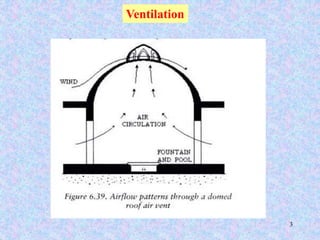
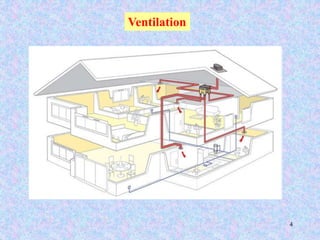
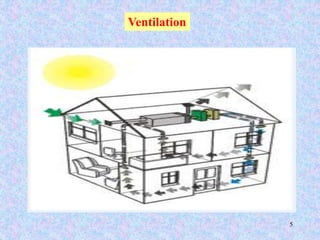
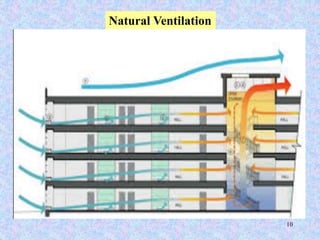
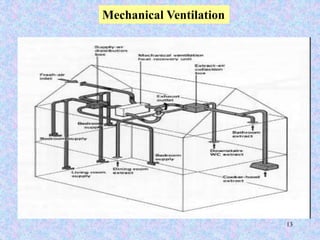
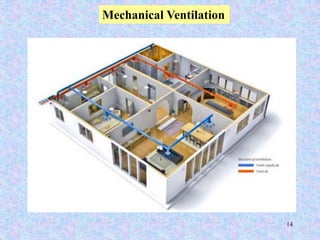
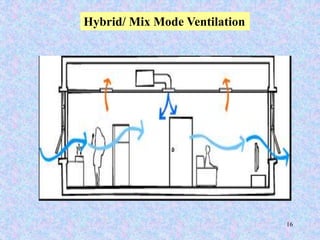
This document discusses different types of ventilation for buildings. It defines ventilation as replacing or circulating air to provide good indoor air quality. The main types discussed are natural ventilation, mechanical ventilation, and hybrid/mixed-mode ventilation. Natural ventilation uses openings to allow air flow via pressure differences without fans. Mechanical ventilation uses powered fans or blowers. Hybrid systems allow controlled introduction of outdoor air using both mechanical and passive means. The document also outlines purposes of ventilation like maintaining comfort, removing odors and contaminants, and creating air movement.