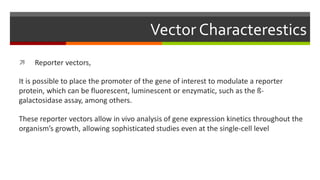
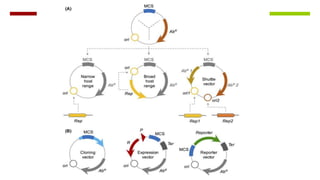
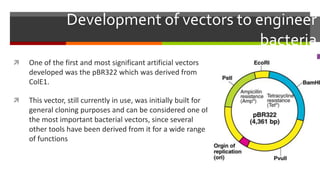
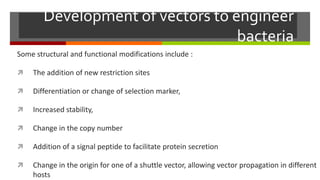
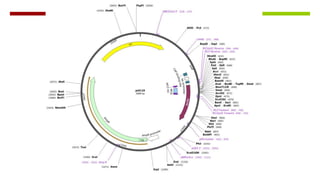
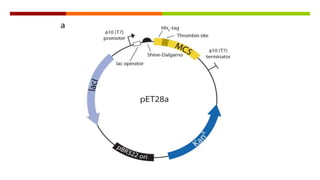
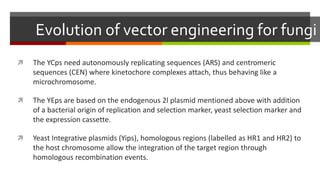
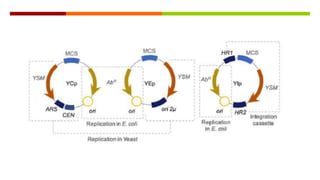
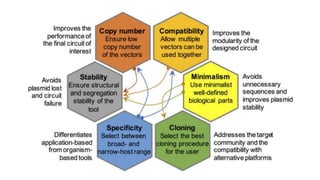
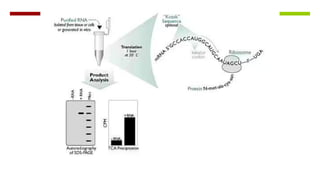
Vector engineering involves designing expression vectors that allow for optimal transcription of heterologous genes transferred between organisms. Key components of expression vectors include an origin of replication for stability in the host, a selection marker for identifying transformed cells, and a multiple cloning site for inserting genes of interest. Vectors are classified as cloning vectors for copying DNA or expression vectors for high-level protein production. Perspectives in vector design focus on copy number control, plasmid incompatibility, stability, use of minimal and characterized parts, and selection of appropriate cloning methods. Codon optimization is also important for high expression, by introducing synonymous mutations that favor translation efficiency in the target host.