The document discusses various vascular closure devices (VCDs), including:
1. Plug-based devices like Angio-Seal, Exoseal, and MynxGrip that use anchors, plugs, or polymers to seal the puncture site.
2. Suture-mediated devices like Perclose Proglide and Prostar that deploy sutures before sheath removal to close the arteriotomy.
3. Mechanical devices like StarClose that use clips, and compressive devices like Catalyst III that use disks, to facilitate hemostasis.
While VCDs can reduce time to hemostasis and ambulation compared to manual compression, meta-




![1)Plug-Based VCDs
A)Angio-Seal Evolution- VIP, and STS Plus (St. Jude Medical, St.
Paul, Minn)
Devices create a mechanical seal by sandwiching the arteriotomy between
a bio absorbable anchor and a collagen sponge.
Dissolve within 60 to 90 days.
Should not be used in small arteries (<5 mm) or arteries
with significant occlusive disease as the anchor can
catch on the side walls.
Leading to failure with continued bleeding or vessel
occlusion.
The device comes in 6F and 8F versions.
RCT of 435 patients:[1]
High deployment success rate (96 %)
Shorter time to hemostasis with 76 % of patients having immediate haemostasis
(within 1 min).
Reduced number of complications for patients with AngioSeal compared to MC.
1. Kussmaul WG, Buchbinder M, Whitlow PL, et al. Rapid arterial hemostasis and decreased access site complications after cardiac catheterization and angioplasty: results of a
randomized trial of a novel hemostatic device. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995;25:1685–92](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vcds-180920072508/85/Vascular-Closure-Devices-5-320.jpg)
![B)Exoseal (Cordis Corp., NJ, USA)
Places a polyglycolic acid plug outside the arteriotomy and is held in place by femoral
fascia.
This plug hydrolyze and resorbed within 60 to 90 days.
Available in 5F, 6F, and 7F sizes.
Potential advantage:
Do not have an intravascular implant thereby diminishing the risks of anchor-
related luminal narrowing, occlusion or embolism.
Two minutes of non-occlusive MC is advised following deployment, and ambulation
is proposed by the manufacturers at 6 h or later.
The ECLIPSE trial (multicenter RCT of 401 patients) randomized to closure with
Exoseal or MC.[2]
Mean time to hemostasis and time to ambulation were significantly shorter in the Exoseal
arm of the study (4.4 vs 20.1 min and 2.5 vs 6.2 h, respectively).
There were no major complications reported in this study.
2. Wong SC, Bachinsky W, Cambier P, et al. A randomized comparison of a novel bioabsorbable vascular closure device versus manual compression in the achievement of hemostasis
after percutaneous femoral procedures: the ECLIPSE (Ensure’s Vascular Closure Device Speeds Hemostasis Trial). JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2009;2:785–93.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vcds-180920072508/85/Vascular-Closure-Devices-6-320.jpg)


![ Sealant is absorbed within 30 days.
A non-randomised single-arm prospective trial of 190 patients (Mynx device) [3]
Successful deployment in 93 % of cases.
Mean time to haemostasis and time to ambulation of 1.3 min and 2.6 hours.
The primary advantage of the Mynx VCD:
Absence of intraluminal material, thereby reducing the risks of luminal narrowing,
vessel occlusion or distal embolisation.
However, there are reports of distal embolisation occurring with the Mynx VCD
3.Scheinert D, Sievert H, Turco MA, et al. The safety and efficacy of an extravascular, water-soluble sealant for vascular closure: initial clinical results for Mynx. Cathet
Cardiovasc Interv. 2007;70:627–33.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vcds-180920072508/85/Vascular-Closure-Devices-9-320.jpg)

![ The intravascular component is very flexible, potentially allowing for closure in small
or diseased vessels.
In a multi-center RCT of 297 patients randomized to FISH or MC:[4]
Mean time to hemostasis and mean time to ambulation were reduced for the FISH
cohort compared to MC (8.9 vs 17.2 min and 2.4 vs 4.3 hours)
There were no significant differences in the rates of adverse events between the two
cohorts in this study
4. Bavry AA, Raymond RE, Bhatt DL, et al. Efficacy of a novel procedure sheath and closure device during diagnostic catheterization: the multicenter randomized clinical trial
of the FISH device. J Invasive Cardiol. 2008;20(4):152–6.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vcds-180920072508/85/Vascular-Closure-Devices-11-320.jpg)






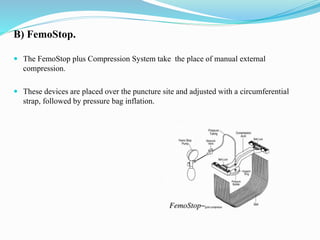

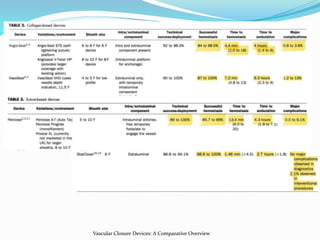
![Complications
Two meta-analyses of randomized trials compared the incidence of individual
complications in patients treated with manual compression versus closure devices.[5]
Closure devices tended to increase the incidence of local bleeding and did not appear
to significantly influence hematoma, pseudo- aneurysm, or arteriovenous fistula
formation.
Closure devices also increased the risk of groin infection and tended to increase the
risk of leg ischemia and a complication requiring surgical repair.
5.Vaitkus PT: A meta-analysis of percutaneous vascular closure devices after diagnostic catheterization and
percutaneous coronary intervention. J Invasive Cardiol 16:243–246, 2004.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vcds-180920072508/85/Vascular-Closure-Devices-21-320.jpg)
