This document discusses different types of genetic variations:
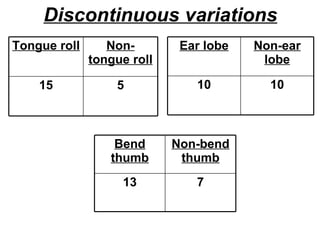
- Discontinuous variations are caused by a single gene and result in distinct traits like rolled vs non-rolled tongue. These can be illustrated with a graph showing two clear categories.
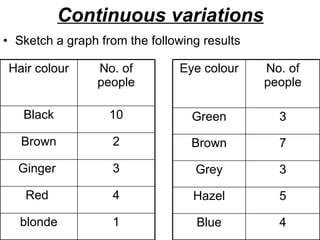
- Continuous variations are influenced by multiple genes and the environment, like eye/hair color or height. These are shown on a graph as a continuous spectrum rather than two clear groups. Environmental factors can influence continuous traits.