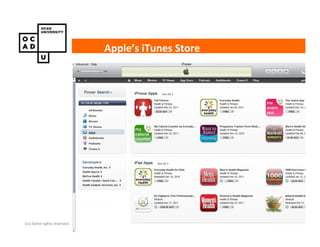
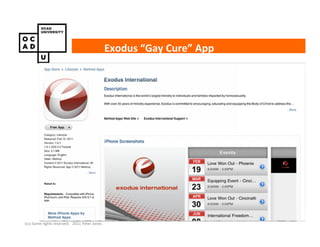
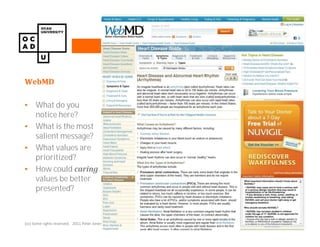
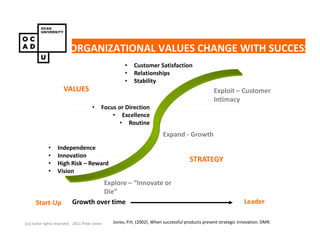
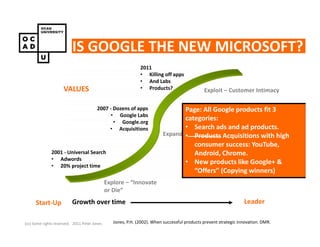
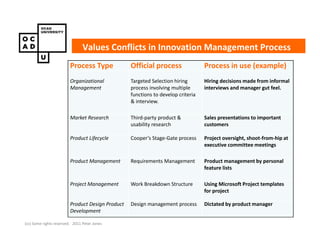
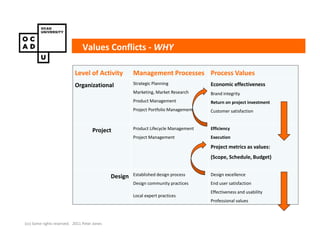
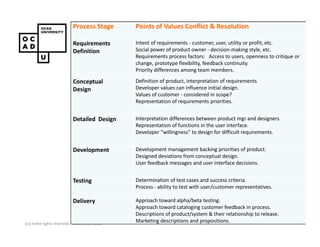
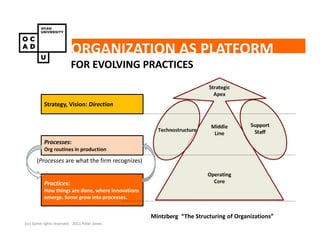
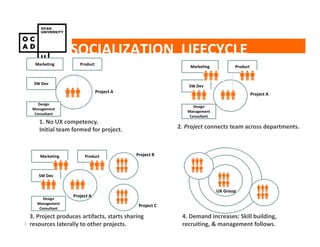
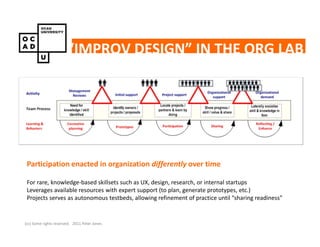
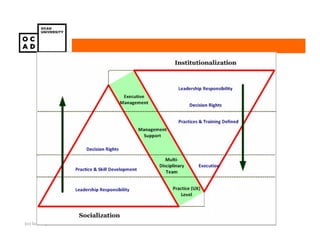
The document discusses values and conflicts in innovation processes. It provides examples of where values tensions can arise in products and services. It also examines how organizational values change as companies grow, which can prevent strategic innovation. Innovation processes are explored, noting where official processes differ from actual practices due to values conflicts. The document aims to identify values as root causes of issues to enable more conscious design of products, services and innovation processes.