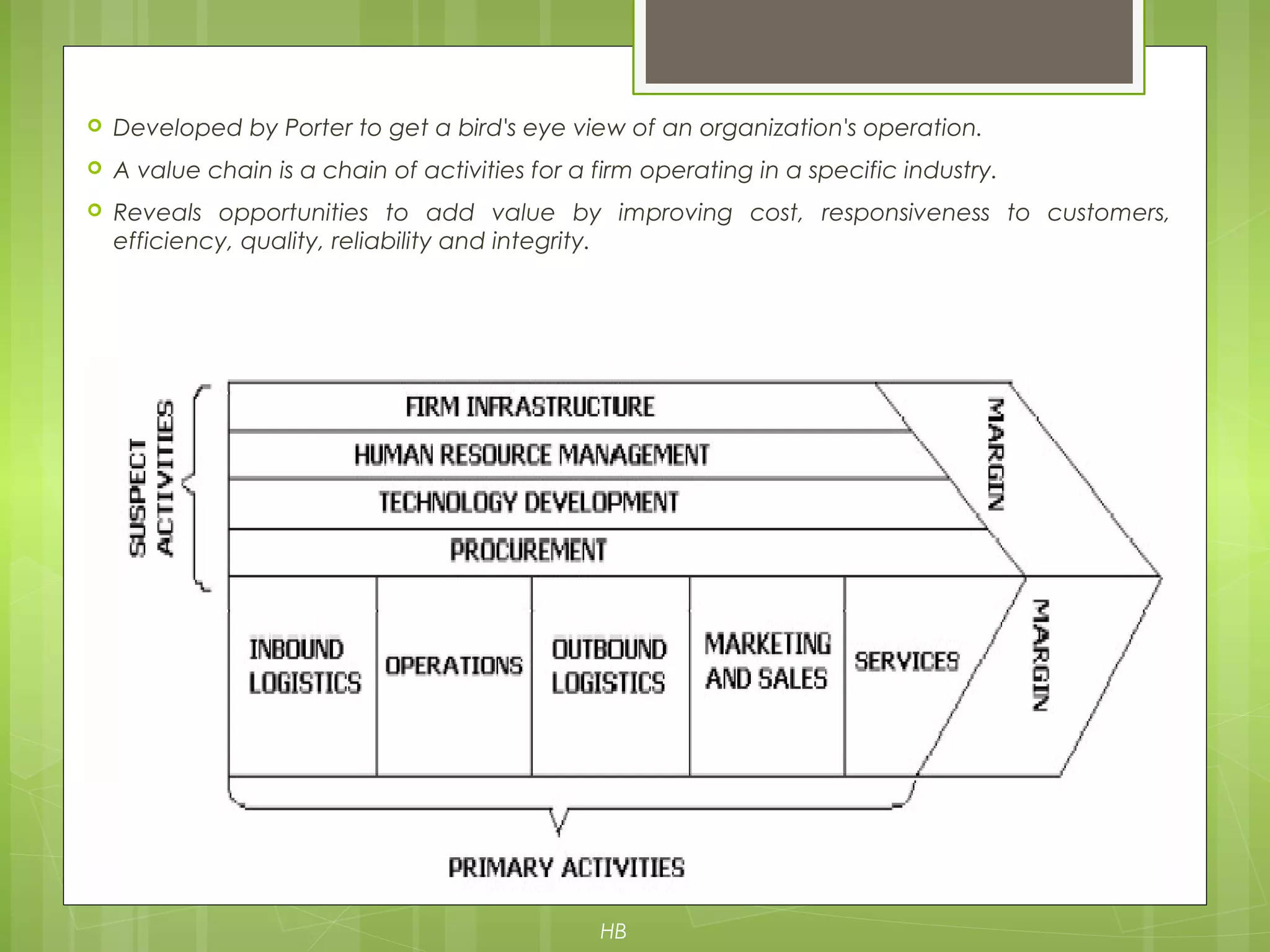
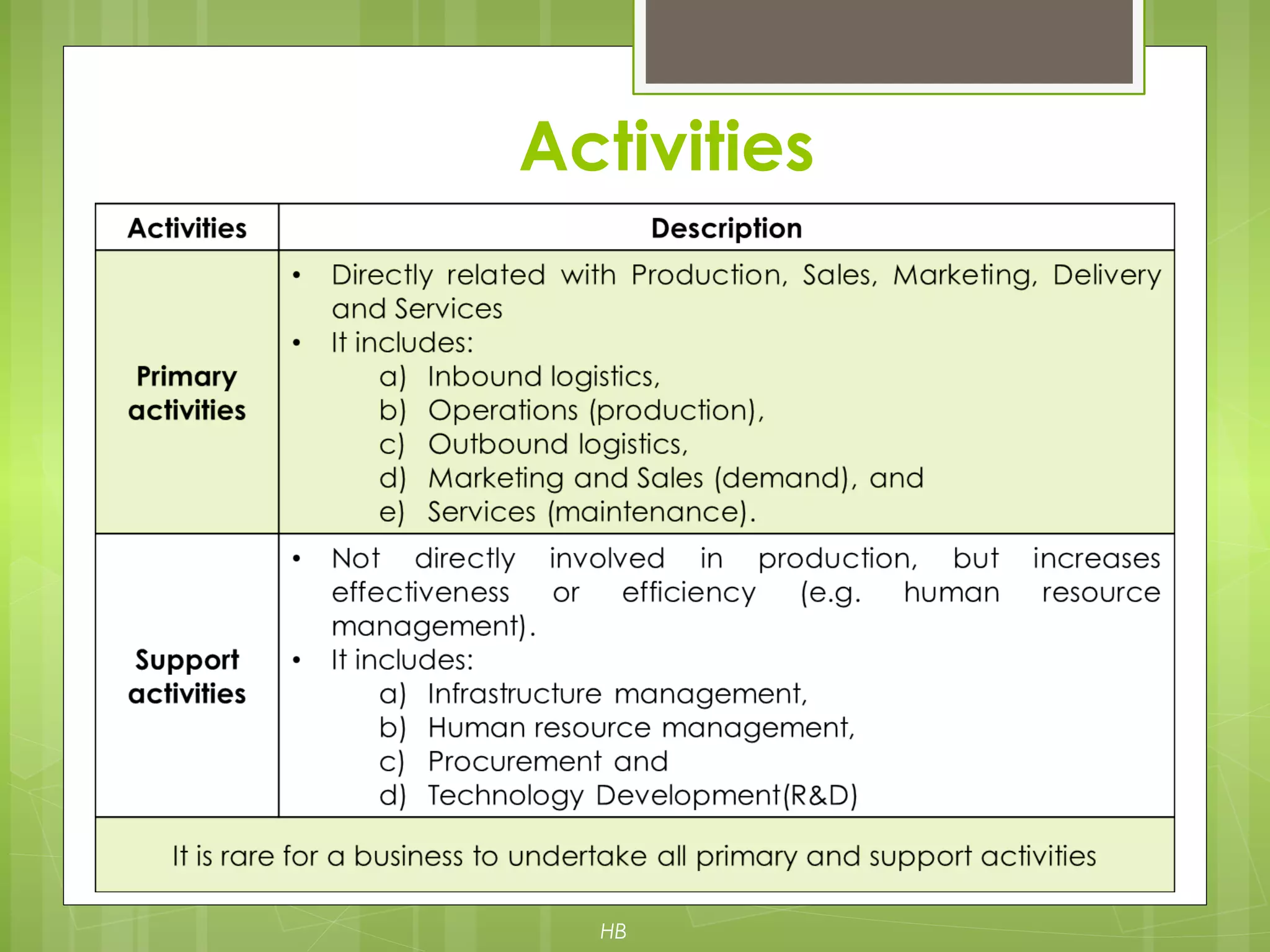
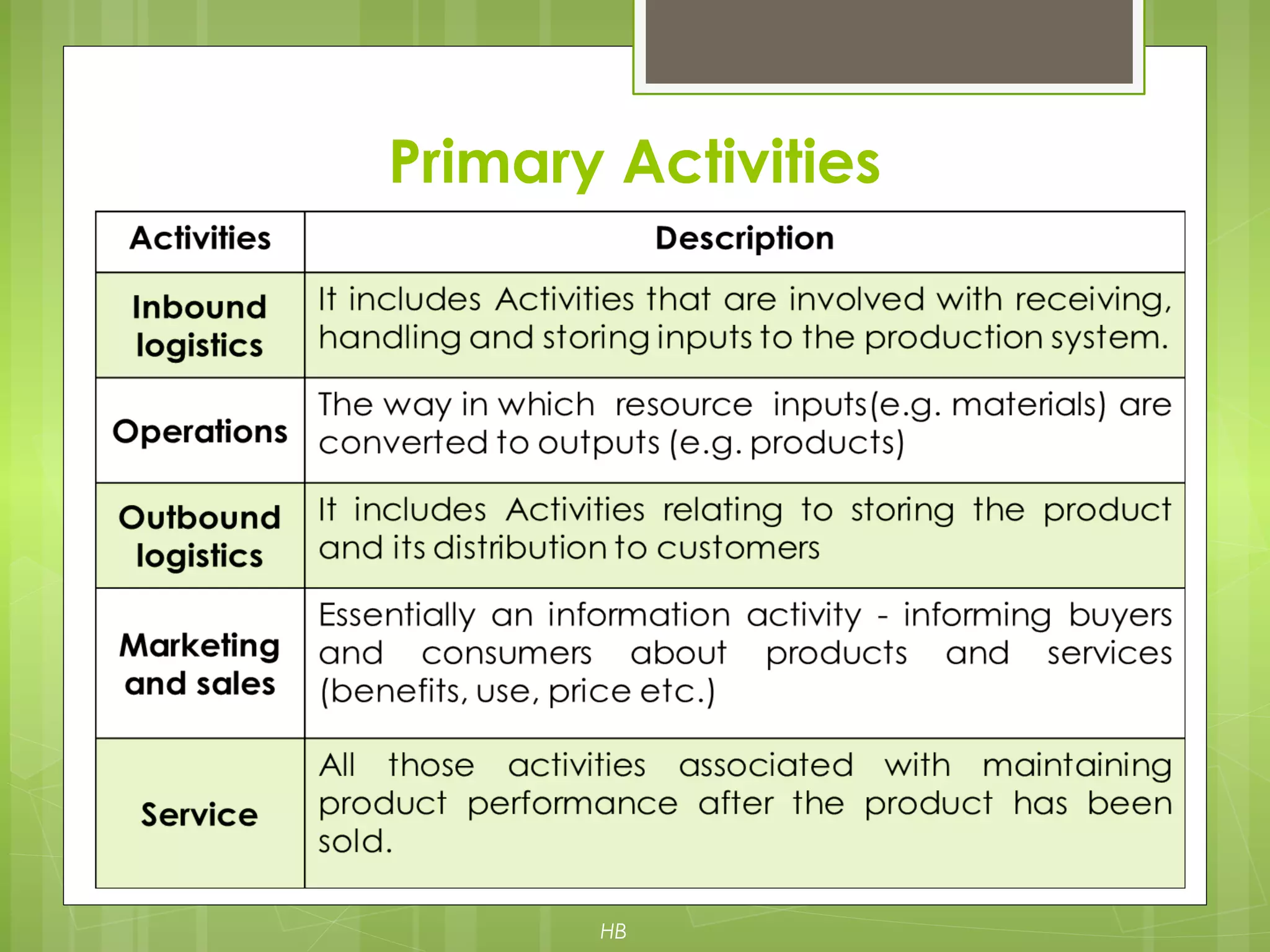
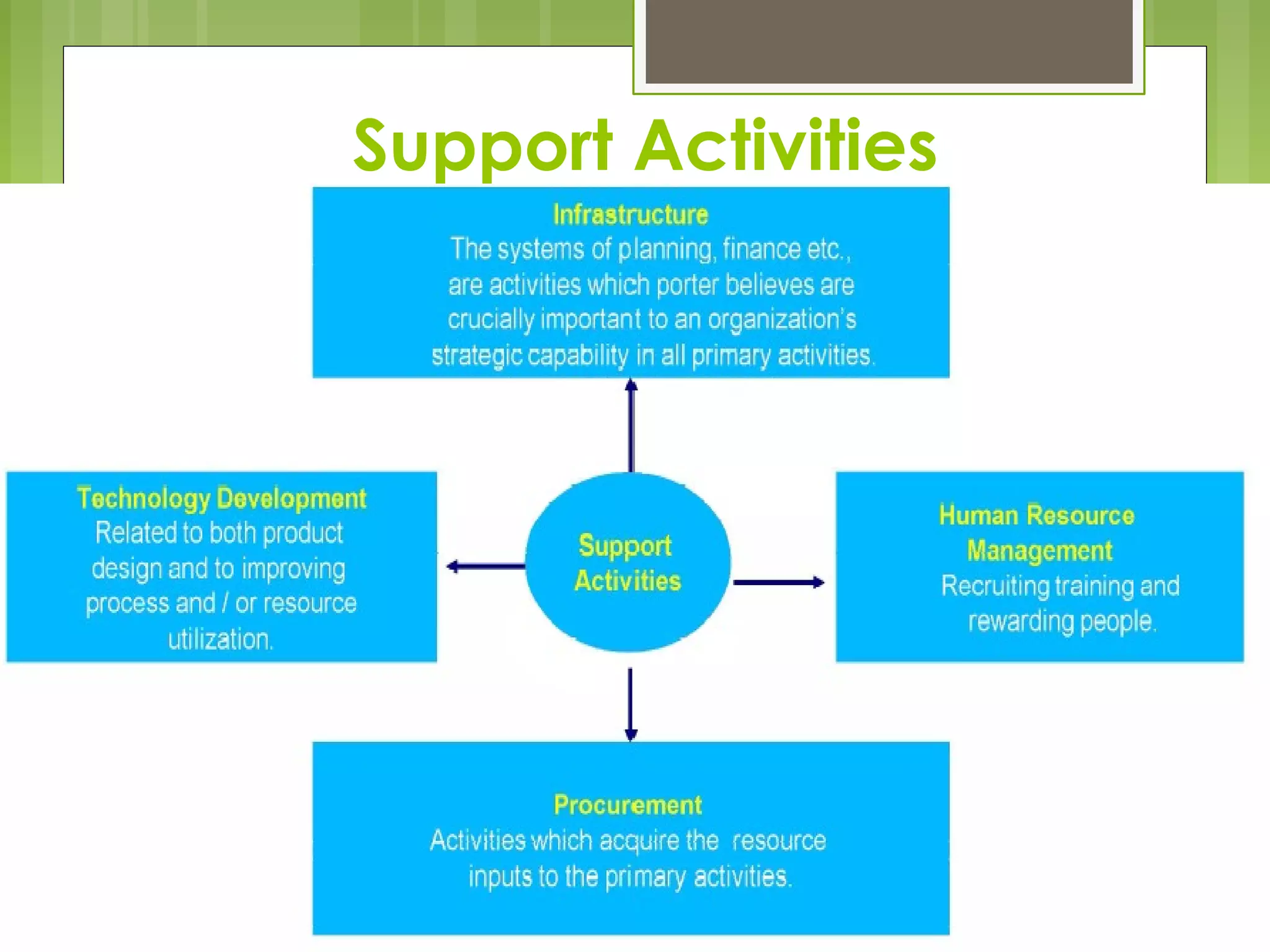
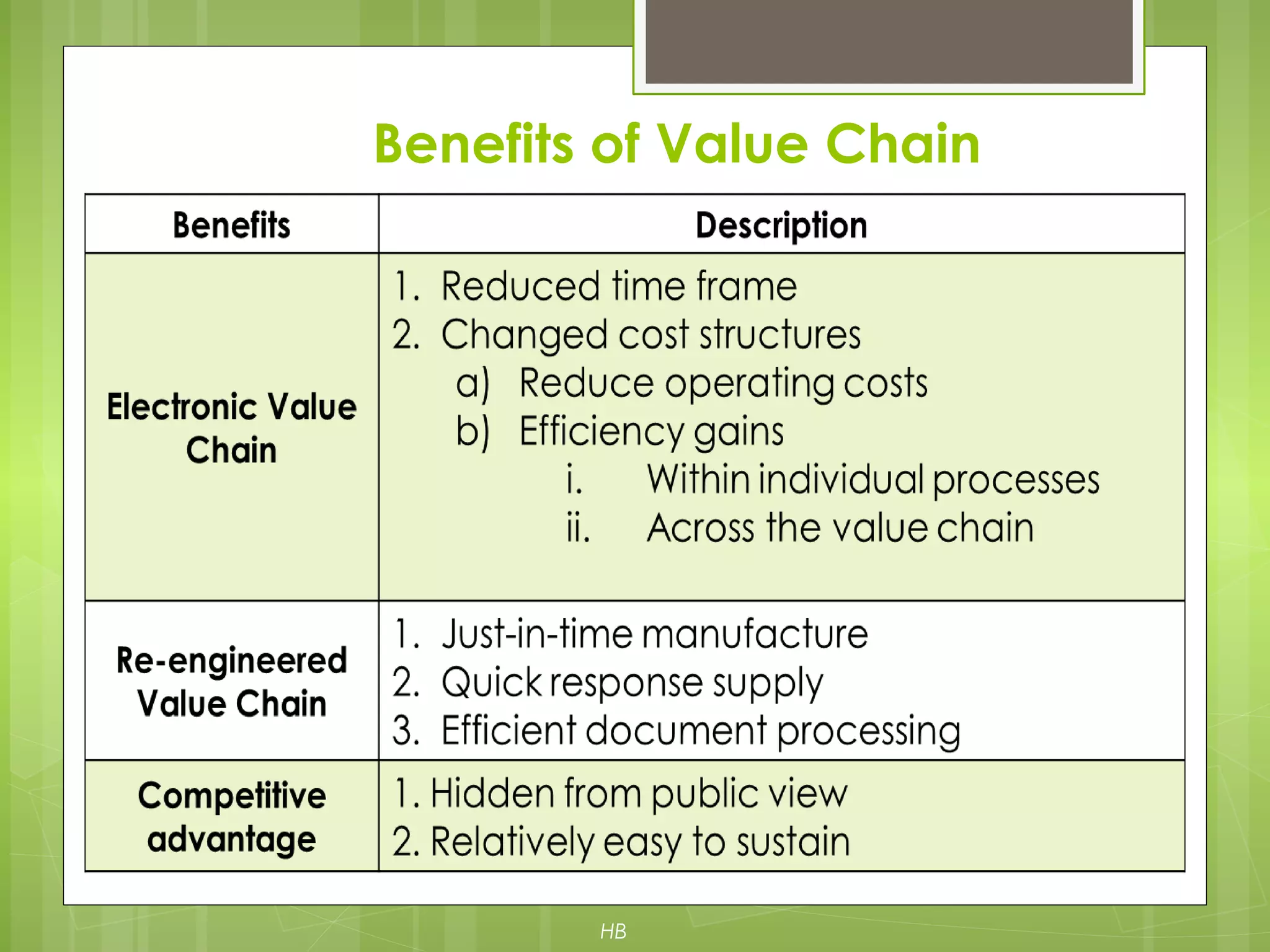
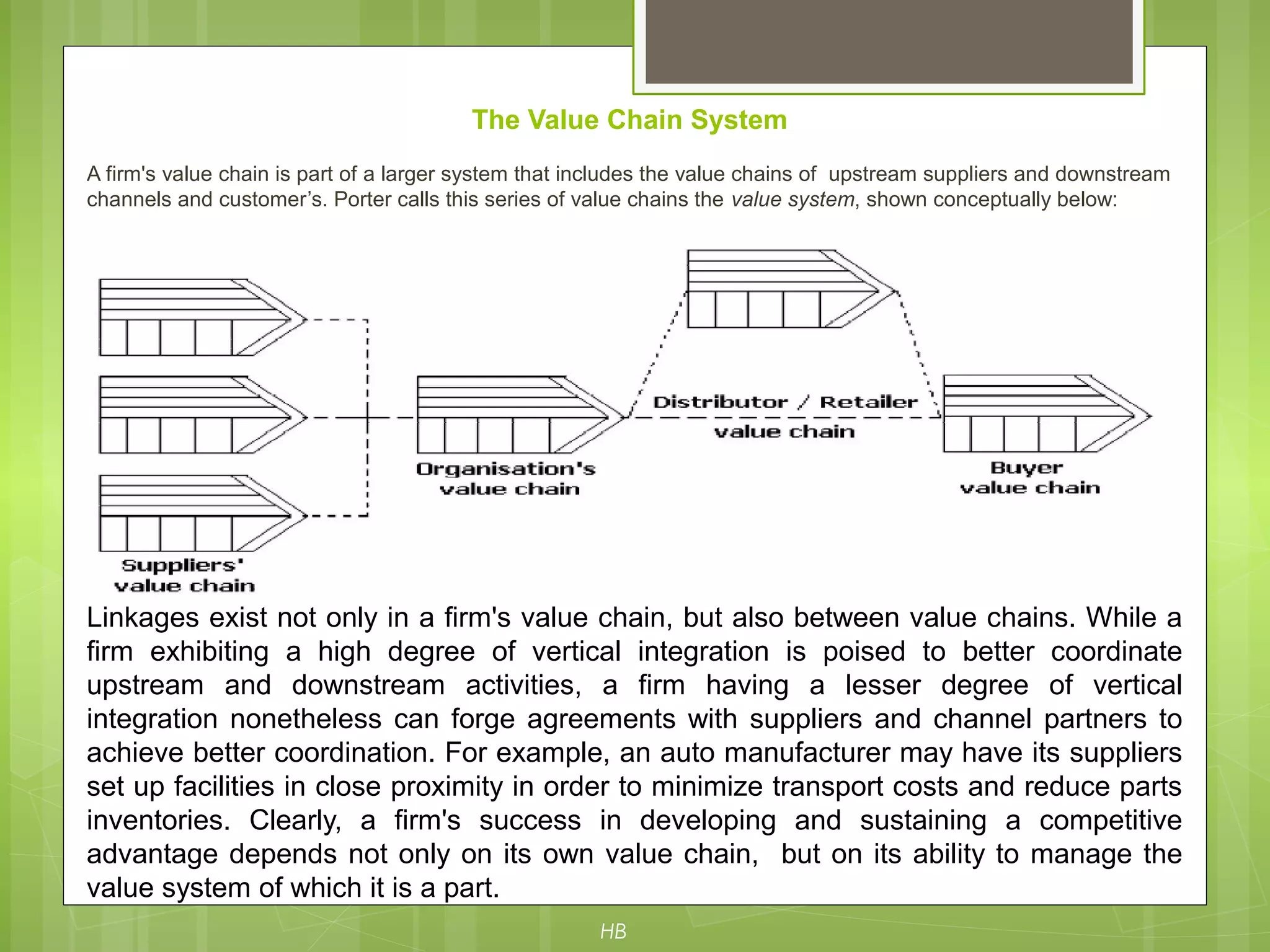
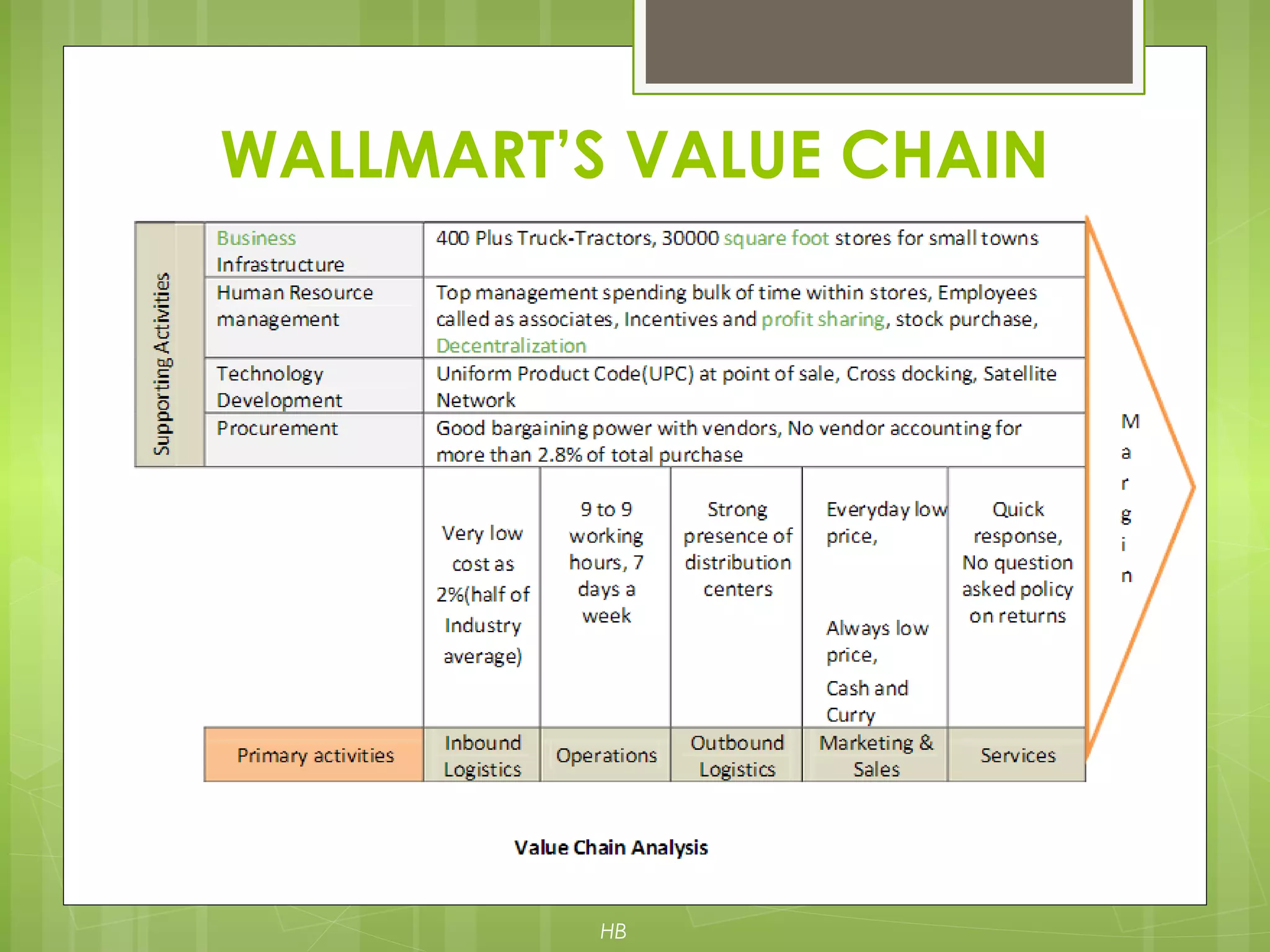
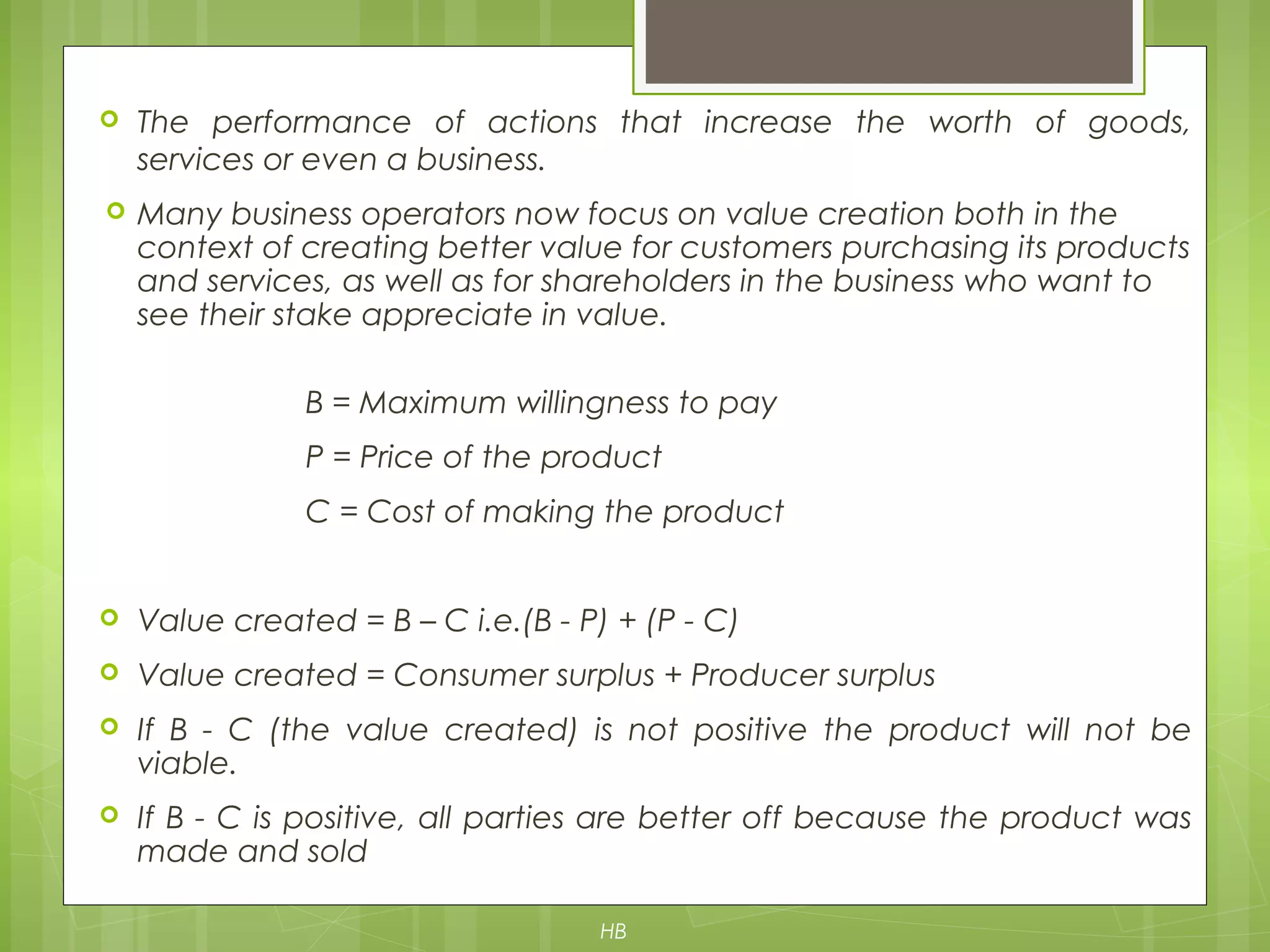
The document discusses value chain analysis developed by Porter, illustrating how firms can enhance competitive advantage by optimizing primary and support activities in their operations. It highlights key cost drivers and the importance of managing linkages with suppliers and customers, detailing steps for achieving cost or differentiation advantages. Additionally, it examines value creation for customers and shareholders, using examples from companies like McDonald's to demonstrate practical applications of value chain analysis.