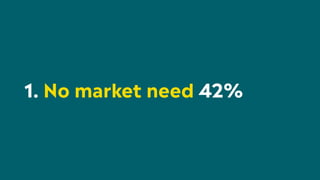
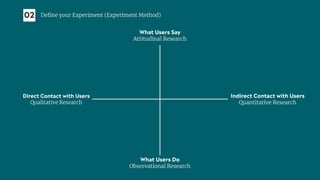
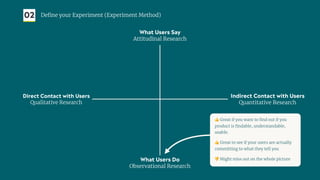
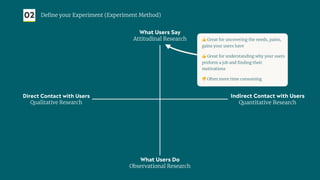
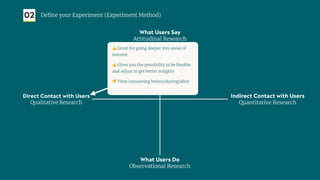
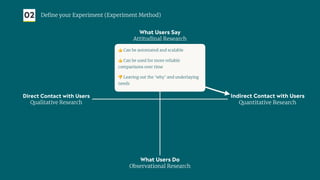
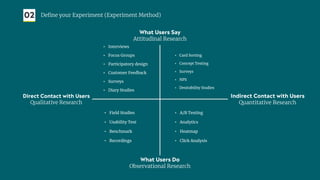
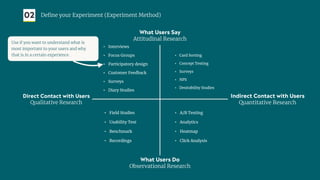
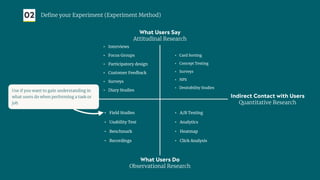
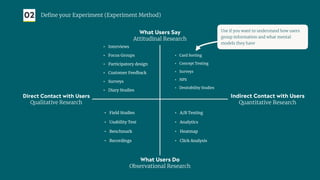
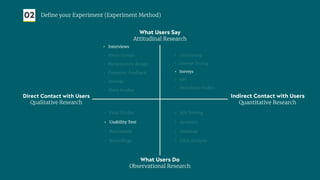
The document outlines a structured approach for validating hypotheses through user research to reduce product failure, highlighting key reasons for failure such as lack of market need and inadequate teams. It details the validation process, including defining hypotheses, conducting various types of experiments (observational, attitudinal, qualitative, and quantitative), and analyzing results to ensure desirability, feasibility, and viability. The importance of understanding users' needs and motivations through methods like interviews, surveys, and usability testing is emphasized, alongside practical tools and strategies for conducting effective research.